Abstract
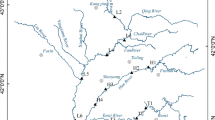
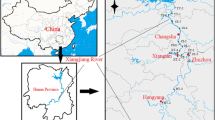
With the change in global climate and environment, water scarcity has been of great concern around the word and exacerbated by serious pollution in water resources. Pollutants accumulated in sediments are threatening water safety and ecological security. Different from others focusing on prevalent heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, As, Cd, Cr, Hg, etc.), in this study, some unheeded metal pollutants Tl, Sb, Mo, Sr, Co, V, Ti, Ca, Mg, Be and Li were monitored in sediments of the Xiangjiang River, China. It was found that there was no remarkable vertical variation with depth, but the seasonal characteristics of Tl, Sb, Mo, Be and Li. The enrichment, pollution and potential ecological risk of Tl, Sb and Mo were revealed by the enrichment factor (EF), geoaccumulation index (Igeo), pollution load index (PLIsite and PLIzone) and potential ecological risk index (RI). It is noticed that the pollution of Tl mainly occurred in summer at midstream and downstream and Mo pollution was much higher than Sb in summer and the reverse in other seasons. Additionally, sediment quality on east side was worse than on west side in Songbai section of the Xiangjiang River. For the first time, the toxic-response factor was figured out as Mo = 18, Tl = 17, Sb = 13, Sr = 6, Co = Be = 1, V = Li = 0, and importantly, the high potential ecological risk of Tl, Sb and Mo needs to be taken seriously for the comprehensive assessment on watershed environmental quality.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen-Gil, S. M., Gubala, C. P., Landers, D. H., Lasorsa, B. K., Crecelius, E. A., & Curtis, L. R. (1997). Heavy metal accumulation in sediment and freshwater fish in U.S. Arctic lakes. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 16(4), 733–741. https://doi.org/10.1897/1551-5028(1997)016%3c0733:hmaisa%3e2.3.co;2.
Audry, S., Schäfer, J., Blanc, G., & Jouanneau, J. M. (2004). Fifty-year sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution (Cd, Zn, Cu, Pb) in the Lot River reservoirs (France). Environmental Pollution, 132(3), 413–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.05.025.
Barbieri, M. (2016). The importance of enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index (I geo) to evaluate the soil contamination. Journal of Geology & Geophysics. https://doi.org/10.4172/2381-8719.1000237.
Chai, L., Li, H., Yang, Z., Min, X., Liao, Q., Liu, Y., et al. (2017). Heavy metals and metalloids in the surface sediments of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan, China: distribution, contamination, and ecological risk assessment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(1), 874–885. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7872-x.
Chen, J., Wei, F., Zheng, C., Wu, Y., & Adriano, D. C. (1991). Background concentrations of elements in soils of China. Water, air, and soil pollution (Vol. 57–58). https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00282934
Chen, J. Q., Wang, Z. X., Wu, X., Zhu, J. J., & Zhou, W. Bin. (2011). Source and hazard identification of heavy metals in soils of Changsha based on TIN model and direct exposure method. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China (English Edition), 21(3), 642–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60761-9.
Emery, R., Klopfer, D. C., & Skalski, J. R. (1981). Incipient toxicity of lithium to freshwater organisms representing a salmonid habitat. Washington. https://doi.org/10.2172/6453668
Farmer, J. G. (1991). The perturbation of historical pollution records in aquatic sediments. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 13(2), 76–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01734298.
Guo, X., Wang, K., He, M., Liu, Z., Yang, H., & Li, S. (2014). Antimony smelting process generating solid wastes and dust: Characterization and leaching behaviors. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 26(7), 1549–1556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.05.022.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8.
Han, Y., Du, P., Cao, J., & Posmentier, E. S. (2006). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Science of the Total Environment, 355(1–3), 176–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.02.026.
Hejabi, A. T., Basavarajappa, H. T., Karbassi, A. R., & Monavari, S. M. (2011). Heavy metal pollution in water and sediments in the Kabini River, Karnataka, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 182, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1854-0.
Jiang, M., Zeng, G., Zhang, C., Ma, X., Chen, M., Zhang, J., et al. (2013). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the surrounding soils and surface sediments in Xiawangang River, Qingshuitang District. PLoS ONE, 8(8), e71176. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071176.
Lal, R. (2007). Soil science and the carbon civilization. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 71(5), 1425. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2007.0001.
Léopold, E. N., Jung, M. C., Auguste, O., Ngatcha, N., Georges, E., & Lape, M. (2008). Metals pollution in freshly deposited sediments from river Mingoa, main tributary to the Municipal lake of Yaounde, Cameroon. Geosciences Journal, 12(4), 337–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-008-0034-5.
Li, J., Zheng, B., He, Y., Zhou, Y., Chen, X., Ruan, S., et al. (2018). Antimony contamination, consequences and removal techniques: A review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 156, 125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.024.
Liu, F., Le, X. C., McKnight-Whitford, A., Xia, Y., Wu, F., Elswick, E., et al. (2010). Antimony speciation and contamination of waters in the Xikuangshan antimony mining and smelting area, China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 32(5), 401–413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-010-9284-z.
Liu, Y., Wang, Q., Zhuang, W., Yuan, Y., Yuan, Y., Jiao, K., et al. (2018). Calculation of Thallium’s toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index: A case study. Chemosphere, 194, 562–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.002.
Looi, L. J., Aris, A. Z., Yusoff, F. M., Isa, N. M., & Hariset, H. (2018). Application of enrichment factor, geoaccumulation index, and ecological risk index in assessing the elemental pollution status of surface sediments. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 1, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0149-1.
Martin, J.-M., & Whitfield, M. (1983). The significance of the river input of chemical elements to the ocean. In Trace metals in sea water (pp. 265–296). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-6864-0_16
Milly, P. C. D., Betancourt, J., Falkenmark, M., Hirsch, R. M., Kundzewicz, Z. W., Lettenmaier, D. P., et al. (2008). Climate change: Stationarity is dead: Whither water management? Science, 319(5863), 573–574. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1151915.
Milly, P. C. D., Betancourt, J., Falkenmark, M., Hirsch, R. M., Kundzewicz, Z. W., Lettenmaier, D. P., et al. (2015). On Critiques of “stationarity is dead: Whither water management?”. Water Resources Research, 51(9), 7785–7789. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015WR017408.
Moore, J. W. (1991). Inorganic contaminants of surface water. Berlin: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-3004-5.
Oyewale, A. O., & Musa, I. (2006). Pollution assessment of the lower basin of Lakes Kainji/Jebba, Nigeria: heavy metal status of the waters, sediments and fishes. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 28(3), 273–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-006-9043-3.
Ozersky, T., Pastukhov, M. V., Poste, A. E., Deng, X. Y., & Moore, M. V. (2017). Long-term and ontogenetic patterns of heavy metal contamination in lake Baikal Seals (Pusa sibirica). Environmental Science and Technology, 51(18), 10316–10325. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b00995.
Peng, B., Tang, X., Yu, C., Tan, C., Yin, C., Yang, G., et al. (2011). Geochemistry of trace metals and Pb isotopes of sediments from the lowermost Xiangjiang River, Hunan Province (P. R. China): Implications on sources of trace metals. Environmental Earth Sciences, 64(5), 1455–1473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-0969-0.
PGHP (People’s Government of Hunan Province). (2012). Xiangjiang River basin control plan for heavy metal pollution (2012–2015) (in Chinese). http://www.hunan.gov.cn/xxgk/wjk/szfbgt/201207/t20120731_4825122.html. Accessed 20 May 2018.
Qian, X., & Li, X. (1988). Investigation of background values of 28 elements in river water from Dongting Lake system. Geographical Research, 8(1), 79–86.
Salati, S., & Moore, F. (2010). Assessment of heavy metal concentration in the Khoshk River water and sediment, Shiraz, Southwest Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 164(1–4), 677–689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0920-y.
SEPA (The State Environmental Protection Administration), & SAQSIQ (The State Administration of Quality Supervision Inspection and Quarantine). (2002). Environmental quality standard for surface water of the People’s Republic of China (GB3838-2002) (in Chinese)
Sharmin, S., Zakir, H. M., & Shikazono, N. (2009). Base metal pollution assessment in water and sediment of Nomi River, Tokyo, Japan. International journal of applied environmental sciences (Vol. 4). Michigan. https://www.highbeam.com. Accessed 20 May 2018.
Sun, G. X., Wang, X. J., & Hu, Q. H. (2011). Using stable lead isotopes to trace heavy metal contamination sources in sediments of Xiangjiang and Lishui Rivers in China. Environmental Pollution, 159(12), 3406–3410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.08.037.
Taylor, S. R., & McLennan, S. M. (1995). The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Reviews of Geophysics, 33(2), 241–265. https://doi.org/10.1029/95RG00262.
Tomlinson, D. L., Wilson, J. G., Harris, C. R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen, 33, 566–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02414780.
Varol, M., & Şen, B. (2012). Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments of the upper Tigris River, Turkey. CATENA, 92, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2011.11.011.
Visser, A., Kroes, J., Vliet, M. Van, Blenkinsop, S., & Broers, H. P. (2011). Climate change impacts on the hydrology of a small lowland catchment and the leaching of a heavy metal contamination. IAHS Publication, 13(GQ10: Groundwater Quality Management in a Rapidly Changing World), 2011.
Vliet, M. T. H. V., & Zwolsman, J. J. G. (2008). Impact of summer droughts on the water quality of the Meuse river. Journal of Hydrology, 353(1–2), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.01.001.
Wu, L., Qi, T., Li, D., Yang, H. J., Liu, G. Q., & Ma, X. Y. (2015). Current status, problems and control strategies of water resources pollution in China. Water Policy, 17(3), 423–440. https://doi.org/10.2166/wp.2014.018.
Zhang, J. L., Peng, B., Chai, L. Y., Wang, J., & Wan, S. (2011). Sintering of electrolysis manganese slag-shale-coal ash for brick. Environmental Science and Technology, 34(1), 144–147. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2011.01.034.
Zhang, L., & Zhao, G. (1996). The species and geochemicals characteristics of heavy metals in the sediments of Kangjiaxi river in the Shuikoushan Mine Sarea, China. Applied. Geochemistry., 11(1–2), 217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/0883-2927(95)00096-8.
Zhang, L., & Zhou, K. (1992). Background values of trace elements in the source area of the Yangtze River. Science of the Total Environment, 125(C), 391–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(92)90403-f.
Zhao, S., Fang, J., Miao, S., Gu, B., Tao, S., Peng, C., et al. (2005). The 7-decade degradation of a large freshwater lake in Central Yangtze River, China. Environmental Science and Technology, 39(2), 431–436. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0490875.
Zhou, Y., He, Y., Xiang, Y., Meng, S., Liu, X., Yu, J., et al. (2019). Single and simultaneous adsorption of pefloxacin and Cu(II) ions from aqueous solutions by oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotube. Science of the Total Environment, 646, 29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.267.
Zhou, Y., Liu, X., Xiang, Y., Wang, P., Zhang, J., Zhang, F., et al. (2017). Modification of biochar derived from sawdust and its application in removal of tetracycline and copper from aqueous solution: Adsorption mechanism and modelling. Bioresource Technology, 245, 266–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.178.
Acknowledgements
This work was sponsored by Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Soil and Groundwater Pollution Control (No. 2017B030301012) and State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Integrated Surface Water-Groundwater Pollution Control. This work was also supported by the Southern University of Science and Technology (Grant No. G01296001) and Environmental Protection Department of Hunan (Grant No. 201783).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Yang, J., Ye, B. et al. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of 11 unheeded metals in sediments of the Chinese Xiangjiang River. Environ Geochem Health 41, 1459–1472 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0230-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0230-9