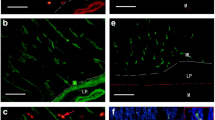
Abstract
Adenosine 5′-triphosphate receptors are known to be involved in fast excitatory postsynaptic currents in myenteric neurons of the digestive tract. In the present study, the distribution of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor mRNA was examined by in situ hybridisation while P2X2 and P2X3 receptor protein was localised by immunohistochemical methods. In addition, P2X2 and P2X3 receptors were colocalised with calbindin and calretinin in the myenteric and submucosal plexus. P2X2- and P2X3-immunoreactive neurons were found in the myenteric and submucosal plexuses throughout the entire length of the rat digestive tract from the stomach to the colon. Approximately 60%, 70% and 50% of the ganglion cells in the myenteric plexus of the gastric corpus, ileum and distal colon, and 56% and 45% in the submucosal plexus of the ileum and distal colon, respectively, showed positive immunoreactivity to the P2X2 receptor. Approximately 10%, 2% and 15% of the ganglion cells in the myenteric plexus of the gastric corpus, ileum and distal colon, and 62% and 40% in the submucosal plexus of the ileum and distal colon, respectively, showed positive immunoreactivity to the P2X3 receptor. Double-labelling studies showed that about 10–25% of the neurons with P2X2 immunoreactivity in myenteric plexus and 30–50% in the submucosal plexus were found to express calbindin or calretinin. About 80% of the neurons with P2X3 receptor immunoreactivity in the myenteric plexus and about 40% in the submucosal plexus expressed calretinin. Approximately 30–75% of the neurons with P2X3 receptor immunoreactivity in the submucosal plexus expressed calbindin, while none of them were found to express calbindin in the myenteric plexus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barajas-Lopez C, Huizinga JD, Collins SM, Gerzanich V, Espinosa-Luna R, Peres AL (1996) P2X-purinoceptors of myenteric neurones from the ileum and their unusual pharmacological properties. Br J Pharmacol 119:1541–1548
Bertrand PP (2003) ATP and sensory transduction in the enteric nervous system. Neuroscientist 9:243–260
Bertrand PP, Bornstein JC (2002) ATP as a putative sensory mediator: activation of intrinsic sensory neurons of the myenteric plexus via P2X receptors. J Neurosci 22:4767–4775
Bian XC, Bertrand PP, Bornstein JC (2000) Descending inhibitory reflexes involve P2X receptor-mediated transmission from interneurons to motor neurons in guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol 528:551–560
Bian XC, Bornstein JC, Bertrand PP (2003a) Nicotinic transmission at functionally distinct synapses in descending reflex pathways of the rat colon. Neurogastroenterol Motil 15:161–171
Bian XC, Ren J, DeVries M, Schnegelsberg B, Cockayne DA, Ford APDW, Galligan JJ (2003b) Peristalsis is impaired in the small intestine of mice lacking the P2X3 subunit. J Physiol 551:309–322
Bo X, Zhang Y, Nassar M, Burnstock G, Schoepfer R (1995) A P2X purinoceptor cDNA conferring a novel pharmacological profile. FEBS Letts 375:129–133
Brake AJ, Wagenbach MJ, Julius D (1995) New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotropic ATP receptor. Nature 317:519–523
Burnstock G (1997) The past, present and future of purine nucleotides as signaling molecules. Neuropharmacology 36:1127–1139
Burnstock G (2001a) Purinergic signalling in gut. In: Abbracchio MP, Williams M (eds) Handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol 151/I. Purinergic and pyrimidinergic signalling. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 141–238
Burnstock G (2001b) Purine-mediated signalling in pain and visceral perception. Trends in Pharmacol Sci 22:82–188
Castelucci P, Robbins HL, Poole DP, Furness JB (2002) The distribution of purine P2X2 receptors in the enteric nervous system. Histochem Cell Biol 117:415–422
Chen CC, Akoplan AN, Sivilotti L, Colquhoun D, Burnstock G, Wood JN (1995) A P2X purinoceptor expressed by a subset of sensory neurons. Nature 277:428–431
Collo G, North RA, Kawashima E, MerloPich E, Neidhart S, Surprenant A, Buell G (1996) Cloning of P2X5 and P2X6 receptors and the distribution and properties of an extended family of ATP-gated ion channels. J Neurosci 16:2495–2507
Dunn PM, Zhong Y, Burnstock G (2001) P2X receptors in peripheral neurones. Prog Neurobiol 65:107–134
Furness JB, Kunze WA, Bertrand PP, Clerc N, Bornstein JC (1998) Intrinsic primary afferent neurons of the intestine. Prog Neurobiol 54:1–18
Heinemann A, Shahbazian A, Bartho L, Holzer P (1999) Different receptors mediating the inhibitory action of exogenous ATP and endogenously released purines on intestinal peristalsis. Br J Pharmacol 128:313–320
Kanjhan R, Houseley GD, Burton LD, Christie DL, Kippenberger Athorne PR, Luo L, Ryan AF (1999) Distribution of the P2X2 receptor subunit of the ATP-gated ion channels in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 407:11–32
Katayama Y, Morita K (1989) Adenosine 5′-triphosphate modulates membrane potassium conductance in myenteric neurons. J Physiol 408:373–390
Kimball BC, Yule DI, Mulholland MW (1996) Extracellular ATP mediates Ca2+ signaling in cultured myenteric neurons via a PLC-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol 270:G587–G593
King BF, Townsend-Nicholson A, Wildman SS, Thomas T, Spyer KM, Burnstock G (2000) Coexpression of rat P2X2 and P2X6 subunits in Xenopus oocytes. J Neurosci 20:4871–4877
Lê KT, Babinski K, Seguela P (1998) Central P2X4 and P2X6 channel subunits coassemble into a novel heteromeric ATP receptor. J Neurosci 18:7152–7159
Lepard KJ, Messori E, Galligan JJ (1997) Purinergic fast excitatory postsynaptic potentials in myenteric neurons of guinea pig: distribution and pharmacology. Gastroenterology 113:1522–1534
Lewis Neidhart S, Holy C, North RA, Buell G, Surprenant A (1995) Co-expression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits can account for ATP-gated currents in sensory neurons. Nature 377:432–435
Li ZS, Furness JB (1998) Immunohistochemical localization of cholinergic markers in putative intrinsic primary afferent neurons of the small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 204:35–43
Liu M, King BF, Dunn PM, Rong W, Townsend-Nicholson A, Burnstock G (2001) Coexpression of P2X3 and P2X2 receptor subunits in varying amounts generates heterogeneous populations of P2X receptors that evoke a spectrum of agonist responses comparable to that seen in sensory neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 296:1043–1050
Loesch A, Burnstock G (1998) Electron-immunocytochemical localization of the P2X1 receptor in the rat cerebellum. Cell Tissue Res 294:253–260
Loesch A, Miah S, Burnstock G (1999) Ultrastructural localization of ATP-gated P2X2 receptor immunoreactivity in the rat hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system. J Neurocytol 28:495–504
Loesch A, Glass R, Burnstock G (2002) Ultrastructural identification of P2Y2 receptor mRNA in the rat thymus. Cells Tissues Organs 172:255–264
Oglesby IB, Lachnit WG, Burnstock G, Ford APDW (1999) Subunit specificity of polyclonal antisera to the carboxy terminal regions of P2X receptors P2X1 through P2X7. Drug Dev Res 47:189–195
Poole DP, Castelucci P, Robbins HL, Chiocchetti R, Furness JB (2002) The distribution of P2X3 purine receptor subunits in the guinea pig enteric nervous system. Auton Neurosci 101:39–47
Rong W, Spyer M, Burnstock G (2002) Activation and sensitisation of low and high threshold afferent fibres mediated by P2X receptors in the mouse urinary bladder. J Physiol 541:591–600
Spencer NJ, Walsh M, Smith TK (2000) Purinergic and cholinergic neuro-neuronal transmission underlying reflexes activated by mucosal stimulation in the isolated ileum. J Physiol 522:321–331
Surprenant A, Rassendern F, Kawshima E, North RA, Buell G (1996) The cytolytic P2z receptor of extracelluar ATP identified as a P2X receptor (P2X7). Science 272:735–738
Valera S, Hussy N, Evans RJ, Adani N, North AR, Surprenant A, Buell G (1995) A new class of ligand-gated ion channels defined by P2X receptor for extracellular ATP. Nature 371:516–519
Van Nassauw LV, Brouns I, Adriaensen D, Burnstock G, Timmermans JP (2002) Neurochemical identification of enteric neurons expressing P2X3 receptors in the ileum. Histochem Cell Biol 118:193–203
Wynn G, Rong W, Xiang Z, Burnstock G (2003) Purinergic mechanisms contribute to mechanosensory transduction in the rat colorectum. Gastroenterology 125:1398–1409
Xiang Z, Bo X, Burnstock G (1998a) P2X receptor immunoreactivity in the rat cochlea, vestibular ganglion and cochlear nucleus. Hearing Res 128:190–196
Xiang Z, Bo X, Oglesby IB, For AP, Burnstock G (1998b) Localization of ATP-gated P2X2 receptor immunoreactivity in the rat hypothalamus. Brain Res 813:390–397
Xiang Z, Jiang L, Kang Z (2001) Transient expression of somatostatin mRNA in developing ganglion cell layers of rat retina. Dev Brain Res 128:25–33
Zhong Y, Dunn PM, Xiang Z, Bo X, Burnstock G (1998) Pharmacological and molecular characterization of P2X purinoceptors in rat pelvic ganglion neurons. Br J Pharmacol 125:771–781
Zhong Y, Dunn PM, Burnstock G (2000a) Sympathetic neurons express varying proportions of two distinct P2X receptors. J Physiol 523:391–402
Zhong Y, Dunn PM, Burnstock G (2000b) Pharmacological comparison of P2X receptors on rat celiac, mouse celiac and mouse pelvic ganglion neurons. Neuropharmacology 39:172–180
Zhong Y, Banning AS, Cockayne DA, Ford APDW, Burnstock G, McMahon SB (2003) Bladder and cutaneous sensory neurons of the rat express different functional P2X receptors. Neuroscience (in press)
Zhou X, Galligan JJ (1996) P2X purinoceptors in cultured myenteric neurons of small intestine. J Physiol 496:719–729
Zhou X, Galligan JJ (1998) Non-additive interaction between nicotinic cholinergic and P2X purine receptors in enteric neurons in culture. J Physiol 513:685–697
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, Z., Burnstock, G. P2X2 and P2X3 purinoceptors in the rat enteric nervous system. Histochem Cell Biol 121, 169–179 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-004-0620-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-004-0620-1