Abstract
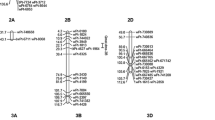
Flowering time is a trait which has a major influence on the quality of forage. In addition, flowering and subsequent seed yields are important traits for seed production by grass breeders. In this study, we have identified quantitative trait loci (QTL) for flowering time and morphological traits of the flowering head in an F1 mapping population in Lolium perenne L (perennial ryegrass), a number of which have not previously been identified in L. perenne mapping studies. QTL for days to heading (DTH) were mapped in both outdoor and glasshouse experiments, revealing three and five QTL for DTH which explained 53% and 42% of the total phenotypic variation observed, respectively. Two QTL for DTH were detected in both environments, although they had contrasting relative magnitudes in each environment. One QTL for spike length and three QTL for spikelets per spike were also identified explaining, a total of 32 and 33% of the phenotypic variance, respectively. Furthermore, the QTL for spike length and spikelets per spike generally coincided with QTL for days to heading, implying co-ordinate regulation by underlying genes. Of particular interest was a region harbouring overlapping QTL for days to heading, spike length and spikelets per spike on the top of linkage group 4, containing the major QTL for spike length identified in this population.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alm V, Fang C, Busso CS, Devos KM, Vollan K, Grieg Z et al (2003) A linkage map of meadow fescue (Festuca pratensis Huds.) and comparative mapping with other Poaceae species. Theor Appl Genet 108:25–40. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1399-5
Andersen JR, Jensen LB, Asp T, Lubberstedt T (2006) Vernalization response in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) involves orthologues of diploid wheat (Triticum monococcum) VRN1 and rice (Oryza sativa) Hd1. Plant Mol Biol 60:481–494. doi:10.1007/s11103-005-4815-1
Anhalt UC, Heslop-Harrison PJ, Byrne S, Guillard A, Barth S (2008) Segregation distortion in Lolium: evidence for genetic effects. Theor Appl Genet 117:297–306
Armstead IP, Turner LB, Farrell M, Skot L, Gomez P, Montoya T et al (2004) Synteny between a major heading-date QTL in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) and the Hd3 heading-date locus in rice. Theor Appl Genet 108:822–828. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1495-6
Donmez E, Sears RG, Shroyer JP, Paulsen GM (2001) Genetic gain in yield attributes of winter wheat in the great plains. Crop Sci 41:1412–1419
Dubcovsky J, Lijavetzky D, Appendino L, Tranquilli G (1998) Comparative RFLP mapping of Triticum monococcum genes controlling vernalization requirement. Theor Appl Genet 97:968–975. doi:10.1007/s001220050978
Elgersma A (1990) Genetic variation for seed yield in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Plant Breed 105:117–125. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0523.1990.tb00464.x
Ergon A, Fang C, Jorgensen O, Aamlid TS, Rognli OA (2006) Quantitative trait loci controlling vernalisation requirement, heading time and number of panicles in meadow fescue (Festuca pratensis Huds.). Theor Appl Genet 112:232–242. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-0115-z
Faville MJ, Vecchies AC, Schreiber M, Drayton MC, Hughes LJ, Jones ES et al (2004) Functionally associated molecular genetic marker map construction in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Theor Appl Genet 110:12–32. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1785-7
Gill GP, Wilcox PL, Whittaker DJ, Winz RA, Bickerstaff P, Echt CE et al (2006) A framework linkage map of perennial ryegrass based on SSR markers. Genome 49:354–364. doi:10.1139/G05-120
Hannaway D, Fransen S, Cropper J, Teel M, Chaney M, Griggs T et al (1999) Perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). A Pacific Northwest Extension Publication, vol PNW 502. Oregon State University, Washington State University, University of Idaho
Inoue M, Gao ZS, Cai HW (2004) QTL analysis of lodging resistance and related traits in Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.). Theor Appl Genet 109:1576–1585. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1791-9
Jensen LB, Andersen JR, Frei U, Xing YZ, Taylor C, Holm PB et al (2005a) QTL mapping of vernalization response in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) reveals co-location with an orthologue of wheat VRN1. Theor Appl Genet 110:527–536. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1865-8
Jensen LB, Muylle H, Arens P, Andersen CH, Holm PB, Ghesquiere M et al (2005b) Development and mapping of a public reference set of SSR markers in Lolium perenne L. Mol Ecol Notes 5:951–957. doi:10.1111/j.1471-8286.2005.01043.x
Jones ES, Dupal MP, Dumsday JL, Hughes LJ, Forster JW (2002a) An SSR-based genetic linkage map for perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Theor Appl Genet 105:577–584. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-0907-3
Jones ES, Mahoney NL, Hayward MD, Armstead IP, Jones JG, Humphreys MO et al (2002b) An enhanced molecular marker based genetic map of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) reveals comparative relationships with other Poaceae genomes. Genome 45:282–295. doi:10.1139/g01-144
Kato K, Miura H, Sawada S (2000) Mapping QTLs controlling grain yield and its components on chromosome 5A of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 101:1114–1121. doi:10.1007/s001220051587
Kubik C, Sawkins M, Meyer WA, Gaut BS (2001) Genetic diversity in seven perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) cultivars based on SSR markers. Crop Sci 41:1565–1572
Lauvergeat V, Barre P, Bonnet M, Ghesquiere M (2005) Sixty simple sequence repeat markers for use in the Festuca-Lolium complex of grasses. Mol Ecol Notes 5:401–405. doi:10.1111/j.1471-8286.2005.00941.x
Minitab Inc (2006) Minitab Statistical Software, Release 15 for Windows, State College, Pennsylvania. Minitab® is a registered trademark of Minitab Inc
Shinozuka H, Hisano H, Ponting RC, Cogan NOI, Jones ES, Forster JW et al (2005) Molecular cloning and genetic mapping of perennial ryegrass casein protein kinase 2 alpha-subunit genes. Theor Appl Genet 112:167–177. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-0119-8
Simpson GG, Dean C (2002) Flowering—Arabidopsis, the rosetta stone of flowering time? Science 296:285–289. doi:10.1126/science.296.5566.285
Skot L, Humphreys MO, Armstead I, Heywood S, Skot KP, Sanderson R et al (2005) An association mapping approach to identify flowering time genes in natural populations of Lolium perenne (L.). Mol Breed 15:233–245. doi:10.1007/s11032-004-4824-9
Takahashi Y, Shomura A, Sasaki T, Yano M (2001) Hd6, a rice quantitative trait locus involved in photoperiod sensitivity, encodes the alpha subunit of protein kinase CK2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:7922–7927. doi:10.1073/pnas.111136798
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap 3.0, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Van Ooijen JW, Boer MP, Jansen RC, Maliepaard C (2002) MapQTL 4.0, Software for the calculation of QTL positions on genetic maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: Software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78. doi:10.1093/jhered/93.1.77
Yamada T, Jones ES, Cogan NOI, Vecchies AC, Nomura T, Hisano H et al (2004) QTL analysis of morphological, developmental, and winter hardiness-associated traits in perennial ryegrass. Crop Sci 44:925–935
Yan L, Loukoianov A, Tranquilli G, Helguera M, Fahima T, Dubcovsky J (2003) Positional cloning of the wheat vernalization gene VRN1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:6263–6268. doi:10.1073/pnas.0937399100
Yano M, Kojima S, Takahashi Y, Lin HX, Sasaki T (2001) Genetic control of flowering time in rice, a short-day plant. Plant Physiol 127:1425–1429. doi:10.1104/pp.127.4.1425
Acknowledgment
S. Byrne was awarded a Teagasc Walsh Fellowship/Ireland to undertake this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Byrne, S., Guiney, E., Barth, S. et al. Identification of coincident QTL for days to heading, spike length and spikelets per spike in Lolium perenne L.. Euphytica 166, 61–70 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9831-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9831-1