Abstract
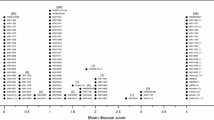
Barley leaf rust, caused by Puccinia hordei, is one of the most destructive foliar pathogens of cultivated barley, causing significant yield losses in many regions throughout the world. In this study, 521 seedling-susceptible barley germplasm obtained from diverse breeding material sourced from the Australian Winter Cereals Collection (AWCC), the University of Western Australia (UWA), and international collections from Australia, China, Germany, Spain, and Uruguay were assessed for adult plant resistance (APR) in field nurseries over multiple growing seasons. Lines (213) that consistently showed APR over multiple seasons were screened with PCR-based markers closely linked to Rph20 (bPb0837) and Rph23 (EBmac0603). About 93 % of the lines that were resistant in the field carried one or more uncharacterised APR genes with or without Rph20 and Rph23. There was high variability for APR within specific international germplasm collections. The presence of bPb0837 was strongly correlated with high APR (TR-MR) responses in the field, while lines that were positive for the EBmac0603 allele had intermediate resistance (MRMS). Both EBmac0603 and bPb0837 were present in three German lines (Lenka, Line 17 and Volla) and in the Australian variety Macquarie, all were thus were postulated to carry both Rph20 and Rph23 and had TR-20MR responses in the field. Molecular markers closely linked to Rph20 and Rph23 provide a valuable resource that can be used to assist the incorporation of these genes into new cultivars and identify uncharacterised APR.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carlborg, O., & Haley, C. (2004). Epistasis: too often neglected in complex trait studies? Nature Reviews Genetics, 5, 618–625.
Clifford, B. C. (1985). Barley leaf rust In: AP Roelfs and WR Bushnell (eds) The Cereal Rusts II (pp173-205) Academic Press New York.
Cotterill, P. J., Rees, R. G., Platz, G. J., & Dill-Macky, R. (1992). Effects of leaf rust on selected Australian barleys. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture, 32, 747–751.
Derevnina, L. D., Singh, D., & Park, R. F. (2013). Identification and characterization of seedling and adult plant resistance to Puccinia hordei in Chinese germplasm. Plant Breeding, 132, 571–579.
Fulton, T., Chunwongse, J., & Tanksley, D. (1995). Microprep protocol for extraction of DNA from tomato and other herbaceous plants. Plant Molecular Biology Reports, 13, 207–209.
Gilmour, J. (1973). Octal notation for designating physiologic races of plant pathogens. Nature (London), 242(7), 355–392.
Golegaonkar, P. G., Park, R. F., & Singh, D. (2009). Evaluation of seedling and adult plant resistance to Puccinia hordei in barley. Euphytica, 166, 183–197.
Golegaonkar, P. G., Park, R. F., & Singh, D. (2010). Genetic analysis of adult plant resistance to Puccinia hordei in barley. Plant Breeding, 129, 162–166.
Hayden, M. J., Nguyen, T. M., Waterman, A., & Chalmers, K. J. (2008). Multiplex-ready PCR: a new method for multiplexed SSR and SNP genotyping. BMC Genomics, 9, 80–85.
Hickey, L. T., Lawson, W., Platz, G. P., Dieters, M., Arief, V. N., German, S., Fletcher, D., Park, R. F., Singh, D., Pereyra, S., & Franckowiak, J. (2011). Mapping Rph20: a gene conferring adult plant resistance to Puccinia hordei in barley. Theoretical Applied Genetics, 123, 55–68.
Hickey, L. T., Lawson, W., Platz, G. P., Dieters, M., Arief, V. N., & Franckowiak, J. (2012). Origin of leaf rust adult plant resistance gene Rph20 in barley. Genome, 55, 396–399.
Johnson, P. A., Niks, R. E., Meiyalaghan, V., Blanchet, E., & Pickering, P. (2013). Rph22: mapping of a novel leaf rust resistance gene introgressed from the non-host Hordeum bulbosum L into cultivated barley (Hordeum vulgare L). Theoretical Applied Genetics, 126(6), 1613–1625.
Liu, F., Gupta, S., Zhang, M., Jones, R., Loughman, R., Lance, R., & Li, C. (2011). PCR markers for selection of adult plant leaf rust resistance in barley (Hordeum vulgare L). Molecular Breeding, 28, 657–666.
Marcel, T. C., Varshney, R. K., Barbieri, M., Jafary, H., de Kock Graner, M. J. D., & Niks, R. (2007). A high-density consensus map of barley to compare the distribution of QTLs for partial resistance to Puccinia hordei and of defense gene homologues. Theoretical Applied Genetics, 114, 487–500.
McIntosh, R. A., Wellings, C. R., & Park, R. F. (1995). Wheat rusts: An atlas of resistance genes. Canberra Australia: CSIRO publications.
Murray, G. M., & Brennan, J. P. (2009). The current and potential costs from diseases of barley in Australia (p. 59). Canberra Australia: Grains Research and Development Corporation.
Newman, R. K., Newman, C. W. (2008). In Barley for food and health John Wiley & Sons Publication.
Park, R. F. (2003). Pathogenic specialization and pathotype distribution of Puccinia hordei in Australia 1992 to 2001. Plant Disease, 87, 1311–1316.
Park, R. F. (2008). Breeding cereals for rust resistance in Australia. Plant Pathology, 57, 591–602.
Park, R. F., & Karakousis, A. (2002). Characterization and mapping of gene Rph19 conferring resistance to Puccinia hordei in cultivar ‘Reka I’ and several Australian barleys. Plant Breeding, 121, 232–236.
Peterson, R. F., Campbell, A. B., & Hannah, A. E. (1948). A diagrammatic scale for estimating rust intensity on leaves and stems of cereals. Canadian Journal Research, 26, 496–500.
Qi, X., Fufa, F., Sijtsma, D., Niks, R., Lindhout, P., & Stam, P. (2000). The evidence for abundance of QTLs for partial resistance to Puccinia hordei on the barley genome. Molecular Breeding, 6, 1–9.
Roelfs, A. P., Singh, R. P., & Saari, R. E. (1992). Rust diseases of wheat, concepts and methods of disease management. Mexico: CIMMYT.
Sandhu, K. (2011). Genetic and molecular analyses of barley for seedling and adult plant resistance against rust diseases PhD thesis University of Sydney.
Sandhu, K. S., Forrest, K. L., Kong, S., Bansal, U. K., Singh, D., Hayden, M. J., & Park, R. F. (2012). Inheritance and molecular mapping of a gene conferring seedling resistance against Puccinia hordei in the barley cultivar Ricardo. Theoretical Applied Genetics, 125(7), 1403–1411.
Singh, R. P. (1992). Genetic association of leaf rust resistance gene Lr34 with adult plant resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat. Phytopathology, 82, 835–838.
Singh, R. P., Huerta-Espino, J., Rajaram, S., & Crossa, J. (1998). Agronomic effects from chromosome translocations 7DL.7Ag and 1BL.1RS in spring wheat. Crop Science, 38, 27–33.
Singh, R. P., Huerta-Espino, J., & Rajaram, S. (2000). Achieving near-immunity to leaf and stripe rusts in wheat by combining slow rusting resistance genes. Acta Phytopathology, 35, 133–139.
Singh, R. P., Huerta-Espino, J., Bhavani, S., Herrera-Foessel, A., Singh, D., Singh, P. K., Velu, G., Mason, R. E., Jin, Y., Njau, P., & Crossa, J. (2011). Race non-specific resistance to rust diseases in CIMMYT spring wheats. Euphytica, 179, 175–186.
Singh, D., Macaigne, N., & Park, R. F. (2013). Rph20: adult plant resistance gene to barley leaf rust can be detected at early growth stages. European Journal Plant Pathology, 137, 719–725.
Singh, D., Dracatos, P., Derevnina, L., Zhou, M., Park, R. (2014). Rph23: A new designated additive adult plant resistance gene to leaf rust in barley on chromosome 7H. Plant Breeding in press
Steffenson, B. J., Jin, Y., & Griffey, C. A. (1993). Pathotypes of Puccinia hordei with virulence for the barley leaf rust resistance gene Rph7 in the United States. Plant Disease, 77, 867–869.
Wallwork, H., Preece, P., & Cotterhill, P. J. (1992). Puccinia hordei on barley and Omithogalum umbellatum in South Australia. Australasian Plant Pathology, 21, 95–97.
Woldeab, G., Fininsa, C., Singh, H., & Yuen, J. (2007). Virulence spectrum of Puccinia hordei in barley production systems in Ethiopia. Plant Pathology, 55, 351–357.
Acknowledgments
The senior author would like to sincerely thank the Grains Research and Development Corporation for funding this research. The authors would like to thank Mr M. Williams for valuable technical assistance in the course of this study and acknowledge the support provided by the University of Sydney and The Australian Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dracatos, P.M., Singh, D., Bansal, U. et al. Identification of new sources of adult plant resistance to Puccinia hordei in international barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) germplasm. Eur J Plant Pathol 141, 463–476 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0556-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0556-9