Abstract
Purpose
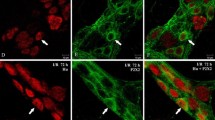
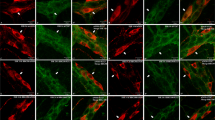
We investigated the effects of ischemia/reperfusion in the intestine (I/R-i) on purine receptor P2X2-immunoreactive (IR) neurons of the rat ileum.
Methods
The superior mesenteric artery was occluded for 45 min with an atraumatic vascular clamp and animals were sacrificed 4 h later. Neurons of the myenteric and submucosal plexuses were evaluated for immunoreactivity against the P2X2 receptor, nitric oxide synthase (NOS), choline acetyl transferase (ChAT), calbindin, and calretinin.
Results
Following I/R-i, we observed a decrease in P2X2 receptor immunoreactivity in the cytoplasm and surface membranes of neurons of the myenteric and submucosal plexuses. These studies also revealed an absence of calbindin-positive neurons in the I/R-i group. In addition, the colocalization of the P2X2 receptor with NOS, ChAT, and calretinin immunoreactivity in the myenteric plexus was decreased following I/R-i. Likewise, the colocalization between P2X2 and calretinin in neurons of the submucosal plexus was also reduced. In the I/R-i group, there was a 55.8% decrease in the density of neurons immunoreactive (IR) for the P2X2 receptor, a 26.4% reduction in NOS-IR neuron, a 25% reduction in ChAT-IR neuron, and a 47% reduction in calretinin-IR neuron. The density of P2X2 receptor and calretinin-IR neurons also decreased in the submucosal plexus of the I/R-i group. In the myenteric plexus, P2X2-IR, NOS-IR, ChAT-IR and calretinin-IR neurons were reduced in size by 50%, 49.7%, 42%, and 33%, respectively, in the I/R-i group; in the submucosal plexus, P2X2-IR and calretinin-IR neurons were reduced in size by 56% and 72.6%, respectively.
Conclusions
These data demonstrate that ischemia/reperfusion of the intestine affects the expression of the P2X2 receptor in neurons of the myenteric and submucosal plexus, as well as density and size of neurons in this population. Our findings indicate that I/R-i induces changes in P2X2-IR enteric neurons that could result in alterations in intestinal motility.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Furness JB. Types of neurons in the enteric nervous system. J Autonom Nerv Syst. 2000;81:87–96. doi:10.1016/S0165-1838(00)00127-2.
Furness JB. The enteric nervous system. Melbourne: Blackwell; 2006.
Burnstock G. The past, present and future of purine nucleotides as signalling molecules. Neuropharmacology. 1997;36:1127–1139. doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(97)00125-1.
Abbrachio MP, Burnstock G, Verkhratsky A, Zimmermann H. Purinergic signaling in the nervous system: an overview. Trends Neurosci. 2009;32:19–29. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2008.10.001.
Baraja-López C, Huizinga JD, Gerzanich V, Espinosa-Luna R, Peres AL. P2X-purinoceptors of myenteric neurones from the guinea-pig ileum and their unusual pharmacological properties. Br J Pharmacol. 1996;119:1541–1548.
Bian XC, Bertrand PP, Bornstein JC. Descending inhibitory reflexes involve P2X receptor–mediated transmission from interneurons to motor neurons in guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 2000;528:551–560. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00551.xPMID:11060131.
Galligan JJ, Lepard KJ, Schneider DA, Zhou X. Multiple mechanisms of fast excitatory synaptic transmission in the enteric nervous system. J Auton Nerv Syst. 2000;81:97–103. doi:10.1016/S0165-1838(00)00130-2PMID:10869707.
Galligan JJ. Ligand-gated ion channels in the enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2002;14:611–623. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2982.2002.00363.xPMID:12464083.
Vulchanova L, Arvidsson U, Riedl M, et al. Differential distribution of two ATP-gated ion channels (P2X receptors) determined by immunohistochemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1996;93:8063–8067. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.15.8063PMID:8755603.
Castelucci P, Robbins HL, Poole DP, Furness JB. The distribution of purine P2X2 receptors in the guinea pig enteric nervous system. Histochem Cell Biol. 2002;117:415–422. doi:10.1007/s00418-002-0404-4PMID:12029488.
Poole DP, Castelucci P, Robbins HL, et al. The distribution of P2X3 purine receptor subunits in the guinea-pig enteric nervous system. Auton Neurosci. 2002;101:39–47. doi:10.1016/S1566-0702(02)00179-0PMID:12462358.
Van Nassauw L, Brouns I, Adraensen D, et al. Neurochemical identification of enteric neurons expressing P2X(3) receptors in the guinea-pig ileum. Histochem Cell Biol. 2002;118:193–203. doi:10.1007/s00418-002-0447-6PMID:12271355.
Hu HZ, Gao N, Lin Z, et al. P2X7 receptors in the enteric nervous system of guinea-pig small intestine. J Comp Neurol. 2001;440:299–310. doi:10.1002/cne.1387PMID:11745625.
Xiang Z, Burnstock G. Distribution of P2Y2 receptors in the guinea pig enteric nervous system and its coexistence with P2X2 and P2X3 receptors, neuropeptide Y, nitric oxide synthase and Calretinin. Histochem Cell Biol. 2005;124:379–390. doi:10.1007/s00418-005-0043-7PMID:16136347.
Xiang Z, Burnstock G. P2X2 and P2X3 purinoceptors in the rat enteric nervous system. Histochem Cell Biol. 2004;12:169–179. doi:10.1007/s00418-004-0620-1PMID:14767775.
Xiang Z, Burnstock G. Development of nerves expressing P2X3 receptors in the myenteric plexus of rat stomach. Histochem Cell Biol. 2004;122:111–119. doi:10.1007/s00418-004-0680-2PMID:15258768.
Yu Q, Zhao Z, Sun J, et al. Expression of P2X6 receptors in the enteric nervous system of the rat gastrointestinal tract. Histochem Cell Biol. 2010;133:177–188. doi:10.1007/s00418-009-0659-0PMID:19946698.
Giaroni C, Knight GE, Ruan H-Z, et al. P2 receptors in the murine gastrointestinal tract. Neuropharmacology. 2002;43:1313–1323. doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(02)00294-0PMID:12527481.
Ruan HZ, Burnstock G. The distribution of P2X5 purinergic receptors in the enteric nervous system of mouse. Cell Tissue Res. 2005;319:191–200. doi:10.1007/s00441-004-1002-7PMID:15551155.
Koike K, Moore FA, Moore EE, et al. Gut ischemia mediates lung injury by a xanthine oxidasedependent neutrophil mechanism. J Surg Res. 1993;54:469–473. doi:10.1006/jsre.1993.1072.
Cavriani G, Oliveira-Filho RM, Trezena AG et al. Lung microvascular permeability and neutrophil recruitment are differently regulated by nitric oxide in a rat model of intestinal ischemia-reperfusion. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004;494:241–249. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.04.048.
Cavriani G, Domingos HV, Trezena AG, et al. Lymphatic system as a path underlying the spread of lung and gut injury after intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Shock. 2005;23:330–336 doi:10.1097/0-1.shk.0000157303.76749.9b.
Cavriani G, Domingos HV, et al. Lymphatic thoracic duct ligation modulates the serum levels of IL-1beta and IL-10 after intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rats with the involvement of tumor necrosis factor alpha and nitric oxide. Shock. 2007;27:209–213. doi:10.1097/01.shk.0000238068.84826.52.
Oldenburg WA, Lau LL, Rodenberg TJ, et al. Acute mesenteric ischemia: A clinical review. Arch Intern Med 2004;164:1054–1062.
Hierholzer C, Kalff JC, Audolfsson G. Molecular and functional contractile sequelae of rat intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Transplantation. 1999;68:1244–1254. doi:10.1097/00007890-199911150-00006.
Mallick IH, Yang W, Winslet MC, Seifalian AM. Ischemia-reperfusion injury of the intestine and protective strategies against injury. Dig Dis Sci. 2004;49:1359–1377. doi:10.1023/B:DDAS.0000042232.98927.91.
Stoney RJ, Cunninghan CG. Acute mesenteric ischemia. Surgery. 1993;114:489–490.
Lindestrom L, Ekblad E. Structural and neuronal changes in rat ileum after ischemia with reperfusion. Dig Dis Sci. 2004;49:1212–1222. doi:0163-2116/04/0800-1212/0.
Piao DX, Jiang CH, Kosata M, et al. Cytoplasmic delayed neuronal death in the myenteric plexus of the rat small intestine after ischemia. Arch Histol Cytol. 1999;62:383–392. doi:10.1679/aohc.62.383.
Rivera LR, Thacker M, Castelucci P, Bron R, Furness JB. The reactions of specific neuron types to intestinal ischemia in the guinea pig enteric nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2009;118:261–270. doi:10.1007/s00401-009-0549-5.
Milano PM, Douillet CD, Riesenman PJ, et al. Intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury alters purinergic receptor expression in clinically relevant extraintestinal organs. J Surg Res. 2008;145:272–278. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2007.03.028.
Ren J, Bian X, DeVries M, et al. P2X2 subunits contribute to fast synaptic excitation in myenteric neurons of the mouse small intestine. J Physiol. 2003;552:809–821.
Calcina F, Barocelli E, Bertoni S, et al. Effect of n-methyl-d-aspartate receptor blockade on neuronal plasticity and gastrointestinal transit delay induced by ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Neuroscience. 2005;134:39–49.
Sayegh AI, Ritter RC. Morphology and distribution of nitric oxide sinthase, neurokin-1 receptor, calretinin, calbindin, and neurofilament-M- immunoreactive neurons in the myenteric and submucosal plexuses of the rat small intestine. Anat Rec. 2003;271A:209–216. doi:10.1002/ar.a.10024PMID:12552637.
Castelucci P, De Souza R, De Angelis RC, Furness JB, Liberti EA. Effects of pre- and postnatal protein deprivation and postnatal re-feeding on myenteric neurons of the rat large intestine: a quantitative morphological study. Cell Tissue Res. 2002;310:1–7. doi:10.1007/s00441-002-0615-yPMID:12242478.
Gomes OA, Castelucci P, Fontes RBV, Liberti EA. Effects of pre- and postnatal protein and postnatal re-feeding on myenteric neurons of the rat small intestine: a quantitative morphological study. Auton Neurosci. 2006;126:277–284. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2006.03.003PMID:16713368.
Liberti EA, Fontes RB, Fuggi VM, et al. Effects of combined pre- and post-natal protein deprivation on the myenteric plexus of the esophagus of weanling rats: a histochemical, quantitative and ultrastructural study. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:3598–3604. doi:1007-9327/13/3598.aspPMID:17659710.
Greggio FM, Fontes RBV, Maifrino LBM, et al. Effects of perinatal protein deprivation and recovery on esophageal myenteric plexus. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:563–570. doi:10.3748/wjg.v16.i5.563PMID:20128023.
Misawa R, Girotti PA, Mizuno MS, et al. Effects of protein deprivation and re-feeding on P2X2 receptors in enteric neurons. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:3651–3663.
Mann PT, Furness JB, Southwell BR. Choline acethyltransferase immunoreactivity of putative intrinsic primary afferent neurons in the rat ileum. Cell Tissue Res. 1999;297:241–248. doi:10.1007/s004410051352PMID:10470494.
Potier B, Krzywkowski P, Lamour Y, et al. Loss of calbindin-immunoreactivity in CA1 hippocampal stratum radiatum and stratum lacunosum-moleculare interneurons in the aged rat. Brain Res 1994;661:181–188.
Zhang JH, Morita Y, Hironaka T, et al. Ontological study of calbindin-D28 k-like and parvalbumin-like immunoreactivities in rat spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia. J Comp Neurol. 1990;302:715–728.
Orrenius S, Nicotera P. The calcium ion and cell death. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1994;43:1–11.
Hwang IK, Kang TC, Lee JC. Chronological alterations of calbindin D-28 k immunoreactivity in the gerbil main olfactory bulb after ischemic insult. Brain Res. 2003;971:250–254.
Kwon OJ, Kim JY, Kim SY, Jeon CJ. Alterations in the localization of calbindin D28 K-, calretinin-, and parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurons of rabbit retinal ganglion cell layer from ischemia and reperfusion. Mol Cells. 2005;19:382–390.
Kamm K, Hoppe S, Breves G, Schröder B. Effects of the probiotic yeast Saccharomyces boulardii on the neurochemistry of myenteric neurones in pig jejunum. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2004;16:53–60.
Kristián T, Siesjö BK. Calcium in ischemic cell death. Stroke. 1998;29:705–718.
Cavaliere F, Florenzano F, Amadio S, et al. Up-regulation of P2X2, P2X4 receptor and ischemic cell death: prevention by antagonists. Neuroscience. 2003;120:85–98.
Franke H, Günther A, Grosche J, et al. P2X7 receptor expression after ischemia in the cerebral cortex of rats. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2004;63:686–699.
Franke H, Krügel U. Illes P. P2 receptors and neuronal injury. Euro Jour Physiol. 2006;452:622–644. doi:10.1007/s00424-006-0071-8PMID:16645849.
Phillips RJ, Kieffer EJ, Powley TL. Aging of the myenteric plexus: neuronal loss is specific to cholinergic neurons. Auton Neurosc. 2003;106:69–83. doi:10.1016/S1566-0702(03)00072-9PMID:12878075.
Chiocchetti R, Poole DP, Robbins HL, et al. Evidence that two forms of choline acetyltransferase are differentially expressed in subclasses of enteric neurons. Cell Tissue Res. 2003;311:11–22. doi:10.1007/s00441-002-0652-6PMID:12483280.
Sang Q, Young HM. Chemical coding of neurons in the myenteric plexus and external muscle of the small and large intestine of the mouse. Cell Tissue Res. 1996;284:53. doi:10.1007/s004410050565PMID:8601295.
Qu ZD, Thacker M, Castelucci P, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of neuron types in the mouse small intestine. Cell Tissue Res. 2008;334:147–161. doi:10.1007/s00441-008-0684-7PMID:18855018.
Nakajima K, Tooyama I, Yasuhara O, et al. Immunohistochemical demonstration of choline acetyltransferase of a peripheral type (pChAT) in the enteric nervous system of rats. J Chem Neuroanat. 2000;18:31–40. doi:10.1016/S0891-0618(99)00058-7PMID:10708917.
Jarvinen MK, Wollmann WJ, Powrozek TA, et al. Nitric oxide synthase-containing neurons in the myenteric plexus of the rat gastrointestinal tract: distribution and regional density. Anat Embriol. 1999;199:99–112. doi:10.1007/s004290050213PMID:9930618.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Professor Edson Aparecido Liberti for facilities, Professor Jackson Cioni Bittencourt and Assistant Professor Carol Fuzeti Elias for use of the Leica Microscope in these analyses. This work was supported by the FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo 05/04752-0) and CNPq.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paulino, A.S., Palombit, K., Cavriani, G. et al. Effects of Ischemia and Reperfusion on P2X2 Receptor Expressing Neurons of the Rat Ileum Enteric Nervous System. Dig Dis Sci 56, 2262–2275 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1588-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1588-z