Abstract.
Background:
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase are anti-oxidant enzymes potentially used by the bacteria to neutralize macrophage microbicidal molecules such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
Objective:
To investigate contribution of bacterial anti-oxidant enzymes in intracellular survival of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) within macrophages.
Materials:
Murine peritoneal macrophages and S. aureus (CMC-524, ICH-629 and ICH-757).
Treatment:
106 colony forming units (CFU) of the 90 minutes (min) intracellularly viable S. aureus were administered (i.v.) per mouse through 0.1 ml saline.
Methods:
Anti-oxidant enzyme assay, phagocytic activity, H2O2 release, Zymography for catalase, serum tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6) level were estimated. One-way Model I ANOVA and one tail Student’s t-test were performed.
Results:
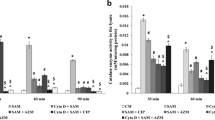
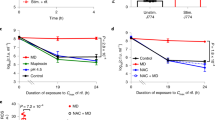
Survival of S. aureus was least after 90 min of reincubation within macrophages. Maximum amount of bacterial anti-oxidant enzymes were released after 90 min of re-incubation. H2O2 released after 90 min of re-incubation with S. aureus was maximum. Higher activity of catalase and SOD by S. aureus occurred in response to the gradual production of H2O2. Serum IL-6 and TNF-α was also elevated 1h post infection.
Conclusions:
Bacterial catalase and SOD combat reactive oxygen species enabling S. aureus to persist within macrophages, inducing local inflammation, causing greater induction of serum TNF-α and IL-6.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 27 July 2007; returned for revision 1 October 2007; received from final revision 7 December 2007; accepted by G. Wallace 17 January 2008
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, D., Saha, S.S. & Bishayi, B. Intracellular survival of Staphylococcus aureus: correlating production of catalase and superoxide dismutase with levels of inflammatory cytokines. Inflamm. res. 57, 340–349 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-007-7206-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-007-7206-z