Abstract
Background:
The Janus kinase (JAK) is a crucial intracellular signaling hub for numerous cytokines, which is extensively involved in the activation of inflammatory cascade and the induction of inflammatory injury. JAK inhibition provides protective effects in several inflammation-based disorders, but the potential effects of JAK inhibitor in inflammation-based acute hepatitis remain to be investigated.
Methods and results:
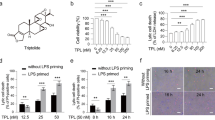
Acute hepatitis is induced by Lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine (LPS/D-Gal) in mice with or without the JAK inhibitor Tofacitinib administration. The degree of liver injury, the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and induction of hepatocytes apoptosis were determined. The results indicated that treatment with Tofacitinib decreased the levels of aminotransferases, attenuated the histological abnormalities in liver and decreased the plasma levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in LPS/D-Gal-insulted mice. In addition, Tofacitinib suppressed the activation of the caspase cascade, decreased the level of cleaved caspase-3, and reduced the count of TUNEL-positive cells.
Conclusion:
Treatment with Tofacitinib alleviated LPS/D-Gal-induced acute hepatitis. JAK maybe become a promising target for the control of inflammation-based liver disorders.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernal W, Auzinger G, Dhawan A et al (2010) Acute liver failure.Lancet190–201
Triantafyllou E, Pop OT, Possamai LA et al (2018) MerTK expressing hepatic macrophages promote the resolution of inflammation in acute liver failure. Gut Feb 67(2):333–347
Rathinam VAK, Zhao Y, Shao F (2019) Innate immunity to intracellular LPS. Nat Immunol May 20(5):527–533
Elliott TG, Welty D et al (1991) The D-Galactosamine Loaded Mouse and Its Enhanced Sensitivity to Lipopolysaccharide and Monophosphoryl Lipid A: A Role for Superoxide. J Immunother 10(1):69–74
Yasuo Endo, Nakamura TKM (1992) Ornithine and histidine decarboxylase activities in mice sensitized to endotoxin, interleukin-1 or tumour necrosis factor by D-galactosamine. Br J Pharmacol 107:888–894
Galanos C, Freudenberg MA, Reutter W (1979) Galactosamine-induced sensitization to the lethal effects of endotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A Nov 76(11):5939–5943
Liu Z, Wang J, Zhang Y et al (2021) Pterostilbene Exerts Hepatoprotective Effects through Ameliorating LPS/D-Gal-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice. Inflamm Apr 44(2):526–535
Huanjin Liao J, Cai L, Zhang et al (2017) A novel acute lethal liver injury mouse model with visualization of NF-κB activity for treatment of severe acute liver injury. Am J Transl Res 9(93):962–970
Banerjee S, Biehl A, Gadina M et al (2017) JAK-STAT Signaling as a Target for Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases: Current and Future Prospects. Drugs Apr 77(5):521–546
Roskoski R Jr (2016) Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors in the treatment of inflammatory and neoplastic diseases. Pharmacol Res Sep 111:784–803
Schwartz DM, Kanno Y, Villarino A et al (2017) JAK inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for immune and inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 16(12):843–862
Li Y, Liu X, Yu J et al (2020) Tofacitinib suppresses mast cell degranulation and attenuates experimental allergic conjunctivitis. Int Immunopharmacol Sep 86:1–10
Jarneborn A, Mohammad M, Engdahl C et al (2020) Tofacitinib treatment aggravates Staphylococcus aureus septic arthritis, but attenuates sepsis and enterotoxin induced shock in mice. Sci Rep Jul 210(1):1–14
Hazem SH, Shaker ME, Ashamallah SA et al (2014) The novel Janus kinase inhibitor ruxolitinib confers protection against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity via multiple mechanisms. Chemico-biological Interact Sep 5:220:116–127
Shaker ME, Hendawy OM, El-Mesery M et al (2022) The JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib abrogates immune hepatitis instigated by concanavalin A in mice. Int Immunopharmacol Feb 103:108463
El Jammal T, Gerfaud-Valentin M, Seve P et al (2020) Inhibition of JAK/STAT signaling in rheumatologic disorders: The expanding spectrum. Joint Bone Spine Mar 87(2):119–129
Hodge JA, Kawabata TT, Krishnaswami S et al (2016) The mechanism of action of tofacitinib – an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 11(34):318–328
Yun Y, Chen J, Wang X et al (2021) Tofacitinib Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Blocking the JAK-STAT1/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Biomed Res Int 2021:1–9
Robles–Diaz M, Lucena MI, Kaplowitz N et al (2014) Use of Hy’s Law and a New Composite Algorithm to Predict Acute Liver Failure in Patients With Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Gastroenterology 147(1):109–118e5
Yang P, Zhou W, Li C et al (2016) Kupffer-cell-expressed transmembrane TNF-alpha is a major contributor to lipopolysaccharide and D-galactosamine-induced liver injury. Cell Tissue Res Feb 363(2):371–383
Li L, Duan C, Zhao Y et al (2017) Preventive effects of interleukin-6 in lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine induced acute liver injury via regulating inflammatory response in hepatic macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol Oct 51:99–106
Miller DK (1997) The role of the Caspase family of cysteine proteases in apoptosis. Semin Immunol Feb 9(1):35–49
Jamilloux Y, El Jammal T, Vuitton L et al (2019) JAK inhibitors for the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun Rev Nov 18(11):1–61
Haikarainen ATV, Raivola T et al (2019) Selective JAKinibs: Prospects in Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases. BioDrugs Feb 33(1):15–32
Calama E, Ramis I, Domenech A et al (2017) Tofacitinib ameliorates inflammation in a rat model of airway neutrophilia induced by inhaled LPS. Pulm Pharmacol Ther Apr 43:60–67
Morris R, Kershaw NJ, Babon JJ (2018) The molecular details of cytokine signaling via the JAK/STAT pathway. Protein Sci Dec 27(12):1984–2009
O’Shea JJ, Schwartz DM, Villarino AV et al (2015) The JAK-STAT pathway: impact on human disease and therapeutic intervention. Annu Rev Med 66:311–328
Salas A, Hernandez-Rocha C, Duijvestein M et al (2020) JAK-STAT pathway targeting for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat reviews Gastroenterol Hepatol Jun 17(6):323–337
Philips RL, Wang Y, Cheon H et al (2022) The JAK-STAT pathway at 30: Much learned, much more to do. Cell Oct 13(21):3857–3876
Zhao J, Yu H, Liu Y et al (2016) Protective effect of suppressing STAT3 activity in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol Nov 1(5):L868–L880
Kim W-H, Radaeva FHongS et al (2003) STAT1 plays an essential role in LPS/D-galactosamine-induced liver apoptosis and injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 8:G761–G768
Olleros ML, Vesin D, Fotio AL et al (2010) Soluble TNF, but not membrane TNF, is critical in LPS-induced hepatitis. J Hepatol Dec 53(6):1059–1068
Zelova H, Hosek J (2013) TNF-alpha signalling and inflammation: interactions between old acquaintances. Inflamm Res Jul 62(7):641–651
Jin L, Cai CL, Lang XL et al (2020) Ghrelin inhibits inflammatory response and apoptosis of myocardial injury in septic rats through JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(22):11740–11746
Freitas MC, Uchida Y, Zhao D et al (2010) Blockade of Janus kinase-2 signaling ameliorates mouse liver damage due to ischemia and reperfusion. Liver Transpl May 16(5):600–610
Totten SP, Im YK, Canedo EC et al (2021) STAT1 potentiates oxidative stress revealing a targetable vulnerability that increases phenformin efficacy in breast cancer. Nat Commun Jun 312(1):1–20
Wang Y, Yu X, Song H et al (2018) The STAT-ROS cycle extends IFNinduced cancer cell apoptosis. Int J Oncol Jan 52(1):305–313
Peng X, Yang Y, Tang L et al (2020) Therapeutic benefits of apocynin in mice with lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury via suppression of the late stage pro-apoptotic AMPK/JNK pathway. Biomed Pharmacother May 125:1–9
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81871606) and the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (No. KJQN201900435).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xinyue Zhang, Li Zhang, and Yongqiang Yang conceived and designed the project. Ling Lin, Longjiang Li and Kai Hu acquired the data. Li Tang, Ruyue Shao and Min Zhu analyzed and interpreted the data. Yuhua Ma, Xinyue Zhang and Yongqiang Yang wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest concerning the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Ethical approval
All animal experiments in this study were approved by the Ethics Committee of Chongqing Medical University.
Data accessibility
The data supporting this study’s findings are available from the corresponding author (fyyyq1984@cqmu.edu.cn) upon reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Lin, L., Li, L. et al. Janus kinase inhibitor Tofacitinib alleviated acute hepatitis induced by lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine in mice. Mol Biol Rep 50, 1477–1485 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08086-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08086-6