Abstract
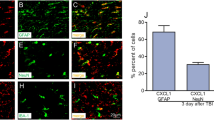
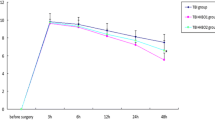
The purpose of this study was to investigate the inhibition neuroinflammation mechanisms of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT). Primary astrocytes were incubated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) after which they underwent HBOT and separate administration of inflammatory cytokine inhibitors. The respective expression of inflammatory factors was then detected. Results showed that LPS significantly induced increases in the expression levels of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (CXCL1), chemokine C-C motif ligand 2 (CCL2), phospho-nuclear factor-kappa B (p-NF-κB), phospho-c-Jun N-terminal kinase (p-JNK), phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (p-ERK), and phospho-p38 (p-p38) in cultured astrocytes and peaked at 3 h. HBOT downregulated the expression of some inflammation mediators including CXCL1 and CCL2. Furthermore, HBOT inhibited the expression of some up-stream regulators of inflammation mediators including p-NF-κB, p-JNK, p-p38 (at 3 and 6 h), and p-ERK (3 h). Inhibitors of NF-κB, ERK, and JNK (BAY117082, PD98059, and SP600125) significantly suppressed the expression of CXCL1 and CCL2 that were induced by LPS for 3 h. However, the p38 inhibitor, SB203580, had no obvious effect on expression levels of CXCL1 and CCL2. In conclusion, we found that HBOT inhibits neuroinflammation via regulation of the LPS-induced NF-κB/mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs, JNK, and ERK) -CCL2/CXCL1 signaling pathways.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiu, C.C., Y.E. Liao, L.Y. Yang, J.Y. Wang, D. Tweedie, H.K. Karnati, N.H. Greig, and J.Y. Wang. 2016. Neuroinflammation in animal models of traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 272: 38–49.
Gyoneva, S., and R.M. Ransohoff. 2015. Inflammatory reaction after traumatic brain injury: Therapeutic potential of targeting cell-cell communication by chemokines. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 36 (7): 471–480.
Yang, T., Y.W. Liu, L. Zhao, H. Wang, N. Yang, S.S. Dai, and F. He. 2017. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 deficiency inhibits neutrophil infiltration after traumatic brain injury in mice. Scientific Reports 7 (1): 9998.
Dalgard, C.L., J.T. Cole, W.S. Kean, J.J. Lucky, G. Sukumar, D.C. McMullen, H.B. Pollard, and W.D. Watson. 2012. The cytokine temporal profile in rat cortex after controlled cortical impact. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 5: 6.
Foerstner P, Rehman R, Anastasiadou S, Haffner-Luntzer M, Sinske D, Ignatius A, Roselli F, Knoell B. Neuroinflammation after traumatic brain injury (TBI) is enhanced in activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) mutant mice. Journal of Neurotrauma 2018.
Liu, S., G.Y. Shen, S.K. Deng, X.B. Wang, Q.F. Wu, and A.S. Guo. 2013. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves cognitive functioning after brain injury. Neural Regeneration Research 8 (35): 3334–3343.
Liu, S., L. Zhang, Q. Wu, Q. Wu, and T. Wang. 2013. Chemokine CCL2 induces apoptosis in cortex following traumatic brain injury. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience 51 (3): 1021–1029.
Chen, X., X.S. Duan, L.J. Xu, J.J. Zhao, Z.F. She, W.W. Chen, Z.J. Zheng, and G.D. Jiang. 2014. Interleukin-10 mediates the neuroprotection of hyperbaric oxygen therapy against traumatic brain injury in mice. Neuroscience 266: 235–243.
Zhang, Y., Y. Yang, H. Tang, W. Sun, X. Xiong, D. Smerin, and J. Liu. 2014. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy ameliorates local brain metabolism, brain edema and inflammatory response in a blast-induced traumatic brain injury model in rabbits. Neurochemical Research 39 (5): 950–960.
Meng, X.E., Y. Zhang, N. Li, D.F. Fan, C. Yang, H. Li, D.Z. Guo, and S.Y. Pan. 2016. Hyperbaric oxygen alleviates secondary brain injury after trauma through inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Medical Science Monitor 22: 284–288.
Wee, H.Y., S.W. Lim, C.C. Chio, K.C. Niu, C.C. Wang, and J.R. Kuo. 2015. Hyperbaric oxygen effects on neuronal apoptosis associations in a traumatic brain injury rat model. The Journal of Surgical Research 197 (2): 382–389.
Geng, F., Y. Ma, T. Xing, X. Zhuang, J. Zhu, and L. Yao. 2016. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on inflammasome signaling after traumatic brain injury. Neuroimmunomodulation 23 (2): 122–129.
Lu, Y., B.C. Jiang, D.L. Cao, Z.J. Zhang, X. Zhang, R.R. Ji, and Y.J. Gao. 2014. TRAF6 upregulation in spinal astrocytes maintains neuropathic pain by integrating TNF-α and IL-1β signaling. Pain 155 (12): 2618–2629.
Gao, Y.J., L. Zhang, O.A. Samad, M.R. Suter, K. Yasuhiko, Z.Z. Xu, J.Y. Park, A.L. Lind, Q. Ma, and R.R. Ji. 2009. JNK-induced MCP-1 production in spinal cord astrocytes contributes to central sensitization and neuropathic pain. The Journal of Neuroscience 29 (13): 4096–4108.
Hui, J., Z.J. Zhang, X. Zhang, Y. Shen, and Y.J. Gao. 2013. Repetitive hyperbaric oxygen treatment attenuates complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced pain and reduces glia-mediated neuroinflammation in the spinal cord. The Journal of Pain 14 (7): 747–758.
Berman, J.W., M.P. Guida, J. Warren, J. Amat, and C.F. Brosnan. 1996. Localization of monocyte chemoattractant peptide-1 expression in the central nervous system in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and trauma in the rat. Journal of Immunology 156 (8): 3017–3023.
Merkel, S.F., A.M. Andrews, E.M. Lutton, R. Razmpour, L.A. Cannella, and S.H. Ramirez. 2017. Dexamethasone attenuates the enhanced rewarding effects of cocaine following experimental traumatic brain injury. Cell Transplantation 26 (7): 1178–1192.
Pineau, I., L. Sun, D. Bastien, and S. Lacroix. 2010. Astrocytes initiate inflammation in the injured mouse spinal cord by promoting the entry of neutrophils and inflammatory monocytes in an IL-1 receptor/MyD88-dependent fashion. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 24 (4): 540–553.
Wu, F., Y. Zhao, T. Jiao, D. Shi, X. Zhu, M. Zhang, M. Shi, and H. Zhou. 2015. CXCR2 is essential for cerebral endothelial activation and leukocyte recruitment during neuroinflammation. Journal of Neuroinflammation 12: 98.
Vargas-Caraveo, A., A. Sayd, S.R. Maus, J.R. Caso, J.L.M. Madrigal, B. García-Bueno, and J.C. Leza. 2017. Lipopolysaccharide enters the rat brain by a lipoprotein-mediated transport mechanism in physiological conditions. Scientific Reports 7 (1): 13113.
Chistyakov, D.V., N.V. Azbukina, A.V. Lopachev, K.N. Kulichenkova, A.A. Astakhova, and M.G. Sergeeva. 2018. Rosiglitazone as a modulator of TLR4 and TLR3 signaling pathways in rat primary neurons and astrocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19 (1).
Moriyama, M., S. Fujitsuka, K. Kawabe, K. Takano, and Y. Nakamura. 2018. Zinc potentiates lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in cultured primary rat astrocytes. Neurochemical Research 43 (2): 363–374.
Liu, H., J.R. Davis, Z.L. Wu, and A. Faez Abdelgawad. 2017. Dexmedetomidine attenuates lipopolysaccharide induced MCP-1 expression in primary astrocyte. BioMed Research International 6352159.
Choi, S.S., H.J. Lee, I. Lim, J. Satoh, and S.U. Kim. 2014. Human astrocytes: Secretome profiles of cytokines and chemokines. PLoS One 9 (4): e92325.
Ma, J., W. Xiao, J. Wang, J. Wu, J. Ren, J. Hou, J. Gu, K. Fan, and B. Yu. 2016. Propofol inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome and attenuates blast-induced traumatic brain injury in rats. Inflammation 39 (6): 2094–2103.
Hellewell, S., B.D. Semple, and M.C. Morganti-Kossmann. 2016. Therapies negating neuroinflammation after brain trauma. Brain Research 1640 (Pt A): 36–56.
Sun, W., J. Liu, Y. Huan, and C. Zhang. 2014. Intracranial injection of recombinant stromal-derived factor-1 alpha (SDF-1α) attenuates traumatic brain injury in rats. Inflammation Research 63 (4): 287–297.
Chu, W., M. Li, F. Li, R. Hu, Z. Chen, J. Lin, and H. Feng. 2013. Immediate splenectomy down-regulates the MAPK-NF-κB signaling pathway in rat brain after severe traumatic brain injury. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery 74 (6): 1446–1453.
Marshall, J., J. Szmydynger-Chodobska, M.S. Rioult-Pedotti, K. Lau, A.T. Chin, S.K.R. Kotla, R.K. Tiwari, K. Parang, S.W. Threlkeld, and A. Chodobski. 2017. TrkB-enhancer facilitates functional recovery after traumatic brain injury. Scientific Reports 7 (1): 10995.
Baratz-Goldstein, R., S. Toussia-Cohen, A. Elpaz, V. Rubovitch, and C.G. Pick. 2017. Immediate and delayed hyperbaric oxygen therapy as a neuroprotective treatment for traumatic brain injury in mice. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences 83: 74–82.
Liu, S., Y. Liu, S.K. Deng, A.S. Guo, X.B. Wang, and G.Y. Shen. 2015. Beneficial effects of hyperbaric oxygen on edema in rat hippocampus following traumatic brain injury. Experimental Brain Research 233 (12): 3359–3365.
Yang, Y., H. Wei, X. Zhou, F. Zhang, and C. Wang. 2017. Hyperbaric oxygen promotes neural stem cell proliferation by activating vascular endothelial growth factor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling after traumatic brain injury. Neuroreport 28 (18): 1232–1238.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 81702223) and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Nantong (MS22016044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Lu, C., Liu, Y. et al. Hyperbaric Oxygen Alleviates the Inflammatory Response Induced by LPS Through Inhibition of NF-κB/MAPKs-CCL2/CXCL1 Signaling Pathway in Cultured Astrocytes. Inflammation 41, 2003–2011 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0843-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0843-2