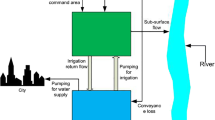
Abstract
Seawater intrusion is one of the causes of groundwater quality degradation in coastal zones. This phenomenon is intensified by overexploitation of coastal aquifers. In this paper, optimal management strategies have been determined to prevent the advance of seawater using a parallel simulation–optimization decision model. This model has been applied to a real case study of Ajabshir aquifer located in Urmia Lake basin, Iran, for a 20-year planning horizon (2015–2034). Four categorizes of new sustainability indices (indices of protection, reliability, vulnerability, and aquifer area with a groundwater problem) as the objective functions have been examined for the first time. The developed management problems based on these four categories have been solved under two different conditions of groundwater elevation and salinity concentration. The results of 20-year period simulations indicate that by changing the extraction pattern in different regions of the aquifer (as the decision variables) based on the solution of management problems, the largest decrease in net recharge (0.065 million cubic meters) occurs in the second half of the hydrologic year (October to March) compared to the continued condition in which all factors are similar to 2014. The contribution of using indices in this study can help the local water managers to identify the high-risk areas for better planning and other coastal settings.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Afshar, M. H., Ketabchi, H., & Rasa, E. (2006). Elitist continuous ant colony optimization algorithm: Application to reservoir operation problems. International Journal of Civil Engineering, 4(3), 274–285.
Ataie-Ashtiani, B., & Ketabchi, H. (2011). Elitist continuous ant colony optimization algorithm for optimal management of coastal aquifers. Water Resources Management, 25(1), 165–190.
Ataie-Ashtiani, B., Ketabchi, H., & Rajabi, M. M. (2014). Optimal management of a freshwater lens in a small island using surrogate models and evolutionary algorithms. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, American Society of Civil Engineers, 19(2), 339–354.
Bhattacharjya, R. K., & Datta, B. (2009). ANN-GA-based model for multiple objective management of coastal aquifers. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, American Society of Civil Engineers, 135(5), 314–322.
Camp, M. V., Radfar, M., & Walraevens, K. (2010). Assessment of groundwater storage depletion by overexploitation using simple indicators in an irrigated closed aquifer basin in Iran. Agricultural Water Management, 97, 1876–1886.
Christelis, V., & Mantoglou, A. (2016). Pumping optimization of coastal aquifers assisted by adaptive metamodelling methods and radial basis functions. Water Resources Management, 30(15), 5845–5859.
Christelis, V., Regis, R. G., & Mantoglou, A. (2018). Surrogate-based pumping optimization of coastal aquifers under limited computational budgets. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 20(1), 164–176.
Dentoni, M., Deidda, R., Paniconi, C., Qahman, K., & Lecca, G. (2015). A simulation/optimization study to assess seawater intrusion management strategies for the Gaza Strip coastal aquifer (Palestine). Hydrogeology Journal, 23(2), 249–264.
Fan, Y., Lu, W., Miao, T., Li, J., & Lin, J,. (2020). Optimum design of a seawater intrusion monitoring scheme based on the image quality assessment method. Water Resources Management, 34, 2485–2502.
Foster, S., Hirata, R., Gomes, D., D'Elia, M., & Paris, M. (2002). Groundwater quality protection: a guide for water utilities, municipal authorities, and environment agencies. Washington, DC: World Bank. © World Bank.
Ghadimi, S., & Ketabchi, H. (2019). Possibility of cooperative management in groundwater resources using an evolutionary hydro-economic simulation-optimization model. Journal of Hydrology, 578, 124094.
Hashimoto, T., Stedinger, J. R., & Loucks, D. P. (1982). Reliability, resiliency, and vulnerability criteria for water resource system performance evaluation. Water Resources Research, 18, 14–20.
Heiß, L., Bouchaou, L., Tadoumant, S., & Reichert, B. (2020). Index-based groundwater vulnerability and water quality assessment in the arid region of Tata city (Morocco). Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 10, 100344.
Hosseini, S. M., Parizi, E., Ataie-Ashtiani, B., & Simmons, C. T. (2019). Assessment of sustainable groundwater resources management using integrated environmental index: Case studies across Iran. Science of the Total Environment, 676(1), 792–810.
IWRMC (Iran Water Resources Management Company). (2014). Updating water resources studies report of Urmia Lake basin. Tabriz, Iran: Ministry of Energy, Regional Water Company of East Azerbaijan.
Javadi, A., Hussain, M., Sherif, M., & Farmani, R. (2015). Multi-objective optimization of different management scenarios to control seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Water Resources Management. Springer, 29(6), 1843–1857.
Javadi, A. A., Abd-Elhamid, H. F., & Farmani, R. (2012). A simulation-optimization model to control seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers using abstraction/recharge wells. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 36(16), 1757–1779.
Karatzas, G. P., & Dokou, Z. (2015). Optimal management of saltwater intrusion in the coastal aquifer of Malia, Crete (Greece), using particle swarm optimization. Hydrogeology Journal, 23(6), 1181–1194.
Ketabchi, H., & Ataie-Ashtiani, B. (2015a). Evolutionary algorithms for the optimal management of coastal groundwater: A comparative study toward future challenges. Journal of Hydrology, 520, 193–213.
Ketabchi, H., & Ataie-Ashtiani, B. (2015b). Review: Coastal groundwater optimization–-Advances, challenges, and practical solutions. Hydrogeology Journal, 23(6), 1129–1154.
Ketabchi, H., & Ataie-Ashtiani, B. (2015c). Assessment of a parallel evolutionary optimization approach for efficient management of coastal aquifers. Environmental Modelling & Software, 74, 21–38.
Kourakos, G., & MantoglouA,. (2009). Pumping optimization of coastal aquifers based on evolutionary algorithms and surrogate modular neural network models. Advances in Water Resources, 32(4), 507–521.
Kourakos, G., & Mantoglou, A. (2013). Development of a multi-objective optimization algorithm using surrogate models for coastal aquifer management. Journal of Hydrology, 479, 13–23.
Lal, A., Datta, B. (2019). Optimal pumping strategies for the management of coastal groundwater resources: Application of Gaussian Process Regression metamodel-based simulation-optimization methodology. ISH Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1–10.
Loucks, D. P. (1997). Quantifying trends in system sustainability. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 42, 513–530.
Majidipour, F., Najafi, S. M. B., Taheri, K., Fathollahi, J., & Missimer, T. M. (2021). Index-based groundwater sustainability assessment in the socio-economic context: A case study in the Western Iran. Environmental Management, 67(4), 648–666.
Mostafaei-Avandari, M., & Ketabchi, H. (2020). Coastal groundwater management by an uncertainty-based parallel decision model. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 146(6), 04020036.
Ndambuki, J. M. (2002). Multi-objective groundwater quantity management: A stochastic approach.
Papadopoulou, M. P., Nikolos, I. K., & Karatzas, G. P. (2010). Computational benefits using artificial intelligent methodologies for the solution of an environmental design problem: Saltwater intrusion. Water Science and Technology, 62(7), 1479–1490.
Parhami, B. (2002). Introduction to parallel processing, algorithms and architectures. University of California, Santa Barbara.
Qahman, K., Larabi, A., Ouazar, D., Naji, A., & Cheng, A. H. D. (2005). Optimal and sustainable extraction of groundwater in coastal aquifers. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 19(2), 99–110.
Qahman, K., Larabi, A., Ouazar, D., Naji, A., & Cheng, A. H. D. (2009). Optimal extraction of groundwater in Gaza coastal aquifer. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 4, 249–259.
Rajabi, M. M., & Ketabchi, H. (2017). Uncertainty-based simulation-optimization using Gaussian process emulation: Application to coastal groundwater management. Journal of Hydrology, 555(Dec):518–534.
Sadek, M., & Hagagg, K. (2020). A Novel Groundwater Sustainability Index using AHP/GIS Approach. International Journal of Research in Environmental Science (IJRES), 6(4), 28–40.
Saghi-Jadid, M., & Ketabchi, H. (2021). Result-based management approach for aquifer restoration problems using a combined numerical simulation–parallel evolutionary optimization model. Journal of Hydrology, 594, 125709.
Sandoval-Solis, S., McKinney, D. C., & Loucks, D. P. (2010). Sustainability index for water resources planning and management. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 137(5), 381–390.
Sedki, A., & Ouazar, D. (2011). Simulation-optimization modeling for sustainable groundwater development: a Moroccan coastal aquifer case study. Water Resources Management, 25(11), 2855–2875.
Semlali. (2021). Spatio-temporal modelling of groundwater resources to improve drought risk assessments: proposal of indexs for Siliana catchment in Tunisia. Faculté des bioingénieurs, Université catholique de Louvain. Prom: Vanclooster, Marnik. http://hdl.handle.net/2078.1/thesis:33051
Senent-Aparicio, J., Pérez-Sánchez, J., García-Aróstegui, J. L., & Bielsa-ArteroA, D.-P. (2015). Evaluating groundwater management sustainability under limited data availability in semiarid zones. Water, 7(8), 4305–4322.
Singh, A. P., & Bhakar, P. (2021). Development of groundwater sustainability index: A case study of western arid region of Rajasthan, India. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23, 1844–1868.
Song, J., Yang, Y., Wu, J., Wu, J., Sun, X., & Lin, J. (2018). Adaptive surrogate model based multiobjective optimization for coastal aquifer management. Journal of Hydrology, 561, 98–111.
Sreekanth, J., & Datta, B. (2010). Multi-objective management of saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers using genetic programming and modular neural network based surrogate models. Journal of Hydrology, 393(3–4), 245–256.
Sreekanth, J., & Datta, B. (2014). Stochastic and robust multi-objective optimal management of pumping from coastal aquifers under parameter uncertainty. Water Resources Management, 28(7), 2005–2019.
Sreekanth, J., Moore, C., & Wolf, L. (2016). Pareto-based efficient stochastic simulation–optimization for robust and reliable groundwater management. Journal of Hydrology, 533, 180–190.
Thomas, B. F. (2019). Sustainability indices to evaluate groundwater adaptive management: A case study in California (USA) for the Sustainable Groundwater Management Act. Hydrogeology Journal, 27, 239–248.
Triki, C., Zekri, S., Al-Maktoumi, A., & Fallahnia, M. (2017). An artificial intelligence approach for the stochastic management of coastal aquifers. Water Resources Management, 31(15), 4925–4939.
Voss, C. I., & Provost, A. M. (2010). SUTRA: A model for saturated/unsaturated, variable-density ground-water flow with solute or energy transport. Water-Resources Investigations Rep, 02–4231. Reston, VA: USGS.
Yang, Y., Song, J., Simmons, C. T., Ataie-Ashtiani, B., Wu, J., Wang, J., & Wu, J. (2021). A conjunctive management framework for the optimal design of pumping and injection strategies to mitigate seawater intrusion. Journal of Environmental Management, 282, 111964.
YCE (Yekom Consulting Engineers). (2006). Ajabshir Groundwater Studies Report, Ministry of Energy, Iran.
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the supports from Iran Water Resources Management Company and Regional Water Companies of East and West Azerbaijan in supplying the required data for the real-case study described in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Mohammad Mostafaei-Avandari, Hamed Ketabchi, and Fatemeh Shaker-Soureh. The first draft of the paper was written by Mohammad Mostafaei-Avandari and all authors completed the previous versions of the paper. All authors read and approved the final paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mostafaei-Avandari, M., Ketabchi, H. & Shaker-Soureh, F. Managerial sustainability indices for improving the coastal groundwater decisions by a parallel simulation–optimization model. Environ Monit Assess 195, 100 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10712-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10712-6