Abstract
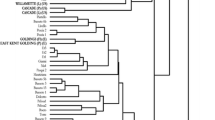
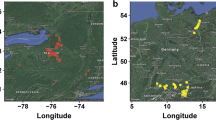
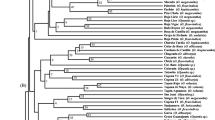
Eight genic SSR loci were evaluated for genetic diversity assessment and genotype identification in Humulus lupulus L. from Europe and North America. Genetic diversity, as measured by three diversity indices, was significantly lower in European cultivars than in North American wild accessions. Neighbor Joining cluster analysis separated the hop genotypes into European and North American groups. These eight SSRs were useful in uniquely identifying each accession with the exception of two sets of European landraces and a pair of Japanese cultivars, ‘Shinshuwase’ and ‘Kirin II’. An accession from Manitoba grouped with the European (EU) cluster reflecting the group’s genetic similarity to older Manitoba germplasm used to develop ‘Brewer's Gold’ and the gene pool arising from this cultivar. Cultivars grouped closely with one of their immediate parents. ‘Perle’ grouped with its parent ‘Northern Brewer and ‘Willamette’ grouped with its parent ‘Fuggle H’. Wild American accessions were divided into two subgroups: a North Central group containing mostly H. lupulus var. lupuloides and a Southwestern group containing H. lupulus var. neomexicanus accessions. These eight SSRs will be valuable for genotype identification in European and wild American germplasm and may potentially prove useful for marker-assisted selection in hop. PCR products from four previously reported primer pairs that amplify the same intronic SSR regions as do the genic SSRs in this study were compared in eight common cultivars. Different primer pairs generated robust markers at the chs2 and chi loci. However, only the HLC-004B and HLC-006 primer pairs amplified successfully at the chs3 and chs4 loci.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassil NV, Gilmore B, Oliphant J, Henning J, Hummer K (2005) Genbank derived microsatellite markers in hop. Acta Hortic 668:47–52
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphism. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Brady JL, Scott NS, Thomas MR (1996) DNA typing of hops (Humulus lupulus) through application of RAPD and microsatellite marker sequences converted to sequence tagged sites (STS). Euphytica 91:277–284
Čerenak A, Jakše J, Javornik B (2004) Identification and differentiation of hop varieties using simple sequence repeat markers. J Am Soc Brew Chem 62:1–7
Čerenak A, Satovic Z, Javornik B (2006) Genetic mapping of hop (Humulus lupulus L.) applied to the detection of QTLs for alpha-acid content. Genome 49:485–494
Cwynar LC, MacDonald GM (1987) Geographical variation of lodgepole pine in relation to population history. Am Nat 129:463–469
Delcourt PA, Delcourt HR (1993) Paleoclimates, paleovegetation, and paleofloras during the late quaternary. In: Flora of North America Editorial Committee (eds) Flora of North America North of Mexico, vol 1. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 71–94
Hadonou AM, Walden R, Darby P (2004) Isolation and characterization of polymorphic microsatellites for assessment of genetic variation of hops (Humulus lupulus L.). Mol Ecol Notes 4:280–282
Henning JA, Moore DL (1999) Hop chitinase gene. [online] Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/viewer.fcgi?db=nucleotide&val=4960048
Henning JA, Steiner JJ, Hummer KE (2004) Genetic diversity among world hop accessions grown in the USA. Crop Sci 44:411–417
Hewitt G (2000) The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages. Nature 405:907–913
Hummer KE (2005) Wild Humulus genetic resources at the US national clonal germplasm repository. Acta Hortic 668:75–80
Hummer KE, Oliphant JM, Taylor AW, Smith JM, Deinzer ML (2005) Xanthogalenol and 4′-O-methylxanthohumol content of some American Humulus. Acta Hortic 668:229–232
Jakše J, Bandelj D, Javornik B (2002) Eleven new microsatellites for hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Mol Ecol Notes 2:544–546
Jakše J, Satovic Z, Javornik B (2004) Microsatellite variability among wild and cultivated hops (Humulus lupulus L.). Genome 47:889–899
Patzak J, Vrba L, Matousek J (2007) New STS molecular markers for assessment of genetic diversity and DNA fingerprinting in hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Genome 50:15–25
Li Y, Korol AB, Fahima T, Beiles A, Nevo E (2002) Microsatellites: genomic distribution, putative functions, and mutational mechanisms: a review. Mol Ecol 11:2453–2465
Liu K, Muse SV (2005) PowerMarker: integrated analysis environment for genetic marker data. Bioinformatics 21:2128–2129
Morgante M, Hanafey M, Powell W (2002) Microsatellites are preferentially associated with nonrepetitive DNA in plant genomes. Nat Genet 30:194–200
Murakami A, Darby P, Javornik B, Pais M, Seigner E, Lutz A, Svoboda P (2006a) Microsatellite DNA analysis of wild hops, Humulus lupulus L. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53:1553–1562
Murakami A, Darby P, Javornik B, Pais M, Seigner E, Lutz A, Svoboda P (2006b) Molecular phylogeny of wild hops, Humulus lupulus L. Heredity 97:66–74
Novak P, Krofta K, Matousek J (2006) Chalcone synthase homologues from Humulus lupulus: some enzymatic properties and expression. Biol Plant 50:48–54
Okada Y, Sugimoto M, Ito K (2001) Molecular cloning and expression of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase gene responsible for essential oil biosynthesis in hop (Humulus lupulus). J Plant Physiol 158:1183–1188
Okada Y, Sano Y, Kaneko T, Abe I, Noguchi H, Ito K (2004) Enzymatic reactions by five chalcone synthase homologs from hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:1142–1145
Patzak J, Vrba L, Matoušek J (2007) New STS molecular markers for assessment of genetic diversity and DNA fingerprinting in hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Genome 50(1):15–25
Pillay M, Kenny ST (1996) Structure and inheritance of ribosomal DNA variants in cultivated and wild hop, Humulus lupulus L. Theor Appl Genet 93:333–340
Salmon ES (1934) Two new hops: Brewer’s favourite and Brewer’s Gold. J Southeast Agric College, Wye, Kent 34:93–105
Small E (1978) A numerical and nomenclatural analysis of morpho-geographical taxa of Humulus. Syst Bot 3:37–76
Small E (1997) Cannabaceae. In: Flora of North America Editorial Committee (Eds) Flora of North America North of Mexico, vol 3. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 381–387
Smith JM, Oliphant JM, Hummer K (2006) Plant exploration for native hop in the American Southwest. Plant Genet Resour Newslett 147:29–37
Stajner N, Jakše J, Kozjak P, Javornik B (2005) The isolation and characterisation of microsatellites in hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Plant Sci 168:213–221
Stevens JF, Taylor AW, Nickerson GB, Ivancic M, Henning J, Haunold A, Deinzer M (2000) Prenylflavonoid variation in Humulus lupulus: distribution and taxonomic significance of xanthogalenol and 4'-O-methylxanthohumol. Phytochem 53:759–775
Varshney RK, Graner A, Sorrells ME (2005) Genic microsatellite markers in plants: features and applications. Trends Biotechnol 23:48–55
Acknowledgements
We thank laboratory technicians April Nyberg and Isabela Mackey for data entry and PCR. This research was supported by USDA-ARS CRIS 5358-150-033-00D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bassil, N.V., Gilmore, B., Oliphant, J.M. et al. Genic SSRs for European and North American hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Genet Resour Crop Evol 55, 959–969 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-007-9303-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-007-9303-9