Abstract
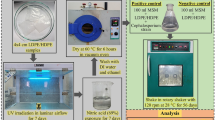
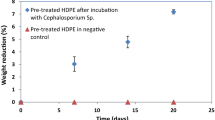
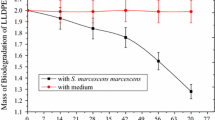
The present analysis deals with the ability of Thermomyces lanuginosus to degrade pre-treated low-density polyethylene (LDPE). The synergistic effect of UV irradiation, heat, and acid pre-treatments on the biodegradability of the polymer was thoroughly assessed. Oxidative structural modifications such as the appearance of carboxylate and carbonyl groups in LDPE chains were recorded post the UV and heat treatments. Furthermore, the nitric acid treatment incorporated NO2 groups into the polymer matrix. Alterations in the polymer thermal stabilities and surface morphologies after each pre-treatment were analyzed using thermogravimetric analysis and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), respectively. The gravimetric analysis revealed a reduction in the weight of the pre-treated LDPE films by 9.21 ± 0.84% after 1 month of the incubation period with Thermomyces lanuginosus. An increase in the thermal stability, disappearance of the incorporated hydrophilic functional groups, and reduction in the carbon content of the polymer samples post the incubation period further justified the biodegradation process. SEM analysis showed modifications in the morphology and texture patterns in pre-treated LDPE after inoculation with Thermomyces lanuginosus. The findings suggest that Thermomyces lanuginosus could be efficient for the decomposition of pre-treated LDPE under laboratory conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Abd El-Rehim, H. A., Hegazy, E. S. A., Ali, A. M., Rabie, A. M., El-rehim, H. A. A., Hegazy, E. S. A., et al. (2004). Synergistic effect of combining UV-sunlight-soil burial treatment on the biodegradation rate of LDPE/starch blends. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology a: Chemistry, 163(3), 547–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2004.02.003
Albertsson, A. C. (1978). Biodegradation of synthetic polymers. II. A limited microbial conversion of 14C in polyethylene to 14CO2 by some soil fungi. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 22(12), 3419–3433.
Albertsson, A. C., Andersson, S. O., & Karlsson, S. (1987). The mechanism of biodegradation of polyethylene. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 18(1), 73–87.
Awasthi, S., Srivastava, P., Singh, P., Tiwary, D., & Mishra, P. K. K. (2017). Biodegradation of thermally treated high-density polyethylene (HDPE) by Klebsiella pneumoniae CH001. 3 Biotech, 7(5), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0959-3
Brown, B. S., Millls, J., & Hulse, J. M. (1974). Chemical and biological degradation of waste plastics. Nature, 250, 161–163.
Chaudhary, A. K., & Vijayakumar, R. P. (2020a). Effect of chemical treatment on biological degradation of high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Environment, Development and Sustainability, 22(2), 1093–1104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-018-0236-6
Chaudhary, A. K., & Vijayakumar, R. P. (2020b). Studies on biological degradation of polystyrene by pure fungal cultures. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 22(5), 4495–4508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00394-5
Chaudhary, A. K., & Vijayakumar, R. P. (2020c). Synthesis of polystyrene/starch/CNT composite and study on its biodegradability. Journal of Polymer Research, 27, 187.
Chaudhary, A. K., Chaitanya, K., & Vijayakumar, R. P. (2021). Synergistic effect of UV and chemical treatment on biological degradation of Polystyrene by Cephalosporium strain NCIM 1251. Archives of Microbiology, 203, 2183–2191.
Coates, J. (2006). Interpretation of infrared spectra, a practical approach. Encyclopedia of analytical chemistry, 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470027318.a5606
Contat-Rodrigo, L., Ribes-Greus, A., & Imrie, C. T. (2002). Thermal analysis of high-density polyethylene and low-density polyethylene with enhanced biodegradability. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 86(3), 764–772. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.10974
Esmaeili, A., Pourbabaee, A. A., Alikhani, H. A., Shabani, F., & Esmaeili, E. (2013). Biodegradation of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) by mixed culture of Lysinibacillus xylanilyticus and Aspergillus niger in soil. PLoS One, 8(9). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071720
Avalos-Belmontes, F., Zapata-Gonzalez, I., Ramos-Devalle, L. F., & Roberto Zitzumbo-Guzman, S. A. R. (2009). Thermo-oxidative degradation of HDPE as a function of its crystalline content. Journal of Polymer Science Part b: Polymer Physics, 47, 1906–1915. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb
Garaeva, S. R., Alper, A., Aydin, A. A. A., Aydin, A. A. A., Yalçin, B., Fatullaeva, P. A., & Medzhidov, A. A. (2010). Composition, properties, and application of products formed in oxidation of polyethylene by nitric acid. Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry, 83(1), 97–101. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070427210010192
Gulmine, J. V., Janissek, P. R., Heise, H. M., & Akcelrud, L. (2002). Polyethylene characterization by FTIR. Polymer Testing, 21(5), 557–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9418(01)00124-6
Hopewell, J., Dvorak, R., & Kosior, E. (2009). Plastics recycling: Challenges and opportunities. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2007, 2115–2126. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2008.0311
Jeon, H. J., & Kim, M. N. (2013). Isolation of a thermophilic bacterium capable of low-molecular-weight polyethylene degradation. Biodegradation, 24(1), 89–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9560-y
Kershaw, M. J., & Talbot, N. J. (1998). Hydrophobins and repellents: Proteins with fundamental roles in fungal morphogenesis. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 33, 18–33.
Koski, L. (1978). A DSC study of thermally treated and UV-treated low-density polyethylene. Journal of Thermal Analysis, 13, 467–472.
Koutny, M., Lemaire, J., & Delort, A. M. (2006). Biodegradation of polyethylene films with prooxidant additives. Chemosphere, 64(8), 1243–1252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.12.060
Lee, B., Pometto, A. L., Fratzke, A., & Bailey, T. B. (1991). Biodegradation of degradable plastic polyethylene by Phanerochaete and Streptomyces species. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 57(3), 678–685.
Maheshwari, R., Bharadwaj, G., & Bhat, M. K. (2000). Thermophilic fungi: Their physiology and enzymes. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 64(3), 461–488. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.64.3.461-488.2000
Manzur, A., Limo, M., Limon-Gonzalez, M., & Favela-Torres, E. (2004). Biodegradation of physicochemically treated LDPE by a consortium of filamentous fungi. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 92, 265–271. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.13644
North, E. J., & Halden, R. U. (2013). Plastics and environmental health: The road ahead. Reviews on Environmental Health, 28(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1515/reveh-2012-0030
Otake, Y., Kobayashi, T., Asabe, H., Murakami, N., & Ono, K. (1995). Biodegradation of low-density polyethylene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride, and urea formaldehyde resin buried under soil for over 32 years. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 56(13), 1789–1796.
Paabo, M., & Levin, B. C. (1987). A literature review of the chemical nature and toxicity of the decomposition products of polyethylenes. Fire and Materials, 11(2), 55–70. https://doi.org/10.1002/fam.810110203
Palmisano, A. C., Pettigrew, C. A., Palmisano, A. C., & Pettigrew, C. A. (1992). Biodegradability of plastics. American Institute of Biological Sciences, 42(9), 680–685.
Pandey, J. K., & Singh, R. P. (2001). UV-irradiated biodegradability of ethylene-propylene copolymers, LDPE, and I-PP in composting and culture environments. Biomacromolecules, 2(3), 880–885. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm010047s
Pramila, R., & Ramesh, K. V. (2011). Biodegradation of low density polyethylene (LDPE) by fungi isolated from marine water – A SEM analysis. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 5(28), 5013–5018. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR11.670
Rajandas, H., Parimannan, S., Sathasivam, K., Ravichandran, M., & Yin, L. S. (2012). Analysis method: A novel FTIR-ATR spectroscopy based technique for the estimation of low-density polyethylene biodegradation. Polymer Testing, 31(8), 1094–1099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2012.07.015
Roy, P. K., Titus, S., Surekha, P., Tulsi, E., Deshmukh, C., & Rajagopal, C. (2008). Degradation of abiotically aged LDPE films containing pro-oxidant by bacterial consortium. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 93(10), 1917–1922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2008.07.016
Seneviratne, G., Tennakoon, N. S., Weerasekara, M. L. M. A. W., & Nandasena, K. A. (2006). Polyethylene biodegradation by a developed Penicillium-Bacillus biofilm. Current Science, 90(1), 20–21.
Sharma, J., Gurung, T., Upadhyay, A., Nandy, K., Agnihotri, P., & Mitra, A. K. (2014). Isolation and characterization of plastic degrading bacteria from soil collected from the dumping grounds of an industrial area. International Journal of Advanced and Innovative Research, 3(3), 225–232.
Sivan, A., Szanto, M., & Pavlov, V. (2006). Biofilm development of the polyethylene-degrading bacterium Rhodococcus ruber. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 72(2), 346–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0259-4
Skariyachan, S., Setlur, A. S., Naik, S. Y., Naik, A. A., Usharani, M., & Vasist, K. S. (2017). Enhanced biodegradation of low and high-density polyethylene by novel bacterial consortia formulated from plastic-contaminated cow dung under thermophilic conditions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(9), 8443–8457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8537-0
Sudhakar, M., Doble, M., Murthy, P. S., & Venkatesan, R. (2008). Marine microbe-mediated biodegradation of low- and high-density polyethylenes. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 61(3), 203–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2007.07.011
Teuten, E. L., Saquing, J. M., Knappe, D. R. U., Rowland, S. J., Barlaz, M. A., Jonsson, S., et al. (2009). Transport and release of chemicals from plastics to the environment and to wildlife. Philosophical transactions of the royal society B: biological sciences, 2027–2045. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2008.0284
Thompson, R. C., Swan, S. H., Moore, C. J., & Saal, F. S. (2009). Our plastic age. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 364, 1973–1976. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2009.0054
Tolinski, M. (2012). Plastics and Sustainability: TOwards a Peaceful Coexistence between Bio-Based and Fossil Fuel-Based Plastics. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118217849
Tribedi, P., & Dey, S. (2017). Pre-oxidation of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) by ultraviolet light (UV) promotes enhanced degradation of LDPE in soil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(12). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6351-2
Trilla, R., Perena, J. M., & Fatou, J. G. (1983). Thermal and mechanical properties of oriented polyethylene treated with nitric acid. Polymer Journal, 15(11), 803–809. https://doi.org/10.1295/polymj.15.803
Usha, R., Sangeetha, T., & Palaniswamy, M. (2011). Screening of polyethylene degrading microorganisms from garbage soil. Libyan Agriculture Research Center Journal International, 2(4), 200–2004.
Volke-Seplveda, T., Saucedo-Castaeda, G., Gutirrez-Rojas, M., Manzur, A., Favela-Torres, E., et al. (2002). Thermally treated low density polyethylene biodegradation by Penicillium pinophilum and Aspergillus niger. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 83(2), 305–314. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.2245
Weiland, M., Daro, A., & David, C. (1995). Biodegradation of thermally oxidized polyethylene. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 48(2), 275–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-3910(95)00040-S
Wierckx, N., Prieto, M. A., Pomposiello, P., Lorenzo, V. De, Connor, K. O., & Blank, L. M. (2015). Opinion: Plastic waste as a novel substrate for industrial biotechnology. Microbial biotechnology, 8(6), 24180–22180. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12312
Zahra, S., Abbas, S. S., Mahsa, M. T., & Mohsen, N. (2010). Biodegradation of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) by isolated fungi in solid waste medium. Waste Management, 30(3), 396–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2009.09.027
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhary, A.K., Chaitanya, K., Dalmia, R. et al. Synergistic effect of UV, thermal, and chemical treatment on biological degradation of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) by Thermomyces lanuginosus. Environ Monit Assess 193, 513 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09296-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09296-4