Abstract
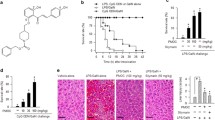
In this study, we induced an acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) model by human serum albumin (HSA), d-galactosamine (d-Gal) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in rats. Anti-TNF-α polyclonal antibody (as TNF-α inhibitor) and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC, a NF-κB inhibitor) were used to treat the liver failure animals, respectively. The results showed that TNF-α inhibition was beneficial, but NF-κB inhibition failed to protect the rats in ACLF. However, HMGB1 levels, cytokine production and activation of TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway were all suppressed by both TNF-α and NF-κB inhibition. In order to verify the effect of PDTC on inflammatory response, we further explored its effect in vitro. Anti-inflammatory activity of PDTC was proved in U937 cell line. To conclude, both inhibitions of TNF-α and NF-κB are able to suppress the activation of TLR4 and NF-κB signaling pathway. However, NF-κB inhibition with PDTC failed to protect the rats in ACLF induced by d-Gal and LPS.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sozinov, A.S. 2002. Systemic endotoxemia during chronic viral hepatitis. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine 133: 153–155.
Beutler, B., and E.T. Rietschel. 2003. Innate immune sensing and its roots: the story of endotoxin. Nature Reviews Immunology 3: 169–176.
Akira, S., S. Uematsu, and O. Takeuchi. 2006. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124: 783–801.
Yang, H., M. Ochani, J. Li, X. Qiang, M. Tanovic, H.E. Harris, S.M. Susarla, L. Ulloa, H. Wang, R. DiRaimo, C.J. Czura, H. Wang, J. Roth, H.S. Warren, M.P. Fink, M.J. Fenton, U. Andersson, and K.J. Tracey. 2004. Reversing established sepsis with antagonists of endogenous high-mobility group box 1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 101: 296–301.
Yasuda, T., T. Ueda, M. Shinzeki, et al. 2007. Increase of high-mobility group box chromosomal protein 1 in blood and injured organs in experimental severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 34: 487–488.
Ueno, H., T. Matsuda, S. Hashimoto, et al. 2004. Contributions of high mobility group box protein in experimental and clinical acute lung injury. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 170: 1310–1316.
Hamada, T., M. Torikai, A. Kuwazuru, et al. 2008. Extracellular high mobility group box chromosomal protein 1 is a coupling factor for hypoxia and inflammation in arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 58: 2675–2685.
Fan, J., Y. Li, R.M. Levy, et al. 2007. Hemorrhagic shock induces NAD(P)H oxidase activation in neutrophils: role of HMGB1-TLR4 signaling. The Journal of Immunology 178: 6573–6580.
Tsung, A., R. Sahai, H. Tanaka, et al. 2005. The nuclear factor HMGB1 mediates hepatic injury after murine liver ischemia-reperfusion. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 201: 1135–1143.
Li, X., L.K. Wang, L.W. Wang, X.Q. Han, F. Yang, and Z.J. Gong. 2013. Blockade of high-mobility group box-1 ameliorates acute on chronic liver failure in rats. Inflammation Research 62: 703–709.
Wang, H., O. Bloom, M. Zhang, et al. 1999. HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science 285: 248–251.
Rendon-Mitchell, B., M. Ochani, J. Li, et al. 2003. IFN-γ induces high mobility group box 1 protein release partly through a TNF-dependent mechanism. The Journal of Immunology 170: 3890–3897.
Gardella, S., C. Andrei, D. Ferrera, et al. 2002. The nuclear protein HMGB1 is secreted by monocytes via a non-classical, vesicle-mediated secretory pathway. EMBO Reports 3: 995–1001.
Bonaldi, T., F. Talamo, P. Scaffidi, et al. 2003. Monocytic cells hyperacetylate chromatin protein HMGB1 to redirect it towards secretion. The EMBO Journal 22: 5551–5560.
Liu, S., D.B. Stolz, P.L. Sappington, et al. 2006. HMGB1 is secreted by immunostimulated enterocytes and contributes to cytomix-induced hyperpermeability of Caco-2 monolayers. American Journal of Physiology - Cellular Physiology 290: C990–C999.
Scaffidi, P., T. Misteli, and M.E. Bianchi. 2002. Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers inflammation. Nature 418: 191–195.
Yang, H., H. Wang, C.J. Czura, et al. 2005. The cytokine activity of HMGB1. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 78: 1–8.
Wang, H., H. Yang, C.J. Czura, K.J. Tracey, et al. 2001. HMGB1 as a late mediator of lethal systemic inflammation. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 164: 1768–1773.
Yong-Chen, Lu., Wen-Chen Yeh, et al. 2008. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokines 42: 145–151.
Karin, M., and A. Lin. 2002. NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nature Immunology 3: 221–227.
Li, Q., and I.M. Verma. 2002. NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nature Reviews Immunology 2: 725–734.
Li, S., S. Zhong, K. Zeng, Y. Luo, et al. 2010. Blockade of NF-kappaB by pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate attenuates myocardial inflammatory response and ventricular dysfunction following coronary microembolization induced by homologous microthrombi in rats. Basic Research in Cardiology 105: 139–150.
Chang, X., C. Shao, Q. Wu, et al. 2009. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate attenuates paraquat-induced lung injury in rats. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology 2009: 619487.
Seifalian, A.M., I.H. Mallick, E. Hajinasrollah, et al. 2009. The in-vivo effect of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on hepatic parenchymal microcirculation and oxygenation of the rat liver. European Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 21: 1184–1190.
Kim S, Kim SY, Pribis JP, et al. Signaling of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) through toll-like receptor 4 in macrophages requires CD14. Mol Med. 2013, doi: 10.2119/molmed. 2012. 00306
Chen, G., and D.V. Goeddel. 2002. TNF-R1 signaling: a beautiful pathway. Science 296: 1634–1635.
Wang, L.W., L.K. Wang, H. Chen, F. Cheng, X. Li, C.M. He, and Z.J. Gong. 2012. Ethyl pyruvate protects against experimental acute-on-chronic liver failure in rats. World Journal of Gastroenterology 18: 5709–5718.
Dretzke, J., R. Edlin, J. Round, et al. 2011. A systematic review and economic evaluation of the use of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors, adalimumab and infliximab, for Crohn's disease. Health Technology Assessment 15: 1–244.
Huang, Z., B. Yang, Y. Shi, et al. 2012. Anti-TNF-α therapy improves Treg and suppresses Teff in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Cellular Immunology 279: 25–29.
Thyagarajan, V., H. Norman, K.A. Alexander, et al. 2012. Risk of mortality, fatal infection, and fatal malignancy related to use of anti-tumor necrosis factor-α biologics by rheumatoid arthritis patients. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 42: 223–233.
Sherman, M.P., E.E. Aeberhard, V.Z. Wong, et al. 1993. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibits induction of nitric oxide synthase activity in rat alveolar macrophages. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 191: 1301–1308.
Han, D.W. 2002. Intestinal endotoxemia as a pathogenetic mechanism in liver failure. World Journal of Gastroenterology 8: 961–965.
Lu, J.W., H. Wang, J. Yan-Li, et al. 2008. Differential effects of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on TNF-α-mediated liver injury in two different models of fulminant hepatitis. Journal of Hepatology 48: 442–452.
Del Bufalo, A., J. Bernad, C. Dardenne, et al. 2011. Contact sensitizers modulate the arachidonic acid metabolism of PMA-differentiated U-937 monocytic cells activated by LPS. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 256: 35–43.
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81071342 and 81371789).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, F., Li, X., Wang, Lk. et al. Inhibitions of NF-κB and TNF-α Result in Differential Effects in Rats with Acute on Chronic Liver Failure Induced by d-Gal and LPS. Inflammation 37, 848–857 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9805-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9805-x