Abstract
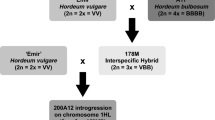
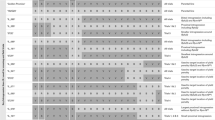
A resistance gene (Rph22) to barley leaf rust caused by Puccinia hordei was introgressed from the non-host species Hordeum bulbosum into cultivated barley. The H. bulbosum introgression in line ‘182Q20’ was located to chromosome 2HL using genomic in situ hybridisation (GISH). Using molecular markers it was shown to cover approximately 20 % of the genetic length of the chromosome. The introgression confers a very high level of resistance to P. hordei at the seedling stage that is not based on a hypersensitive reaction. The presence of the resistance gene increased the latency period of the leaf rust fungus and strongly reduced the infection frequency relative to the genetic background cultivar ‘Golden Promise’. An F2 population of 550 individuals was developed and used to create a genetic map of the introgressed region and to determine the map position of the underlying resistance gene(s). The resistance locus, designated Rph22, was located to the distal portion of the introgression, co-segregating with markers H35_26334 and H35_45139. Flanking markers will be used to reduce the linkage drag, including gene(s) responsible for a yield penalty, around the resistance locus and to transfer the gene into elite barley germplasm. This genetic location is also known to harbour a QTL (Rphq2) for non-hypersensitive leaf rust resistance in the barley cultivar ‘Vada’. Comparison of the ‘Vada’ and H. bulbosum resistances at this locus may lead to a better understanding of the possible association between host and non-host resistance mechanisms.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IL:
-
Introgression line (H. bulbosum chromatin in a barley genetic background)
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait locus
- NBS-LRR:
-
A class of resistance gene NBS (nuclear binding site) LRR (leucine-rich repeat)
References
Altschul S, Madden T, Schaffer A, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman D (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Anikster Y (1989) Host specificity versus plurivority in barley leaf rusts and their microcyclic relatives. Mycol Res 93:175–181
Baum M, Lagudah ES, Appels R (1992) Wide crosses in cereals. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 43:117–143
Blattner FR (2004) Phylogenetic analysis of Hordeum (Poaceae) as inferred by nuclear rDNA ITS sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 33:289–299
Büschges R, Hollricher K, Panstruga R, Simons G, Wolter M, Frijters A, van Daelen R, van der Lee T, Diergaarde P, Groenendijk J, Töpsch S, Vos P, Salamini F, Schulze-Lefert P (1997) The barley mlo gene: a novel control element of plant pathogen resistance. Cell 88:695–705
Canady M, Ji Y, Chetelat R (2006) Homeologous recombination in Solanum lycopersicoides introgression lines of cultivated tomato. Genetics 174:1775–1788
Chao S, Somers D (2012) Wheat and barley DNA extraction in 96-well plates; WheatMAS. http://maswheat.ucdavis.edu/protocols/general_protocols/DNA_extraction_003.htm. Accessed 10th July 2012
Chisholm ST, Coaker G, Day B, Staskawicz BJ (2006) Host-microbe interactions: shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell 124:803–814
Clifford BC (1985) Barley leaf rust. In: Roelfs AP, Bushnell WR (eds) The cereal rusts volume II: diseases, distribution and control. Academic Press, New York
Close T, Bhat P, Lonardi S, Wu Y, Rostoks N, Ramsay L, Druka A, Stein N, Svensson J, Wanamaker S, Bozdag S, Roose M, Moscou M, Chao S, Varshney R, Szucs P, Sato K, Hayes P, Matthews D, Kleinhofs A, Muehlbauer G, DeYoung J, Marshall D, Madishetty K, Fenton R, Condamine P, Graner A, Waugh R (2009) Development and implementation of high-throughput SNP genotyping in barley. BMC Genomics 10:582
Drummond A, Ashton B, Buxton S, Cheung M, Cooper A, Duran C, Field M, Heled J, Kearse M, Markowitz S, Moir R, Stones-Havas S, Sturrock S, Thierer T, Wilson A (2011) Geneious. version 5.4; Available from http://www.geneious.com/
Fu XL, Lu YG, Liu XD, Li JQ (2008) Progress on transferring elite genes from non-aa genome wild rice into oryza sativa through interspecific hybridization. Rice Sci 15:79–87
Goff SA, Ricke D, Lan TH, Presting G, Wang R, Dunn M, Glazebrook J, Sessions A, Oeller P, Varma H, Hadley D, Hutchison D, Martin C, Katagiri F, Lange BM, Moughamer T, Xia Y, Budworth P, Zhong J, Miguel T, Paszkowski U, Zhang S, Colbert M, Sun WL, Chen L, Cooper B, Park S, Wood TC, Mao L, Quail P, Wing R, Dean R, Yu Y, Zharkikh A, Shen R, Sahasrabudhe S, Thomas A, Cannings R, Gutin A, Pruss D, Reid J, Tavtigian S, Mitchell J, Eldredge G, Scholl T, Miller RM, Bhatnagar S, Adey N, Rubano T, Tusneem N, Robinson R, Feldhaus J, Macalma T, Oliphant A, Briggs S (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica). Science 296:92–100
Griffey CA, Das MK, Baldwin RE, Waldenmaier CM (1994) Yield losses in winter barley resulting from a new race of Puccinia hordei in North America. Plant Dis 78:256–260
Heath M (1985) Implications of non-host resistance for understanding host-parasite interactions. In: Groth J, Bushnell W (eds) Genetic basis of biochemical mechanisms of plant disease. APS Press, St. Paul, pp 25–42
Johnston P (2007) Molecular characterisation of chromatin introgressed from Hordeum bulbosum L. into Hordeum vulgare L. PhD thesis. PhD Thesis, Department of Biochemistry. University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand. p 340
Johnston P, Timmerman-Vaughan G, Farnden K, Pickering R (2009) Marker development and characterisation of Hordeum bulbosum introgression lines: a resource for barley improvement. Theor Appl Genet 118:1429–1437
Kasha KJ, Kao KN (1970) High frequency haploid production in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Nature 225:874–876
Krattinger SG, Lagudah ES, Spielmeyer W, Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, McFadden H, Bossolini E, Selter LL, Keller B (2009) A putative ABC transporter confers durable resistance to multiple fungal pathogens in wheat. Science 323:1360–1363
Manly K, Cudmore R, Meer J (2001) Map manager QTX, cross-platform software for genetic mapping. Mamm Genome 12:930–932
Marcel T, Varshney R, Barbieri M, Jafary H, de Kock M, Graner A, Niks R (2007a) A high-density consensus map of barley to compare the distribution of QTLs for partial resistance to Puccinia hordei and of defence gene homologues. Theor Appl Genet 114:487–500
Marcel TC, Aghnoum R, Durand J, Varshney RK, Niks RE (2007b) Dissection of the barley 2L1.0 region carrying the ‘Laevigatum’ quantitative resistance gene to leaf rust using near-isogenic lines (NIL) and subNIL. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:1604–1615
Marcel TC, Gorguet B, Ta MT, Kohutova Z, Vels A, Niks RE (2008) Isolate specificity of quantitative trait loci for partial resistance of barley to Puccinia hordei confirmed in mapping populations and near-isogenic lines. New Phytol 177:743–755
Mayer KFX, Martis M, Hedley PE, Šimková H, Liu H, Morris JA, Steuernagel B, Taudien S, Roessner S, Gundlach H, Kubaláková M, Suchánková P, Murat F, Felder M, Nussbaumer T, Graner A, Salse J, Endo T, Sakai H, Tanaka T, Itoh T, Sato K, Platzer M, Matsumoto T, Scholz U, Doležel J, Waugh R, Stein N (2011) Unlocking the barley genome by chromosomal and comparative genomics. Plant Cell Online 23:1249–1263
Niks RE (1986) Failure of haustorial development as a factor in slow growth and development of Puccinia hordei in partially resistant barley seedlings. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 28:309–322
Niks RE (1987) Nonhost plant species as donors for resistance to pathogens with narrow host range. I. Deter-mina-tion of nonhost status. Euphytica 36:841–852
Niks RE, Marcel TC (2009) Nonhost and basal resistance: how to explain specificity? New Phytol 182:817–828
Nürnberger T, Brunner F, Kemmerling B, Piater L (2004) Innate immunity in plants and animals: striking similarities and obvious differences. Immunol Rev 198:249–266
Parlevliet J (1975) Partial resistance of barley to leaf rust, Puccinia hordei. I. Effect of cultivar and development stage on latent period. Euphytica 24:21–27
Parlevliet J (1976) Partial resistance of barley to leaf rust, Puccinia hordei. III. The inheritance of the host plant effect on latent period in four cultivars. Euphytica 25:241–248
Parlevliet J (1978) Further evidence of polygenic inheritance of partial resistance in barley to leaf rust, Puccinia hordei. Euphytica 27:369–379
Parlevliet J (2002) Durability of resistance against fungal, bacterial and viral pathogens; present situation. Euphytica 124:147–156
Parlevliet JE, Kuiper HJ (1985) Accumulating polygenes for partial resistance in barley to barley leaf rust, Puccinia hordei. I Selection for increased latent periods. Euphytica 34:7–13
Pickering R (1992) Monosomic and double monosomic substitutions of Hordeum bulbosum L. chromosomes into H. vulgare L. Theor Appl Genet 84:466–472
Pickering R, Hill A, Michel M, Timmerman-Vaughan G (1995) The transfer of a powdery mildew resistance gene from Hordeum bulbosum L. to barley (H. vulgare L.) chromosome 2 (2I). Theor Appl Genet 91:1288–1292
Pickering R, Steffenson B, Hill A, Borovkova I (1998) Association of leaf rust and powdery mildew resistance in a recombinant derived from a Hordeum vulgare × Hordeum bulbosum hybrid. Plant Breed 117:83–84
Pickering R, Malyshev S, Kunzel G, Johnston P, Korzun V, Menke M, Schubert I (2000) Locating introgressions of Hordeum bulbosum chromatin within the H. vulgare genome. Theor Appl Genet 100:27–31
Pickering R, Niks RE, Johnston PA, Butler RC (2004) Importance of the secondary genepool in barley genetics and breeding. II. Disease resistance, agronomic performance and quality. Czech J Genet Plant Breed 40:79–85
Pickering R, Johnston P, Meiyalaghan V, Ebdon S, Morgan E (2010) Hordeum vulgare–H. bulbosum introgression lines. Barley Genet Newsl 40:1
Qi X, Niks R, Stam P, Lindhout P (1998) Identification of QTLs for partial resistance to leaf rust (Puccinia hordei) in barley. Theor Appl Genet 96:1205–1215
Qi X, Fufa F, Sijtsma D, Niks R, Lindhout P, Stam P (2000) The evidence for abundance of QTLs for partial resistance to Puccinia hordei on the barley genome. Mol Breed 6:1–9
Sato K, Nankaku N, Takeda K (2009) A high-density transcript linkage map of barley derived from a single population. Heredity 103:110–117
Schulze-Lefert P, Panstruga R (2011) A molecular evolutionary concept connecting nonhost resistance, pathogen host range, and pathogen speciation. Trends Plant Sci 16:117–125
Schweizer P (2007) Nonhost resistance of plants to powdery mildew—new opportunities to unravel the mystery. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 70:3–7
Shtaya M, Sillero J, Flath K, Pickering R, Rubiales D (2007) The resistance to leaf rust and powdery mildew of recombinant lines of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) derived from H. vulgare · H. bulbosum crosses. Plant Breed 126:259–267
Szigat G, Pohler W (1982) Hordeum bulbosum × H. vulgare hybrids and their backcrosses with cultivated barley. Cereal Res Commun 10:73–78
Turuspekov Y, Mano Y, Honda I, Kawada N, Watanabe Y, Komatsuda T (2004) Identification and mapping of cleistogamy genes in barley. Theor Appl Genet 109:480–487
von Bothmer R, Jacobsen N, Baden C, Jorgensen R, Linde-Laursen I (1995) An ecogeographical study of the genus Hordeum, 2nd edn. International Plant Genetic Resources Institute (IPGRI), Rome
Voorrips R (2002) Mapchart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78
Xu J, Kasha KJ (1992) Transfer of a dominant gene for powdery mildew resistance and DNA from Hordeum bulbosum into cultivated barley (H. vulgare). Theor Appl Genet 84:771–777
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Mrs. Merle Forbes for crossing and maintaining all plant material. Also thanks to Dr. David Chagné, Dr. Soonie Chng and Dr. Sue Gardiner for critical reading of this manuscript. Funding for this work was provided by the New Zealand Foundation for Research Science and Technology contract number C06X0810.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Graner.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnston, P.A., Niks, R.E., Meiyalaghan, V. et al. Rph22: mapping of a novel leaf rust resistance gene introgressed from the non-host Hordeum bulbosum L. into cultivated barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 126, 1613–1625 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2078-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2078-9