Abstract
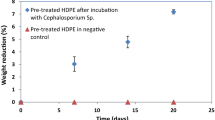
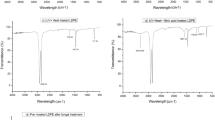
In the present work, the potential of Cephalosporium strain in degrading the pre-treated (ultraviolet irradiation followed by nitric acid treatment) low-density polyethylene and high-density polyethylene films was investigated. Our observations revealed a significant weight reduction of 24.53 ± 0.73% and 18.22 ± 0.31% in pre-treated low-density polyethylene and high-density polyethylene films respectively, after 56 days of incubation with the Cephalosporium strain. Changes in the physicochemical properties of the mineral salt medium (MSM) were studied to assess the extent of biodegradation. The pH of the MSM decreased gradually during the incubation period, whereas its total dissolved solids and conductivity values increased steadily. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) indicated the formation of hydroxyl and C = C groups in biodegraded low-density polyethylene films, while in the case of biodegraded high-density polyethylene films it indicated the \(-\)CH2 stretching. Furthermore, the thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) revealed an enhancement in the thermal stabilities of both the LDPE and HDPE films post the biodegradation. Modifications in the polymer surface morphologies after UV irradiation, chemical treatment, and biodegradation steps were visualized via scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis. All our observations confirm the ability of the Cephalosporium strain in biodegrading the pre-treated LDPE and HDPE films.







Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Albertsson, A. C. (1978). Biodegradation of synthetic polymers. II. A limited microbial conversion of 14C in polyethylene to 14CO2 by some soil fungi. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 22(12), 3419–3433. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1978.070221207
Avalos Belmontes, F., Zapata Gonzalez, I., Ramos De Valle, L. F., Zitzumbo Guzman, R., & Alonso Romero, S. (2009). Thermo-oxidative degradation of HDPE as a function of its crystalline content. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics, 47(19), 1906–1915. https://doi.org/10.1002/POLB.21785
Awasthi, S., Srivastava, N., Singh, T., Tiwary, D., & Mishra, P. K. (2017a). Biodegradation of thermally treated low density polyethylene by fungus Rhizopus oryzae NS 5. 3 Biotech, 7(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/S13205-017-0699-4
Awasthi, S., Srivastava, P., Singh, P., Tiwary, D., & Mishra, P. K. K. (2017b). Biodegradation of thermally treated high-density polyethylene (HDPE) by Klebsiella pneumoniae CH001. 3 Biotech, 7(5), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0959-3
Bhatia, M., Girdhar, A., Tiwari, A., & Nayarisseri, A. (2014). Implications of a novel Pseudomonas species on low density polyethylene biodegradation: an in vitro to in silico approach. SpringerPlus, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-3-497
Brown, B. S., Mills, J., & Hulse, J. M. (1974). Chemical and biological degradation of waste plastics. Nature, 250(5462), 161–163. https://doi.org/10.1038/250161a0
Cassidy, D. P., Werkema, D. D., Sauck, W., Atekwana, E., Rossbach, S., & Duris, J. (2001). The effects of LNAPL biodegradation products on electrical conductivity measurements. Journal of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, 6(1), 47–52. https://doi.org/10.4133/JEEG6.1.47
Chaudhary, A. K., Chaitanya, K., & Vijayakumar, R. P. (2021). Synergistic effect of UV and chemical treatment on biological degradation of Polystyrene by Cephalosporium strain NCIM 1251. Archives of Microbiology, 203(5), 2183–2191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02228-3
Chaudhary, A. K., Chitriv, S. P., & Vijayakumar, R. P. (2022). Influence of nitric acid on biodegradation of polystyrene and low - density polyethylene by Cephalosporium species. Archives of Microbiology, 204(8), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03089-0
Chaudhary, A. K., & Vijayakumar, R. P. (2020a). Effect of chemical treatment on biological degradation of high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Environment, Development and Sustainability, 22(2), 1093–1104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-018-0236-6
Chaudhary, A. K., & Vijayakumar, R. P. (2020b). Studies on biological degradation of polystyrene by pure fungal cultures. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 22(5), 4495–4508. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10668-019-00394-5
Chemical and Petrochemical Statistics at a Glance - 2021. (2021). https://chemicals.nic.in/sites/default/files/ChemicalandPetrochemicalStatisticsataGlance-20170.pdf.
Das, M. P., Kumar, S., & Das, J. (2018). Fungal-mediated deterioration and biodegradation study of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) isolated from municipal dump yard in Chennai, India. Energy, Ecology and Environment, 3(4), 229–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-018-0085-z
Farzi, A., Dehnad, A., & Fotouhi, A. F. (2019). Biodegradation of polyethylene terephthalate waste using Streptomyces species and kinetic modeling of the process. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 17, 25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BCAB.2018.11.002
Garaeva, S. R., Aydin, A. A., Aydin, A., Yalçin, B., Fatullaeva, P. A., & Medzhidov, A. A. (2010). Composition, properties, and application of products formed in oxidation of polyethylene by nitric acid. Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry, 83(1), 97–101. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070427210010192
Ghatge, S., Yang, Y., Ahn, J. H., & Hur, H. G. (2020). Biodegradation of polyethylene: A brief review. Applied Biological Chemistry, 63(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13765-020-00511-3
Gu, J. D. (2003). Microbiological deterioration and degradation of synthetic polymeric materials: Recent research advances. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 52(2), 69–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0964-8305(02)00177-4
Hace, D., Kovacevic, V., & Pajc-liplin, D. (1996). Thermally stimulated oxidative degradation of high impact polystyrene with nitric acid. Polymer Engineering and Science, 36(8), 1140–1151. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.10508
Hasan, F., Shah, A. A., Hameed, A., & Ahmed, S. (2007). Synergistic effect of photo- and chemical treatment on the rate of biodegradation of low density polyethylene by Fusarium sp. AF4. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 105(3), 1466–1470. https://doi.org/10.1002/APP.26328
Jamil, S. U. U., Zada, S., Khan, M., Sajjad, W., Rafiq, M., Alishah, A., & Hasan, F. (2017). Biodegradation of polyethylene by bacterial strains isolated from Kashmir cave, Buner, Pakistan. Journal of Cave and Karst Studies, 79(1), 73–80. https://doi.org/10.4311/2015MB0133
Jeon, H. J., & Kim, M. N. (2013). Isolation of a thermophilic bacterium capable of low-molecular-weight polyethylene degradation. Biodegradation, 24(1), 89–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9560-y
Koutny, M., Lemaire, J., & Delort, A. M. (2006). Biodegradation of polyethylene films with prooxidant additives. Chemosphere, 64(8), 1243–1252. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2005.12.060
Kowalczyk, A., Chyc, M., Ryszka, P., & Latowski, D. (2016). Achromobacter xylosoxidans as a new microorganism strain colonizing high-density polyethylene as a key step to its biodegradation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(11), 11349–11356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6563-y
Li, D., Zhou, L., Wang, X., He, L., & Yang, X. (2019). Effect of crystallinity of polyethylene with different densities on breakdown strength and conductance property. Materials, 12(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/MA12111746
Maroof, L., Khan, I., Yoo, H. S., Kim, S., Park, H. T., Ahmad, B., & Azam, S. (2021). Identification and characterization of low density polyethylenedegrading bacteria isolated from soils of waste disposal sites. Environmental Engineering Research, 26(3), 0–2. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2020.167
Miltz, J., & Narkis, M. (1976). The effect of ultraviolet radiation on chemically crosslinked low-density polyethylene. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 20(6), 1627–1633. https://doi.org/10.1002/APP.1976.070200620
Muhonja, C. N., Makonde, H., Magoma, G., & Imbuga, M. (2018). Biodegradability of polyethylene by bacteria and fungi from Dandora dumpsite Nairobi-Kenya. PLoS One, 13(7), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0198446
Mukherjee, S., RoyChaudhuri, U., & Kundu, P. P. (2017). Anionic surfactant induced oxidation of low density polyethylene followed by its microbial bio-degradation. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 117, 255–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IBIOD.2017.01.013
Munir, E., Harefa, R. S. M., Priyani, N., & Suryanto, D. (2018). Plastic degrading fungi Trichoderma viride and Aspergillus nomius isolated from local landfill soil in Medan. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 126(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/126/1/012145
Novotný, Č, Malachová, K., Adamus, G., Kwiecień, M., Lotti, N., Soccio, M., et al. (2018). Deterioration of irradiation/high-temperature pretreated, linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 132, 259–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IBIOD.2018.04.014
Ojha, N., Pradhan, N., Singh, S., Barla, A., Shrivastava, A., Khatua, P., et al. (2017a). Evaluation of HDPE and LDPE degradation by fungus, implemented by statistical optimization. Scientific Reports, 7, 39515. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39515
Ojha, N., Pradhan, N., Singh, S., Barla, A., Shrivastava, A., Khatua, P., et al. (2017b). Evaluation of HDPE and LDPE degradation by fungus, implemented by statistical optimization. Scientific Reports, 7. https://doi.org/10.1038/SREP39515
Rajandas, H., Parimannan, S., Sathasivam, K., Ravichandran, M., & Yin, L. S. (2012). A novel FTIR-ATR spectroscopy based technique for the estimation of low-density polyethylene biodegradation. Polymer Testing, 31(8), 1094–1099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2012.07.015
Satlewal, A., Soni, R., Zaidi, M., Shouche, Y., & Goel, R. (2008). Comparative biodegradation of HDPE and LDPE using an indigenously developed microbial consortium. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 18(3), 477–482.
Shabani, F., Kumar, L., & Esmaeili, A. (2015). A modelling implementation of climate change on biodegradation of Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) by Aspergillus niger in soil. Global Ecology and Conservation, 4, 388–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GECCO.2015.08.003
Sheik, S., Chandrashekar, K. R., Swaroop, K., & Somashekarappa, H. M. (2015). Biodegradation of gamma irradiated low density polyethylene and polypropylene by endophytic fungi. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 105, 21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IBIOD.2015.08.006
Singh, R., & Pant, D. (2016). Polyvinyl chloride degradation by hybrid (chemical and biological) modification. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 123, 80–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.POLYMDEGRADSTAB.2015.11.012
Skariyachan, S., Setlur, A. S., Naik, S. Y., Naik, A. A., Usharani, M., & Vasist, K. S. (2017). Enhanced biodegradation of low and high-density polyethylene by novel bacterial consortia formulated from plastic-contaminated cow dung under thermophilic conditions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(9), 8443–8457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8537-0
Sojobi, A. O., Nwobodo, S. E., & Aladegboye, O. J. (2016). Recycling of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic bottle wastes in bituminous asphaltic concrete. Cogent Engineering, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2015.1133480
Sojobi, A., & Owamah, H. (2014). Evaluation of the suitability of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) waste as fine aggregate in concrete. Nigerian Journal of Technology, 33(4), 409. https://doi.org/10.4314/njt.v33i4.1
Sojobi, A. O., & Zayed, T. (2022). Impact of sewer overflow on public health: A comprehensive scientometric analysis and systematic review. Environmental Research, 203. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2021.111609
Soni, R., Kapri, A., Zaidi, M. G. H., & Goel, R. (2009). Comparative biodegradation studies of non-poronized and poronized LDPE using indigenous microbial consortium. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 17(4), 233–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-009-0143-x
Teare, D. O. H., Emmison, N., Ton-That, C., & Bradley, R. H. (2001). Effects of serum on the kinetics of CHO attachment to ultraviolet-ozone modified polystyrene surfaces. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 234(1), 84–89. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2000.7282
Tribedi, P., & Dey, S. (2017). Pre-oxidation of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) by ultraviolet light (UV) promotes enhanced degradation of LDPE in soil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(12). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6351-2
Tribedi, P., & Sil, A. K. (2013). Low-density polyethylene degradation by Pseudomonas sp. AKS2 biofilm. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(6), 4146–4153. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-012-1378-Y
Vasilets, V. N., Kuznetsov, A. V., & Sevastianov, V. I. (2004). Vacuum ultraviolet treatment of polyethylene to change surface properties and characteristics of protein adsorption. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research - Part A, 69(3), 428–435. https://doi.org/10.1002/JBM.A.30005
Wang, H., Chen, S. J., & Zhang, J. (2009). Surface treatment of LLDPE and LDPE blends by nitric acid, sulfuric acid, and chromic acid etching. Colloid and Polymer Science, 287(5), 541–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-009-2000-9
Wu, S., Zhang, J., & Xu, X. (2003). Studies on high density polyethylene (HDPE) functionalized by ultraviolet irradiation and its application. Polymer International, 52(9), 1527–1530. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.1251
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ashutosh Kr Chaudhary: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, investigation, writing—original draft. Shubham P. Chitriv: data curation, investigation, draft revising. Kundrapu Chaitanya: data curation, investigation, draft revising. R. P. Vijayakumar: conceptualization, validation, resources, supervision, draft revising.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhary, A.K., Chitriv, S.P., Chaitanya, K. et al. Influence of ultraviolet and chemical treatment on the biodegradation of low-density polyethylene and high-density polyethylene by Cephalosporium strain. Environ Monit Assess 195, 395 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-10982-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-10982-8