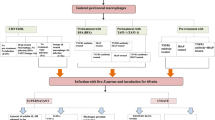
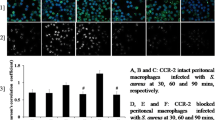
Abstract
Interaction with the live Staphylococcus aureus promotes secretion of interleukin-8 (IL-8), although the expressions of functional CXCR1 (IL-8RA) in murine macrophages have not been identified. Expression of CXCR1 was induced in S. aureus-infected macrophages, whereas, CXCR1 was undetectable in control macrophages. CXCR1 blocking significantly reduced the phagocytosis of S. aureus and TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, IFN-γ, IL-12, and IL-8 production and increased release of MIP-2 and soluble TNF-R1. Increased bacterial catalase and decreased superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities by S. aureus with concomitant decrease in hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), superoxide anion, and nitric oxide (NO) release were observed in case of prior CXCR1 blocking. In the presence of cytochalasin D, S. aureus-mediated induction of IL-8 was inhibited concomitant with decreased bacterial count suggesting that internalization of S. aureus was necessary for induction of IL-8. Shedding of TNF-R1 due to CXCR1 blocking after S. aureus inoculation was critical for neutralization of TNF-α signaling and arrests the inflammation.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CPCSEA:
-
Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animal
- CXC-chemokine:
-
Having a single amino acid residue interposed between the first two canonical cysteines
- CXCL-8:
-
Interleukin-8
- CXCR1-CXC:
-
Chemokine receptor-1
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- ELR+ :
-
Glutamate–leucine–arginine (ELR) motif near the N terminal
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- HBSS:
-
Hank’s balanced salt solution
- IL-8RA:
-
Interleukin-8 receptor A
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- JNK:
-
C jun N-terminal kinase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MHC-II:
-
Major histocompatibility complex II
- NaNo3 :
-
Sodium nitrate
- NaOH:
-
Sodium hydroxide
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear transcription factor kappa beta
- NOS2:
-
Nitric oxide synthase-2
- PBMC:
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PIP3:
-
Phospho inositol trisphosphate
- PMSF:
-
Phenyl methyl sulfonyl fluoride
- RIPA:
-
Radio immune precipitation assay buffer
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- sTNF-R1:
-
Soluble TNF receptor type1
References
Matsushima, K., K. Morishita, T. Yoshimura, S. Lavu, Y. Kobyashi, W. Lew, E. Appella, H.F. Kung, E.J. Leonard, and J.J. Oppenheim. 1988. Molecular cloning of a human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor (MDNCF) and the induction of MDNCF mRNA by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 167: 1883–1893.
Brennan, F.M., C.O. Zachariae, D. Chantry, C.G. Larsen, M. Turner, R.N. Maini, K. Matsushima, and M. Feldmann. 1990. Detection of interleukin 8 biological activity in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and production of interleukin 8 mRNA by isolated synovial cells. European Journal of Immunology 20: 2141–2144.
Charo, I.F., and R.M. Ransohoff. 2006. The many roles of chemokines and chemokine receptors in inflammation. North England Journal Medicine 354: 610–621.
Murphy, P.M. 1994. The molecular biology of leukocyte chemoattractant receptors. Annual Review Immunology 1: 593–633.
Leonard, E.J., A. Skeel, T. Yoshimura, K. Noer, S. Kutvirt, and D. Van Epps. 1990. Leukocyte specificity and binding of human neutrophil attractant/activation protein-1. Journal of Immunology 144: 1323–1330.
Murphy, P.M., and H.L. Tiffany. 1991. Cloning of complementary DNA encoding a functional human interleukin-8 receptor. Science 253: 1280–1283.
Lee, J., G. Cacalano, T. Camerato, K. Toy, M.W. Moore, and W.I. Wood. 1995. Chemokine binding and activities mediated by the mouse IL-8 receptor. Journal of Immunology 155: 2158–2164.
Cacalano, G., J. Lee, K. Kikly, A.M. Ryan, S. Pitts-Meek, B. Hultgren, W.I. Wood, and M.W. Moore. 1994. Neutrophil and B cell expansion in mice that lack the murine IL-8 receptor homolog. Science 265: 682–684.
Moepps, B., E. Nuesseler, M. Braun, and P. Gierschik. 2006. A homolog of the human chemokine receptor CXCR1 is expressed in the mouse. Molecular Immunology 43: 897–914.
Fu, W., Y. Zhang, J. Zhang, and W.F. Chen. 2005. Cloning and characterization of mouse homolog of the CXC chemokine receptor CXCR1. Cytokine 31: 9–17.
Fan, X.D., A.C. Patera, and A. Pong-Kennedy. 2007. Murine CXCR1 is a functional receptor for GCP-2/CXCL6 and interleukin-8/CXCL8. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 282: 11658–11666.
Balish, E., R.D. Wagner, and A. Vazquez-Torres. 1999. Mucosal and systemic candidiasis in IL-8Rh−/− BALB/c mice. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 66: 144–150.
Murdoch, C., and A. Finn. 2000. Chemokine receptors and their role in inflammation and infectious diseases. Blood 95: 3032–3043.
Fournier, B., and D.J. Philpott. 2005. Recognition of Staphylococcus aureus by the innate immune system. Clinical Microbiology Review 18: 521–540.
Nakane, A., M. Okamoto, M. Asano, M. Kohanawa, and T. Minagawa. 1995. Endogenous gamma interferon, tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin-6 in Staphylococcus aureus infection in mice. Infection and Immunity 63: 1165–1172.
Kim, H.K., V. Thammavongsa, O. Schneewind, and D. Missiakas. 2012. Recurrent infections and immune evasion strategies of Staphylococcus aureus. Current Opinion in Microbiology 15: 92–99.
Garofalo, A., C. Giai, S. Lattar, N. Gardella, M. Molerach, B.C. Kahl, K. Becker, A.S. Prince, D.O. Sordelli, and M.I. Gomez. 2012. The length of the Staphylococcus aureus protein-A polymorphic region regulates inflammation: impact on acute and chronic infection. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 206: 81–90.
Foster, T.J. 2012. Immune evasion by staphylococci. Nature Reviews. Microbiology 3: 948–958.
Bremell, T., A. Abdelnour, and A. Tarkowski. 1992. Histopathological and serological progression of experimental Staphylococcus aureus arthritis. Infection and Immunity 60: 2976–2985.
Abdelnour, A., and A. Tarkwoski. 1993. Polyclonal B-cell activation by an arthritogenic Staphylococcus aureus strain: contribution of T-cells and monokines. Cellular Immunology 147: 279–293.
Miller, R.A., and B.E. Britigan. 1997. Role of oxidants in microbial pathophysiology. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 10: 1–18.
Kaplan, S.S., J.R. Lancaster, R.E. Basford, and R.L. Simmons. 1996. Effect of nitric oxide on staphylococcal killing and interactive effect with superoxide. Infection and Immunity 64: 69–76.
Beaman, L., and B.L. Beaman. 1984. The role of oxygen and its derivatives in microbial pathogenesis. Annals Review Microbiology 38: 27–48.
Bekkar, L.G., S. Freeman, P.J. Murray, B. Ryffel, and G. Kaplan. 2001. TNF-α controls intracellular mycobacterial growth by both inducible nitric oxide synthase dependent and independent pathways. Journal of Immunology 166: 6728–6734.
Bizzarri, C., A.R. Beccari, R. Bertini, M.R. Cavicchia, S. Giorgini, and M. Allegretti. 2006. ELR + CXC chemokines and their receptors (CXC chemokine receptor 1 and CXC chemokine receptor 2) as new therapeutic targets. Pharmacology Therapeutic 112: 139–149.
Baggioloni, M. 2001. Chemokines in pathology and medicine. Journal of Internal Medicine 250: 91–104.
Hussain, F., M. Freissmuth, D. Volkel, M. Theile, P. Doulliard, G. Antoine, P. Thuner, H. Erhlich, H.P. Schwarz, F. Scheifinger, and R.J. Kerschbaumer. 2013. Human anti-macrophage migration inhibitory factor antibodies inhibit growth of human prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 12: 1223–1234.
Campbel, L.M., P.J. Maxwell, and D.J. Waugh. 2013. Rationale and means to target pro-inflammatory interleukin-8 (CXCL8) signaling in cancer. Pharmaceuticals 6: 929–959.
Citro, A., E. Cantarelli, P. Maffi, R. Nano, R. Melzi, A. Mercalli, E. Dugnani, V. Sordi, P. Maqistretti, L. Daffonchio, P.A. Ruffini, M. Alleqretti, A. Sechhi, E. Bonifacio, and L. Piemonti. 2012. CXCR1/2 inhibition enhances pancreatic islet survival after transplantation. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 122: 3647–3651.
Barsante, M.M., T.M. Cunha, M. Aleqretti, F. Catteni, F. Policani, C. Bizzari, W.L. Tafuri, S. Poole, F.Q. Cunha, R. Bertini, and M.M. Teixeira. 2008. Blockade of the chemokines receptor (CXC R2) ameliorates adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. British Journal of Pharmacology 153: 992–1002.
Hsu, M., S.Y. Wu, S.S. Chang, I.J. Su, C.H. Tsai, S.J. Lai, A.L. Shiau, K. Takada, and Y. Chang. 2008. Epstein-Barr virus lytic transactivator zeta enhances chemotactic activity through induction of interleukin‑8 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Journal of Virology 82: 3679–3688.
Baggiloni, M., and B. Moser. 1997. Blocking chemokines receptors. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 186: 1189.
Graigner, D.J., and J. Reckless. 2003. Broad-spectrum chemokines inhibitors (BSCI) and their anti-inflammatory effects in vivo. Biochemical Pharmacology 65: 1027–1034.
Godaly, G., L. Hang, B. Frendeus, and C. Svanborg. 2000. Transepithelial neutrophil migration is CXCR1 dependent in vitro and is defective in IL-8 receptor knockout mice. Journal of Immunology 165: 5287–5294.
Hang, L., B. Frendeus, G. Godaly, and C. Svanborg. 2000. Interleukin-8 receptor knockout mice have subepithelial neutrophil entrapment and renal scarring following acute pyelonephritis. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 182: 1738–1748.
Tsai, W.C., R.M. Streiter, B. Mehrad, M.W. Newstead, X. Zeng, and T.J. Standiford. 2000. CXC chemokines receptor CXCR2 is essential for protective innate response in murine Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. Infection and Immunity 68: 4289–4296.
Mal, P., S. Dutta, D. Bandyopadhyay, K. Dutta, A. Basu, and B. Bishayi. 2012. Gentamicin in combination with ascorbic acid regulates the severity of Staphylococcus aureus infection-induced septic arthritis in mice. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology 76: 528–540.
Das, D., and B. Bishayi. 2010. Contribution of catalase and superoxide dismutase to the intracellular survival of clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus in murine macrophages. Industrial Journal Microbiology 50: 375–384.
Svanborg, C., B. Frendeus, G. Godaly, L. Hang, M. Hedlund, and C. Wachtler. 2001. Toll-like receptor signaling and chemokines receptor expression influence the severity of urinary tract infection. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 183: 61–65.
Bishayi, B., and A.K. Samanta. 1996. Identification and characterization of specific receptor for interleukin-8 from the surface of human monocytes. Scanning Journal Immunology 43: 531–536.
Bishayi, B., and A.K. Samanta. 2002. Modulation of interleukin-8 receptor expression by lipopolysaccharide and phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) in human peripheral monocytes—a preliminary study. Industrial Journal Physiology Pharmacology 46: 407–422.
Leigh, P.C.J., R. van Furth, and T.L. van Zwet. 1986. In vitro determination of phagocytosis and intracellular killing by polymorphonuclear and mononuclear phagocytes. In Handbook of experimental immunology, ed. D.M. Weir, 46.1–46.26. Oxford: Blackwell.
Absolom, D. 1986. Basic methods for the study of phagocytosis. Methods Enzymology 1986: 95–180.
Nandi, D., M.K. Mishra, A. Basu, and B. Bishayi. 2010. Protective effects of interleukin-6 in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced experimental endotoxemia is linked to alteration in hepatic anti-oxidant enzymes and endogenous cytokines. Immunobiology 215: 443–451.
Das, D., and B. Bishayi. 2009. Staphylococcal catalase protects intracellularly survived bacteria by destroying H2O2 produced by the murine peritoneal macrophages. Microbial Pathogenesis 47: 57–67.
Mal, P., D. Ghosh, D. Bandyopadhyay, K. Dutta, and B. Bishayi. 2012. Ampicillin alone and in combination with riboflavin modulates Staphylococcus aureus infection induced septic arthritis in mice. Industrial Journal Experimentalitis Biology 50: 677–689.
Mal, P., K. Dutta, D. Bandyopadhyay, A. Basu, R. Khan, and B. Bishayi. 2013. Azithromycin in combination with riboflavin decreases the severity of Staphylococcus aureus infection induced septic arthritis by modulating the production of free radicals and endogenous cytokines. Inflammation Research 62: 259–273.
Cosgrove, K., A. Coutts, I.M. Jonsson, A. Tarkwoski, J.F. Kokai-kun, J.J. Mond, and S.J. Foster. 2007. Catalase (KatA) and alkyl hydroperoxide reductase (AhpC) have compensatory roles in peroxide stress resistance and are required for survival, persistence, and nasal colonization in Staphylococcus aureus. Journal of Bacteriology 189: 1025–1035.
Das, D., S.S. Saha, and B. Bishayi. 2008. Intracellular survival of Staphylococcus aureus: correlating production of catalase and superoxide dismutase with levels of inflammatory cytokines. Inflammation Research 57: 340–349.
Bozic, C.R., N.P. Gerard, C. von Uexkull-Guldenband, L.F. Kolakowski, M.J. Conklyn, R. Breslow, H.J. Showell, and C. Gerard. 1994. The murine interleukin-8 type B receptor homologue and its ligand. J Biol Chem 169: 29355–29358.
Kang, H.J., J. Ha, H.S. Kim, H. Lee, K. Kurokawa, and B.L. Lee. 2011. The role of phagocytosis in IL-8 production by human monocytes in response to lipoproteins on Staphylococcus aureus. Biochemistry Biophysica Research Communication 406: 449–453.
Ferrante, A., A.J. Martin, E.J. Bates, D.H. Goh, D.P. Harvey, D. Parson, D.A. Rathjen, G. Russ, and J.M. Dayer. 1993. Killing of Staphylococcus aureus by tumor necrosis factor-alpha-activated neutrophils. The role of serum opsonins, integrin receptors, respiratory burst, and degranulation. Journal of Immunology 151: 4821–4828.
Frendeus, B., G. Godaly, L. Hang, D. Karpman, A.C. Lundstedt, and C. Svanborg. 2000. Interleukin 8 receptor deficiency confers susceptibility to acute experimental pyelonephritis and may have a human counterpart. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 192: 881–890.
Basu, M., S.J. Czinn, and T.G. Blanchard. 2004. Absence of catalase reduces long term survival of Helicobacter pylori in macrophage phagosomes. Helicobacter 9: 211–216.
Lu, Y., Y. Wang, B. Ling, X. Ke, J. Ying, Y. Yu, M. He, and X. Li. 2013. Catalase-negative Staphylococcus lugdunensis strain with a novel point mutation in the catalase gene isolated from a patient with chronic suppurative otitis media. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 51: 1310–1312.
DeYulia, G.J., J.M. Carcamo, O. Borquez-Ojeda, C.C. Shelton, and D.W. Golde. 2005. Hydrogen peroxide generated extracellularly by receptor-ligand interaction facilitates cell signaling. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 102: 5044–5049.
Xue, X., J.H. Piao, A. Nakajima, S. Sakan-komazawa, Y. Kojima, K. Mori, H. Yagita, K. Okumara, H. Harding, and H. Nakano. 2005. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) induces unfolded protein response (UPR) in a reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent fashion and the UPR counteracts ROS accumulation by TNF-alpha. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 280: 33917–33925.
DeForge, L.E., A.M. Preston, E. Takeuchi, J. Kenney, L.A. Boxer, and D.G. Remick. 1993. Regulation of interleukin 8 gene expression by oxidant stress. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 268: 25568–25576.
Gilmour, P.S., I. Rahman, K. Donaldson, and W. MacKnee. 2003. Histone acetylation regulates epithelial IL-8 release mediated oxidative stress from environmental particles. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 284: 533–540.
Rosenthal, G.J., D.R. Germolec, M.E. Blazka, E. Korsini, P. Simeonova, P. Pollock, L.Y. Kong, J. Kwon, and M.I. Luster. 1994. Asbestos stimulates IL-8 production from human lung epithelial cells. Journal of Immunology 153: 3237–3244.
van Dissel, J.T., P. van Langevelde, R.G. Westendorp, K. Kwappenberg, and M. Frolich. 1998. Anti-inflammatory cytokine profile and mortality in febrile patients. Lancet 351: 950–953.
Giese, N.A., L. Gabriele, T.M. Doherty, D.M. Klinman, L. Tadesse-Heath, C. Contursi, S.L. Epstein, and H.C. Morse. 1997. Interferon (IFN) consensus sequence binding protein, a transcription factor of the IFN regulatory factor family, regulates immune responses in vivo through control of interleukin 12 expression. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 186: 1535–1546.
Giai, C., C. Gonzalez, C. Ledo, A. Garofalo, M.S. Di-Genaro, D.O. Sordelli, and M.I. Gomez. 2013. Shedding of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 induced by protein-A decreases tumor necrosis factor alpha availability and inflammation during systemic Staphylococcus aureus infection. Infection and Immunity 81: 4200–4207.
Czuprynski, C.J., H.J.F. Brown, H. Steinberg, and D. Carroll. 1998. Mice lacking the murine interleukin-8 receptor homologue demonstrate paradoxical responses to acute and chronic experimental infection with Listeria monocytogenes. Microbial Pathogenesis 24: 17–23.
Andrea, J.W., A. Arruda, N.R. Christopher, A.T. Kaplan, T. Shimada, K. Shimada, A. Moshe, L. George, and D.M. Underhil. 2011. Phagosomal degradation increases TLR access to bacterial ligands and enhances macrophage sensitivity to bacteria. J Immunol. doi:10.4049/jimmunol 1100232.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India, New Delhi, India [grant number SR/SO/HS/0013/2012, dated 21 May 2013 to BB] for funding this project. The author (Biswadev Bishayi) is indebted to the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India for providing us with the instruments procured under the DST-PURSE program to the Department of Physiology, University of Calcutta.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bishayi, B., Bandyopadhyay, D., Majhi, A. et al. Expression of CXCR1 (Interleukin-8 Receptor) in Murine Macrophages After Staphylococcus aureus Infection and its Possible Implication on Intracellular Survival Correlating with Cytokines and Bacterial Anti-Oxidant Enzymes. Inflammation 38, 812–827 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9991-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9991-1