Abstract
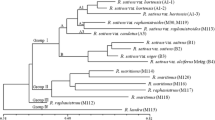
The Arachis genus is native to South America, and contains 70–80 described species assembled into nine sections. A better understanding of the level of speciation and taxonomic relationships is a prerequisite to the effective use of Arachis species in peanut breeding programs. Forty-eight genotypes representing 19 species in 6 sections were evaluated to assay the genetic variability within and among species, and 10 recombinant lines and those parents were identified with introgression of Arachis species chromosome segments into A. hypogaea genome using SRAP markers. Sixty of sixty-four SRAP primers tested were selected for DNA amplification reactions. A dendrogram and principal component analysis were constructed based on 353 SRAP polymorphic bands of the accessions. The number of scored polymorphic bands per each primer combination varied from 1 to 25 with an average of 5.9 per reaction. Estimates of genetic distance among the 48 accessions Arachis species ranged from 0.11 to 0.76. A-genome accessions 475845 (A. duranensis), and 331197 (A. villosa) were most closely associated to A. hypogaea. The first two PCAs accounted for 77.74% (62.02 and 15.72%) of the total variation observed and separated the different genomic groups. SRAPs also identified introgression of Arachis species chromosome segments into A. hypogaea. genome with 10 recombinant lines and those parents. The present results indicated that SRAPs can be used to determine the genetic relationships among species of the different sections of the genus Arachis and to identify introgression of Arachis genus chromosome segments into A. hypogaea genome.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen BY, Jiang HF, Ren XP, Liao BSh, Huang JQ (2008a) Identification and molecular traits of Arachis species with resistance to bacterial wilt. Acta Agri Boreali-Sinica 23(3):170–175
Chen BY, Jiang HF, Liao BSh, Ren XP, Huang JQ, Lei Y, Wang ShY (2008b) Genetic diversity analysis of Arachis Germplasm by SSR. J Trop Subtrop Bot 16(4):296–303
Creste S, Tsai SM, Valls JFM, Gimenes MA, Lopes CP (2005) Genetic characterization of Brazilian annual Arachis species from sections Arachis and Heteranthae using RAPD markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 52:1079–1086
Cunha FB, Nobile PM, Hoshino AA, Moretzsohn MC, Lopes CR, Gimenes MA (2008) Genetic relationships among Arachis hypogaea L. (AABB) and diploid Arachis species with AA and BB genomes. Genet Resour Crop Evol 55:15–20
Ferguson ME, Burow MD, Schulze SR, Bramel PJ, Paterson AH, Kresovich S, Mitchell S (2004) Microsatellite identification and characterization in peanut (A. hypogaea L.). Theor Appl Genet 108(6):1064–1070
Ferriol M, Pico B, Nuez F (2003) Genetic diversity of a germplasm collection of Cucurbita pepo using SRAP and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 107:271–282
Garcia GM, Stalker HT, Kochert G (1995) Introgression analysis of an interspecific hybrid population in peanuts (Arachis hypogaea L.) using RFLP and RAPD markers. Genome 38:166–176
Garcia GM, Stalker HT, Shroeder E, Kochert G (1996) Identification of RAPD, SCAR, and RFLP markers tightly linked to nematode resistance genes introgressed from Arachis cardenasii into Arachis hypogaea. Genome 39:836–845
Garcia GM, Tallury SP, Stalker HT, Kochert G (2006) Molecular analysis of Arachis interspecific hybrids. Theor Appl Genet 112:1342–1348
Gimenes MA, Lopes CR, Galgaro ML, Valls JFM, Kochert G (2000) Genetic variation and phylogenetic relationships based on RAPD analysis in section Caulorrhizae, genus Arachis (Leguminosae). Euphytica 116:187–195
Gimenes MA, Lopes CR, Valls JFM (2002a) Genetic relationships among Arachis species based on AFLP. Genet Mol Biol 25:349–353
Gimenes MA, Lopes CR, Galgaro ML, Valls JFM, Kochert G (2002b) RFLP analysis of genetic variation in species of section Arachis, genus Arachis (Leguminosae). Euphytica 123:421–429
Holbrook CC, Stalker HT (2003) Peanut breeding and genetic resources. Plant Breed Rev 22:297–356
Kochert G, Stalker HT, Gimenes M, Galgaro L, Lopes CR, Moore K (1996) RFLP and cytogenetic evidence on the origin and evolution of allotetraploid domesticated peanut, Arachis hypogaea (Leguminosae). Amer J Bot 83:1282–1291
Krapovickas A, Gregory WC (1994) Taxonomía del género Arachis (Leguminoseae). Bonplandia 8:1–186
Lavia GI (1998) Karyotypes of Arachis palustris and A. praecox (section Arachis), two species with basic chromosome number x = 9. Cytologia 63:177–181
Li G, Quiros CF (2001) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 103:455–461
Mallikarjuna N (2002) Gene introgression from Arachis glabrata into A. hypogaea, A. duranensis and A. diogoi. Euphytica 124:99–105
Milla SR, Isleib TG, Stalker HT (2005) Taxonomic relationships among Arachis sect. Arachis species as revealed by AFLP markers. Genome 48:1–11
Moretzsohn MC, Hopkins MS, Mitchell SE, Kresovich S, Valls JFM, Ferreira ME (2004) Genetic diversity of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) and its wild relatives based on the analysis of hypervariable regions of the genome. BMC Plant Biol 4:11
Nóbile PM, Gimenes MA, Valls JFM, Lopes CR (2004) Genetic variation within and among species of genus Arachis, section Rhizomatosae. Genet Resour Crop Evol 51:299–307
Pande S, Rao NJ (2001) Resistance of wild Arachis species to late leaf spot and rust in greenhouse trials. Plant Dis 85:851–856
Raina S, Mukai Y (1999) Genomic in situ hybridisation identifies the diploid wild progenitors of cultivated (A. hypogaea) and related wild (A. monticola) peanut species. Plant System Evol 214:251–262
Riaz A, Potter D, Stephen M (2004) Genotyping of peach and nectarine cultivars with SSR and SRAP molecular markers. J Am Soc Hort Sci 129:204–210
Santos VSED, Gimenes MA, Valls JFM, Lopes CR (2003) Genetic variation within and among species of five sections of the genus Arachis L. (Leguminosae) using RAPDs. Genet Resour Crop Evol 50:841–848
Seijo JG, Lavia GI, Fernández A, Krapovickas A, Ducasse D, Moscone EA (2004) Physical mapping of the 5s and 18s–25s rRNA genes by FISH as evidence that Arachis duranensis and A. ipaënsis are the wild diploid progenitors of A. hypogaea (Leguminosae). Amer J Bot 91:1294–1303
Stalker HT, Wynne JC (1979) Cytology of interspecific hybrids in section Arachis of peanuts. Peanut Sci 6:110–114
Stalker HT, Dhesi JS, Parry D, Hahn JH (1991) Cytological and interfertility relationships of Arachis section Arachis. Amer J Bot 78:238–246
Tallury SP, Hilu KW, Milla SR, Friend SA, Alsaghir M, Stalker HT, Quandt D (2005) Genomic affinities in Arachis section Arachis (Fabaceae): molecular and cytogenetic evidence. Theor Appl Genet 111:1229–1237
Valls JFM, Simpson CE (2005) New species of Arachis from Brazil, Paraguay and Bolivia. Bonplandia 14:35–63
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the research grants from National Science & Technology Pillar Program (2006BAD13B05-2), Chinese National “863” High Tech Project (2006AA10A115), Chinese National Natural Science Fund (30571132), Plant Germplasm Resources Sharing Platform (2005DKA21002-13), Director Foundation of the Institute Oil Crop Research, CAAS (2007-05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, X., Huang, J., Liao, B. et al. Genomic affinities of Arachis genus and interspecific hybrids were revealed by SRAP markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 57, 903–913 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-010-9532-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-010-9532-1