Abstract
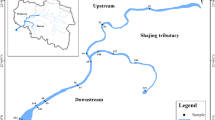
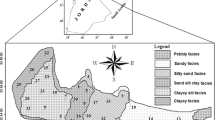
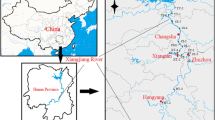
To reveal seasonal and spatial variations of heavy metals and metalloids (HMMs) in sediment of the Xiangjiang River, a total of 24 water and 649 sediment samples were collected from six sampling stations in the Songbai section of the river which had been polluted by HMMs for 100 years. Their contamination statuses and ecological risk were determined by enrichment factor (EF), geo-accumulation index (Igeo), pollution load index (PLI), and mean probable effect concentration quotients (mPECQs) analyses. The results revealed a unique seasonal distribution of metals in the sampling stations: The highest concentrations were revealed in the dry seasons (autumn and winter) and the lowest during the wet seasons (spring and summer). It exhibited a greater seasonal variation in the estuary sediment cores (sites ME and MW) than in the cores of other sites. Moreover, the highest concentrations of the tested metals were also found in the estuary sediment cores in the dry seasons (autumn and winter). The highest vertical concentrations of Pb, Zn, Cu, Ni, As, Fe, and Mn were observed at the depths of 16–36 cm in all of the sampled sediment cores. The EF, Igeo, PLI, and mPECQs values of all samples in autumn were higher than in summer. Cd posed the highest ecological risk in all seasons, although its concentrations were lower compared to other studied elements. Our results will benefit to develop feasible sediment quality guidelines for government monitor and remediate the local sediments in the Xiangjiang River.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antunes, I., Albuquerque, M. T. D., & Roque, N. (2018). Spatial environmental risk evaluation of potential toxic elements in stream sediments. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 40(6), 2573–2585.
Balistrieri, L. S., Seal, R. R., Piatak, N. M., & Paul, B. (2007). Assessing the concentration, speciation, and toxicity of dissolved metals during mixing of acid-mine drainage and ambient river water downstream of the Elizabeth Copper Mine, Vermont, USA. Applied Geochemistry, 22(5), 930–952.
Belabed, B.-E., Meddour, A., Samraoui, B., & Chenchouni, H. (2017). Modeling seasonal and spatial contamination of surface waters and upper sediments with trace metal elements across industrialized urban areas of the Seybouse watershed in North Africa. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(6), 265.
Bi, N. S., Yang, Z. S., Wang, H. J., Xu, C. L., & Guo, Z. G. (2014). Impact of artificial water and sediment discharge regulation in the Huanghe (Yellow River) on the transport of particulate heavy metals to the sea. CATENA, 121, 232–240.
Bian, B., Zhou, Y., & Fang, B. B. (2016). Distribution of heavy metals and benthic macroinvertebrates: Impacts from typical inflow river sediments in the Taihu Basin, China. Ecological Indicators, 69, 348–359.
Birch, G. F., Melwani, A., Lee, J. H., & Apostolatos, C. (2014). The discrepancy in concentration of metals (Cu, Pb and Zn) in oyster tissue (Saccostrea glomerata) and ambient bottom sediment (Sydney estuary, Australia). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 80(1–2), 263–274.
Ca Ador, I., Vale, C., & Catarino, F. (2000). Seasonal variation of Zn, Pb, Cu and Cd concentrations in the root–sediment system of Spartina maritima and Halimione portulacoides from Tagus estuary salt marshes. Marine Environmental Research, 49(3), 279–290.
Chai, L. Y., Ding, C. L., Tang, C. J., Yang, W. C., Yang, Z. H., Wang, Y. Y., et al. (2018a). Discerning three novel chromate reduce and transport genes of highly efficient Pannonibacter phragmitetus BB: From genome to gene and protein. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 162, 139–146.
Chai, L. Y., Li, H., Yang, Z. H., Min, X. B., Liao, Q., Liu, Y., et al. (2017). Heavy metals and metalloids in the surface sediments of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan, China: distribution, contamination, and ecological risk assessment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(1), 1–12.
Chai, L. Y., Wang, X., Wang, H. Y., Yang, W. C., Liao, Q., & Wu, Y. J. (2018b). Formation of one-dimensional composites of poly(m-phenylenediamine)s based on Streptomyces for adsorption of hexavalent chromium. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 15(7), 1411–1422.
Chai, L. Y., Wang, Z. X., Wang, Y. Y., Yang, Z. H., Wang, H. Y., & Wu, X. (2010). Ingestion risks of metals in groundwater based on TIN model and dose-response assessment—A case study in the Xiangjiang watershed, central-south China. Science of the Total Environment, 408(16), 3118–3124.
Chen, C. F., Ju, Y. R., Chen, C. W., & Dong, C. D. (2016). Vertical profile, contamination assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in sediment cores of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Chemosphere, 165, 67–79.
Dai, S. B., Yang, S. L., Zhu, J., Gao, A., & Li, P. (2005). The role of Lake Dongting in regulating the sediment budget of the Yangtze River. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 9(6), 692–698.
Duivenvoorden, L. J., Roberts, D. T., & Tucker, G. M. (2017). Serpentine geology links to water quality and heavy metals in sediments of a stream system in central Queensland, Australia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76(8), 320.
Duman, F., Aksoy, A., & Demirezen, D. (2007). Seasonal variability of heavy metals in surface sediment of Lake Sapanca, Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 133(1–3), 277–283.
ElBishlawi, H., Shin, J. Y., & Jaffe, P. R. (2013). Trace metal dynamics in the sediments of a constructed and natural urban tidal marsh: The role of iron, sulfide, and organic complexation. Ecological Engineering, 58, 133–141.
Elzwayie, A., Afan, H. A., Allawi, M. F., & El-Shafie, A. (2017). Heavy metal monitoring, analysis and prediction in lakes and rivers: State of the art. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(13), 12104–12117.
Farkas, A., Erratico, C., & Viganò, L. (2007). Assessment of the environmental significance of heavy metal pollution in surficial sediments of the River Po. Chemosphere, 68(4), 761–768.
Fernandes, L. L., & Nayak, G. N. (2014). Characterizing metal levels and their speciation in intertidal sediments along Mumbai coast, India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 79(1–2), 371–378.
Haris, H., Looi, L. J., Aris, A. Z., Mokhtar, N. F., Ayob, N. A. A., Yusoff, F. M., et al. (2017). Geo-accumulation index and contamination factors of heavy metals (Zn and Pb) in urban river sediment. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 39(6), 1259–1271.
He, M. Y., Zheng, H. B., Bookhagen, B., & Clift, P. D. (2014). Controls on erosion intensity in the Yangtze River basin tracked by U–Pb detrital zircon dating. Earth-Science Reviews, 136, 121–140.
Himmelheber, D. W., Taillefert, M., Pennell, K. D., & Hughes, J. B. (2008). Spatial and temporal evolution of biogeochemical processes following in situ capping of contaminated sediments. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(11), 4113–4120.
Hou, D. K., He, J., Lü, C. W., Ren, L. M., Fan, Q. Y., Wang, J. H., et al. (2013). Distribution characteristics and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd) in water and sediments from Lake Dalinouer, China. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 93(4), 135–144.
Jamshidi-Zanjani, A., & Saeedi, M. (2017). Multivariate analysis and geochemical approach for assessment of metal pollution state in sediment cores. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(19), 16289–16304.
Kowalska, J. B., Mazurek, R., Gasiorek, M., & Zaleski, T. (2018). Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination—A review. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 40(6), 2395–2420.
Li, H., Yang, J. Q., Ye, B., & Jiang, D. Y. (2018). Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of 11 unheeded metals in sediments of the Chinese Xiangjiang River. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0230-9.
Liao, J. B., Chen, J., Ru, X., Chen, J. D., Wu, H. Z., & Wei, C. H. (2016). Heavy metals in river surface sediments affected with multiple pollution sources, South China: Distribution, enrichment and source apportionment. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 176, 9–19.
Liu, H., Zhang, K. J., Chai, L. Y., Yang, Z. H., Yang, W. C., Liao, Q., et al. (2017). A comparative evaluation of different sediment quality guidelines for metal and metalloid pollution in the Xiangjiang River, Hunan, China. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 73, 593–606.
Lu, J. M., Yuan, F. Q., Zhang, F. Y., & Zhao, Q. (2016). The study on heavy metal distribution in the sediment of middle tidal flat in Yangtze Estuary, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(7), 1–12.
Ma, X. L., Zuo, H., Tian, M. J., Zhang, L. Y., Meng, J., Zhou, X. N., et al. (2016). Assessment of heavy metals contamination in sediments from three adjacent regions of the Yellow River using metal chemical fractions and multivariate analysis techniques. Chemosphere, 144, 264–272.
MacDonald, D. D., Ingersoll, C. G., & Berger, T. A. (2000). Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39(1), 20–31.
Mao, L. J., Mo, D. W., Guo, Y. Y., Fu, Q., Yang, J. H., & Jia, Y. F. (2013). Multivariate analysis of heavy metals in surface sediments from lower reaches of the Xiangjiang River, southern China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 69(3), 765–771.
Min, X. B., Wang, Y. Y., Chai, L. Y., Yang, Z. H., & Liao, Q. (2017). High-resolution analyses reveal structural diversity patterns of microbial communities in chromite ore processing residue (COPR) contaminated soils. Chemosphere, 183, 266–276.
Mna, H. B., Oueslati, W., Helali, M. A., Zaaboub, N., Added, A., & Aleya, L. (2017). Distribution and assessment of heavy metal toxicity in sediment cores from Bizerte Lagoon, Tunisia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(7), 356.
Monteiro, C. E., Cesário, R., O’Driscoll, N. J., Nogueira, M., Válega, M., Caetano, M., et al. (2016). Seasonal variation of methylmercury in sediment cores from the Tagus Estuary (Portugal). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 104(1–2), 162–170.
Muller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal, 2(108), 108–118.
Najamuddin, P. T. S. H. (2016). Seasonal distribution and geochemical fractionation of heavymetals from surface sediment in a tropical estuary of Jeneberang River, Indonesia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1–2(111), 456–462.
Ni, L. X., Li, D. D., Su, L. L., Xu, J. J., Li, S. Y., Ye, X., et al. (2016). Effects of algae growth on cadmium remobilization and ecological risk in sediments of Taihu Lake. Chemosphere, 151, 37–44.
Pal, D., & Maiti, S. K. (2018). Heavy metal speciation, leaching and toxicity status of a tropical rain-fed river Damodar, India. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 40(6), 2303–2324.
Pandey, L. K., Park, J., Son, D. H., Kim, W., Islam, M. S., Choi, S., et al. (2019). Assessment of metal contamination in water and sediments from major rivers in South Korea from 2008 to 2015. Science of the Total Environment, 651, 323–333.
Patel, P., Raju, N. J., Reddy, B., Suresh, U., Sankar, D. B., & Reddy, T. V. K. (2018). Heavy metal contamination in river water and sediments of the Swarnamukhi River Basin, India: Risk assessment and environmental implications. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 40(2), 609–623.
Qi, J. Y., Zhang, H. L., Li, X. P., Lu, J., & Zhang, G. S. (2016). Concentrations, spatial distribution, and risk assessment of soil heavy metals in a Zn–Pb mine district in southern China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(7), 413.
Qiu, G. L., & Chen, H. L. (2016). Concentration and pollution assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the Xiangjiang River (Hengyang section), China. Environment and Sustainable Development, 41(3), 207–210.
Ranjbar Jafarabadi, A., Riyahi Bakhtiyari, A., Shadmehri Toosi, A., & Jadot, C. (2017). Spatial distribution, ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in marine surface sediments and coastal seawaters of fringing coral reefs of the Persian Gulf, Iran. Chemosphere, 185, 1090–1111.
Redwan, M., & Elhaddad, E. (2017). Heavy metals seasonal variability and distribution in Lake Qaroun sediments, El-Fayoum, Egypt. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 134, 48–55.
Rodriguez-Freire, L., Avasarala, S., Ali, A.-M. S., Agnew, D., Hoover, J. H., Artyushkova, K., et al. (2016). Post gold king mine spill investigation of metal stability in water and sediments of the animas river watershed. Environmental Science and Technology, 50(21), 11539–11548.
Sakan, S., Devic, G., Relic, D., Andelkovic, I., Sakan, N., & Dordevic, D. (2015). Evaluation of sediment contamination with heavy metals: The importance of determining appropriate background content and suitable element for normalization. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 37(1), 97–113.
Sakan, S., Popovic, A., Andelkovic, I., & Dordevic, D. (2016). Aquatic sediments pollution estimate using the metal fractionation, secondary phase enrichment factor calculation, and used statistical methods. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 38(3), 855–867.
Shikazono, N., Tatewaki, K., Mohiuddin, K. M., Nakano, T., & Zakir, H. M. (2012). Sources, spatial variation, and speciation of heavy metals in sediments of the Tamagawa River in Central Japan. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 34, 13–26.
Song, Y. X., Chai, L. Y., Tang, C. J., Xiao, R. Y., Li, B. R., Wu, D., et al. (2018). Influence of ZnO nanoparticles on anammox granules: The inhibition kinetics and mechanism analysis by batch assays. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 133, 122–129.
Sun, W. L., Sang, L. X., & Jiang, B. F. (2012). Trace metals in sediments and aquatic plants from the Xiangjiang River, China. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 12(10), 1649–1657.
Tamim, U., Khan, R., Jolly, Y. N., Fatema, K., Das, S., Naher, K., et al. (2016). Elemental distribution of metals in urban river sediments near an industrial effluent source. Chemosphere, 155, 509–518.
Tomlinson, D. L., Wilson, J. G., Harris, C. R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen, 1–4(33), 566–575.
Wang, H. J., Wang, A. M., Bi, N. S., Zeng, X. M., & Xiao, H. H. (2014). Seasonal distribution of suspended sediment in the Bohai Sea, China. Continental Shelf Research, 90, 17–32.
Wang, J., Liu, G. J., Lu, L. L., Zhang, J. M., & Liu, H. Q. (2015). Geochemical normalization and assessment of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, and Ni) in sediments from the Huaihe River, Anhui, China. CATENA, 129, 30–38.
Wang, Z. X., Chai, L. Y., Wang, Y. Y., Yang, Z. H., Wang, H. Y., & Wu, X. (2011). Potential health risk of arsenic and cadmium in groundwater near Xiangjiang River, China: A case study for risk assessment and management of toxic substances. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 175(1), 167–173.
Wang, Z. X., Chai, L. Y., Yang, Z. H., Wang, Y. Y., & Wang, H. Y. (2010). Identifying sources and assessing potential risk of heavy metals in soils from direct exposure to children in a mine-impacted city, Changsha, China. Journal of Environmental Quality, 39(5), 1616–1623.
Wu, C., Zou, Q., Xue, S. G., Mo, J. Y., Pan, W. S., Lou, L. Q., et al. (2015). Effects of silicon (Si) on arsenic (As) accumulation and speciation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes with different radial oxygen loss (ROL). Chemosphere, 138, 447–453.
Yang, Z. F., Wang, Y., Shen, Z. Y., Niu, J. F., & Tang, Z. W. (2009). Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from the mainstream, tributaries, and lakes of the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166(2–3), 1186–1194.
Yang, Z. H., Liang, L. F., Yang, W. C., Shi, W., Tong, Y. P., Chai, L. Y., et al. (2018a). Simultaneous immobilization of cadmium and lead in contaminated soils by hybrid bio-nanocomposites of fungal hyphae and nano-hydroxyapatites. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(12), 11970–11980.
Yang, Z. H., Shi, W., Yang, W. C., Liang, L. F., Yao, W. B., Chai, L. Y., et al. (2018b). Combination of bioleaching by gross bacterial biosurfactants and flocculation: A potential remediation for the heavy metal contaminated soils. Chemosphere, 206, 83–91.
Zhang, W., Yu, L., & Hutchinson, S. M. (2001). Diagenesis of magnetic minerals in the intertidal sediments of the Yangtze Estuary, China, and its environmental significance. Science of the Total Environment, 266(1–3), 169–175.
Zhu, J. Y., Zhang, J. X., Qian, L., Tao, H., Xie, J. P., Hu, Y. H., et al. (2013). Phylogenetic analysis of bacterial community composition in sediment contaminated with multiple heavy metals from the Xiangjiang River in China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 70(1–2), 134–139.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key R&D Plan (2016YFC0403003), key project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (51634010), Key Scientific Research Project of Hunan Province, China, (2016SK2004), and Environmental Protection Department of Hunan [(2017)83] for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Chai, L., Yang, Z. et al. Seasonal and spatial contamination statuses and ecological risk of sediment cores highly contaminated by heavy metals and metalloids in the Xiangjiang River. Environ Geochem Health 41, 1617–1633 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00245-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00245-2