Abstract
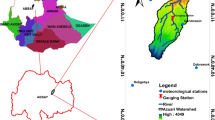
In Taiwan, nonpoint source (NPS) pollution is one of the major causes of the impairment of surface waters. I-Liao Creek, located in southern Taiwan, flows approximately 90 km and drains toward the Kaoping River. Field investigation results indicate that NPS pollution from agricultural activities is one of the main water pollution sources in the I-Liao Creek Basin. Assessing the potential of NPS pollution to assist in the planning of best management practice (BMP) is significant for improving pollution prevention and control in the I-Liao Creek Basin. In this study, land use identification in the I-Liao Creek Basin was performed by properly integrating the skills of geographic information system (GIS) and global positioning system (GPS). In this analysis, 35 types of land use patterns in the watershed area of the basin are classified with the aid of Erdas Imagine® process system and ArcView® GIS system. Results indicate that betel palm farms, orchard farms, and tea gardens dominate the farmland areas in the basin, and are scattered around on both sides of the river corridor. An integrated watershed management model (IWMM) was applied for simulating the water quality and evaluating NPS pollutant loads to the I-Liao Creek. The model was calibrated and verified with collected water quality and soil data, and was used to investigate potential NPS pollution management plans. Simulated results indicate that NPS pollution has significant contributions to the nutrient loads to the I-Liao Creek during the wet season. Results also reveal that NPS pollution plays an important role in the deterioration of downstream water quality and caused significant increase in nutrient loads into the basin’s water bodies. Simulated results show that source control, land use management, and grassy buffer strip are applicable and feasible BMPs for NPS nutrient loads reduction. GIS system is an important method for land use identification and waste load estimation in the basin. Linking the information of land utilization with the NPS pollution simulation model may further provide essential information of potential NPS pollution for all subregions in the river basin. Results and experience obtained from this study will be helpful in designing the watershed management and NPS pollution control strategies for other similar river basins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (American Public Health Association) (2001). Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 21th ed. Washington, DC: APHA-AWWA-WPCF.
Chang, N. B., Chen, H. W., Ning, S. K., Jeng, K. Y., & Lee, C. S. (2001). Prediction and evaluation of non-point pollutant loads for the reservoir watershed via the use of GIS/GPS/RS information technologies and numerical models. Water International, 26, 1617–1627.
Chen, C. L. (2003). Application of multimedia modeling on watershed management. In The 9th international workshop on drinking water quality management and treatment technology. (pp. 6–11). Taipei, Taiwan
Chen, S. W., Chao, A. C., Chen, T. Y., Kao, C. M., Lai, Y. C., & Lin, C. E. (2006). Application of water quality modeling on river basin management. WSEAS Transactions on Mathematics, 5, 1078–1083.
Choi, J. (2003). Management of storm runoff to reduce non-point pollution. In Diffuse pollution conference. Dublin.
Codner, G. P. (1991). Tale of two models. SWMM and HSPF. In Challenges for sustainable development, national conference publication—institution of engineers. Australia.
CPA, Construction and Planning Administration (2001). Study on quantitative criteria of affecting factors, delineation guidelines, and performance indicators for delineating the source water protection area of water quality and quantity for water supply. Taipei, Taiwan.
Donigian, A. S., & Davis, H. H. (1978). User manual for Agricultural Runoff Management (ARM) model. Washington, DC: US EPA.
Dougherty, M., Dymond, R. L., Thomas, J., Godrej, A. N., Zipper, C. E., & Randolph, J. (2006). Quantifying long-term NPS pollutant flux in an urbanizing watershed. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 132, 547–554. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2006)132:4(547).
EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency) (2000). Test methods for evaluating solid waste physical/chemical methods, SW-846. US EPA.
Holas, J., & Klir, J. (2003). Diffuse pollution management in the Czech Republic at the example of selected watersheds case study. In Diffuse pollution conference. Dublin.
Kao, J. J., Chen, W. J., Ju, C. L., Tsai, C. H., & Lin, W. L. (2002). Analyses of watershed non-point source pollution management strategies. In Proceedings of the IWA third world water congress. Australia: Melbourne, April.
Kao, C. M., Wu, F. C., Chen, K. F., Lin, T. F., Yen, Y. E., & Chiang, P. C. (2003). Pollutant sources investigation and remedial strategies development for the Kaoping River basin. Taiwan. Water Science and Technology 48, 97–103.
Kavvas, M. L., Yoon, J., Chen, Z. Q., Liang, L., Dogrul, E. C., Ohara, N., et al. (2006). Watershed environmental hydrology model: Environmental module and its application to a California watershed. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 11, 450–464. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(2006)11:3(261).
NIEA (National Institute of Environmental Analysis, Taiwan EPA) (2004). Method of River Flow Rate Analysis, NIEA W022.51C.
Ning, S. K., Jeng, K. Y., & Chang, N. B. (2002). Evaluation of non-point sources pollution impacts by integrated 3S information technologies and GWLF modeling. Water Science and Technology, 46, 217–224.
Papanicolaou, T., & Abaci, O. (2005). An integrated watershed model. In Managing watersheds for human and natural impacts: Engineering, ecological, and economic challenges, managing watersheds for human and natural impacts: Engineering, ecological, and economic challenges—proceedings of the 2005 watershed management conference (p 189).
Peterson, E. W., & Wicks, C. M. (2006). Assessing the importance of conduit geometry and physical parameters in karst systems using the storm water management model (SWMM). Journal of Hydrology (Amsterdam), 329, 294–305. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.02.017.
Ping, W., & Linker, L. W. (2006). A correction of DIN uptake simulation by Michaelis–Menten saturation kinetics in HSPF watershed model to improve DIN export simulation. Environmental Modelling & Software, 21, 45–60. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2004.09.025.
Shan, W. L. (2006). Application of multimedia modeling to develop non-point source control strategies for the I-Liao Creek basin. Master of Science Thesis, National Sun Yat-Sen University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
TEPA, Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration (2001). Investigation of non-point source pollution in the drinking water source water protection area of Kaoping River Basin. Taipei, Taiwan.
TEPA, Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration (2002). Development of non-point source pollutant remedial strategy. Taipei, Taiwan.
TEPA, Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration (2006). Evaluation of soil erosion and development of sediment control strategies for Kaoping River Basin. Taipei, Taiwan.
Trauth, K. M., & Adams, D. S. (2004). Watershed-based modeling with AGNPS for storm water management. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 130, 206–214. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2004)130:3(206).
Yang, T. C., Kao, C. M., Yeh, T. Y., Lin, C. E., & Lai, Y. C. (2006a). Application of multimedia model for the development of watershed management strategies: A case study. WSEAS Transactions on Mathematics, 5, 409–415.
Yang, T. C., Kao, C. M., Yeh, T. Y., Lin, C. E., & Lai, Y. C. (2006b). Evaluation of NPS pollution in drinking water protection area of Kaoping River Watershed. WSEAS Transactions on Mathematics, 5, 1131–1137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, C.E., Kao, C.M., Lai, Y.C. et al. Application of integrated GIS and multimedia modeling on NPS pollution evaluation. Environ Monit Assess 158, 319–331 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0586-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0586-x