Abstract
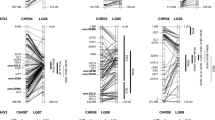
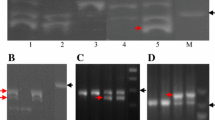
The adaptability of Triticum aestivum to a large range of environments is partially due to genetic differences in sensitivity to vernalization. The most potent gene reducing the vernalization requirement in hexaploid wheat is Vrn-A1. An orthologous vernalization gene, designated Vrn-A m 1, was mapped in the diploid wheat Triticum monococcum between RFLP markers Xwg908 and Xabg702 on the long arm of chromosome 5AmL. The orthology of VrnA m 1 with Vrn-A1 (5A wheat, originally Vrn1), Vrn-D1 (5D wheat, originally Vrn3), Vrn-R1 (5R rye, originally Sp1) and Vrn-H1 (5H barley, originally Sh2) was shown by mapping RFLP markers linked to these vernalization genes on the T. monococcum linkage map. A second vernalization gene, designated Vrn-A m 2, was found in the distal region of chromosome 5AmL within a segment translocated from homoeologous group 4. This gene is completely linked to RFLP marker Xbcd402 and located between the same RFLP markers (Xβ-Amy-1 and Xmwg616) as the Vrn-H2 (originally Sh) locus in Hordeum vulgare.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 6 January 1998 / Accepted: 31 March 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dubcovsky, J., Lijavetzky, D., Appendino, L. et al. Comparative RFLP mapping of Triticum monococcum genes controlling vernalization requirement. Theor Appl Genet 97, 968–975 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050978
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050978