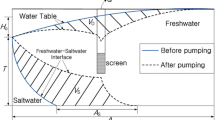
Abstract
Four examples are investigated for the optimal and sustainable extraction of groundwater from a coastal aquifer under the threat of seawater intrusion. The objectives and constraints of these management scenarios include maximizing the total volume of water pumped, maximizing the profit of selling water, minimizing the operational and water treatment costs, minimizing the salt concentration of the pumped water, and controlling the drawdown limits. The physical model is based on the density-dependent advective-dispersive solute transport model. Genetic algorithm is used as the optimization tool. The models are tested on a hypothetical confined aquifer with four pumping wells located at various depths. These solutions establish the feasibility of simulating various management scenarios under complex three-dimensional flow and transport processes in coastal aquifers for the optimal and sustainable use of groundwater.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharmouch A, Larabi A (2004) 3D finite element model for seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. In: Proceeding of 15th international conference on computational methods in water resources (CMWR), North Carolina
Aly AH, Peralta PC (1999a) Comparison of a genetic algorithm and mathematical programming to the design of groundwater cleanup systems. Water Resour Res 35:2415–2425
Aly AH, Peralta PC (1999b) Optimal design of aquifer cleanup systems under uncertainty using a neural network and a genetic algorithm. Water Resour Res 35:2523–2532
Benhachmi MK, Ouazar D, Naji A, Cheng AH-D, EL Harrouni K (2003a) Pumping optimization in saltwater intruded aquifers by simple genetic algorithm—Deterministic model. Proceedings of 2nd international conference of saltwater intrusion and coastal aquifers—monitoring, modeling, and management. In: Marin L, Cheng AH-D, (eds) Merida, Mexico
Benhachmi MK, Ouazar D, Naji A, Cheng AH-D, EL Harrouni K, (2003b) Chance-constrained pumping optimization in saltwater intruded aquifers by simple genetic algorithm—stochastic model. Proceedings of 2nd international conference on saltwater intrusion and coastal aquifers—monitoring, modeling, and management. In: Marin L, Cheng AH-D (eds) Merida, Mexico
Charnes A, Cooper WW (1959) Chance-constrained programming. Manage Sci 6:73–79
Cheng AH-D, Halhal D, Naji A, Ouazar D (2000) Pumping optimization in saltwater-intruded coastal aquifers. Water Resour Res 36:2155–2165
Cheng AH-D, Benhachmi MK, Halhal D, Ouazar D, Naji A, and EL Harrouni K (2003) Pumping optimization in saltwater-intruded aquifers. In: Cheng AH-D, Ouazar D (eds) Coastal aquifer management—monitoring, modeling, and case studies. chap. 11. Lewis Publishers, pp 233–256
Das A, Datta B (1995) Simulation of density dependent 2-D seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers using nonlinear optimization algorithm. Proceedings of the American Water Resource Association Annual summer Symposium Water Resource Environment Emphasis Hydrological Cultural Insight in Pacific Rim. American Water Association, Herndon, VA, pp 277–286
Das A, Datta B (1999a) Development of multi-objective management models for coastal aquifers. J Water Resour Plann Manage 125:76–87
Das A, Datta B (1999b) Development models for sustainable use of coastal aquifers. J Irrig Drain Eng 125:112–121
Das A, Datta B (2000) Optimization based solution of density dependent seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. J Hydrologic Eng ASCE 5:82–89
DasGupta A, Nobi AN, Paudyal GN (1996) Groundwater management model for an extensive multiaquifer system and an application. J Ground Water 34:349–357
Diersch H-JG, Kolditz O (2002) Variable-density flow and transport in porous media: approaches and challenges. Adv Water Resour 25:899–944
El Harrouni K, Ouazar D, Walters GA, Cheng AH-D (1998) Groundwater optimization and parameter estimation by genetic algorithm and dual reciprocity boundary element method. Eng Anal Boundary Elem 124:129–139
Emch PG, Yeh WWG (1998) Management model for conjunctive use of coastal surface water and groundwater. J Water Resour Plann Manage 124:129–139
Essaid HI (1990) Multi-layered sharp interface model of coupled freshwater and saltwater in coastal systems: model development and application. Water Resour Res 27:1431–1454
Finney B, Samsuhadi A, Willis R (1992) Quasi-3-dimensional optimization of Jakarta Basin. J Water Resour Plann Manage 118:18–31
Galeati G, Gambolati G, Neuman SP (1992) Coupled and partially coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian model of freshwater-seawater mixing. Water Resour Res 28:147–165
Gambolati G, Putti M, Paniconi C (1999) Three-dimensional model of coupled density- dependent flow and miscible transport in groundwater. In: Bear et al (eds) Seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: concepts, methods, and practices. Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 315–362
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization and machine learning. Addison-Wesley-Longman, Reading, Mass
Gordon E, Shamir U, Bensabat J (2001) Optimal extraction of water from regional aquifer under salinization. J Water Resour Plann Manage 127:71–77
Gorelick SM (1983) A review of distributed parameter groundwater management modeling methods. Water Resour Res 19:305–319
Halhal D, Walters GA, Ouazar D, Savic DA (1997) Water network rehabilitation with structured messy genetic algorithm. J Water Resours Plann Manage 123:137–146
Haupt R, Haupt SE (1998) Practical Genetic Algorithms. Wiley, Reading, New York
Henry HR (1964) Effects of dispersion on salt encroachment in coastal aquifers. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper 1613-C, C71-C84
Holland J (1975) Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor
Huang C, Mayer AS (1997) Pump-and-treat optimization using well locations and pumping rates as decision variables. Water Resour Res 33:1001–1012
Huber AT (1999) A hydrologic-economic model of salinity in a coastal aquifer—Strategies for sustainable water management in an arid region. PhD thesis, Harvard University, Cambridge
Huyakorn PS, Anderson PF, Mercer JW, White WO Jr (1987) Saltwater intrusion in aquifers: development and testing of a three dimensional finite element model. Water Resour Res 23:293–312
Johannsen K, Kinzelbach W, Oswald S, Wittum G (2002) The saltpool benchmark problem-numerical simulation of saltwater upconning in a porous medium. Adv Water Resour 25:335–348
Langevin C, Guo W (2002) User’s guide to SEAWAT, a computer program for simulation of three-dimensional variable density groundwater flow. U.S.G.S, Florida
Larabi A, De Smedt F (1994a) Three-dimensional finite element model for saltwater intrusion into aquifers. In: Proceedings of 10th international conference on computational methods in water resources (CMWR), Vol 2. Heidelberg, pp 1019–1026
Larabi A, De Smedt F (1994b) Solving 3-D hexahedral finite elements groundwater models by preconditioned conjugate gradient methods. Water Resour Res 30:509–521
Larabi A, De Smedt F (1997) Numerical solution of 3-D groundwater flow involving free boundaries by a fixed finite element method. J Hydrol 201:161–182
Lecca G (2000) Implementation and testing of the CODESA-3D model for density-dependent flow and transport problems in porous media. CRS4-TECH-REP-00/40, Cagliari, Italy
McKinney DC, Lin M (1994) Genetic algorithms solution of groundwater management models. J Water Resour Res 30:1897–1906
Mercer JW, Larson SP, Paut CR (1980) Simulation saltwater interface motion. Ground Water 18:374–385
Murtagh BA, Saunders MA (1993) MINOS 5.4 user’s guide. Technical Report SOL 83–20R, Systems Optimization Laboratory Department Operations Research Stanford University, Stanford, CA
Naji A, Ouazar D, Cheng AH-D (1998a) Locating saltwater/freshwater interface using nonlinear programming and h-adaptive BEM. Eng Anal Boundary Elem 21:253–259
Naji A, Ouazar D, Cheng AH-D (1998b) Analytical stochastic solutions of saltwater/freshwater interface in coastal aquifers. Stochastic Hydrol Hydraulics 12:413–430
Naji A, Ouazar D, Cheng AH-D (1999) BEM solution of stochastic seawater intrusion. Eng Anal Boundary Elem 23:529–537
Oswald SE, Kinzelbasch W (2004) Three-dimensional physical benchmark experiments to test variable-density flow models. J Hydrol 290:22–42
Ouazar D, Cheng AH-D (1999) Application of genetic algorithms in water resources. In: Katsifarakis KL (ed) Groundwater Pollution Control. WIT Press, Boston, pp 293–316
Park C-H, Aral MM (2004) Multi-objective optimization of pumping rates and well placement in coastal aquifers. J Hydrol 290:80–99
Polo JF, Ramis FJR (1983) Simulation of salt water fresh water interface motion. Water Resour Res 19:61–68
Putti M, Paniconi C (1995) Finite element modeling of saltwater intrusion problems. In: Advanced methods for groundwater pollution control, CISM Courses and Lectures. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 65–84
Shamir U, Bear J, Gamliel A (1984) Optimal annual operation of a coastal aquifer. J Water Resour Res 20:435–444
Strack ODL (1976) A single-potential solution for regional interface problems in coastal aquifers. Water Resour Res 12:1165–1174
Willis R, Finney BA (1988) Planning model for optimal control of saltwater intrusion. Water Resour Plann Manage 114:333–347
Acknowledgements
David L. Carroll is gratefully acknowledged for the use of his genetic algorithms driver in this study. CRS4-Italy kindly provided the CODESA-3D code. This work was conducted on behalf of Gaza Islamic University, Palestine and Ecole Mohammadia d’Ingénieurs, Université Mohammed V, Morocco within the framework of the SWIMED project under contract number ICA3-CT2002-10004 funded by EU. The last author’s participation is supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation grant OISE-0422868 “Optimal groundwater models for sustainable management of coastal aquifers.” The encouragement of the program director Dr. Osman Shinaishin for this international cooperation is deeply appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qahman, K., Larabi, A., Ouazar, D. et al. Optimal and sustainable extraction of groundwater in coastal aquifers. Stoch Environ Res Ris Assess 19, 99–110 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-004-0218-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-004-0218-0