Abstract
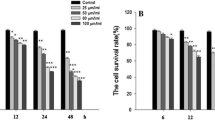
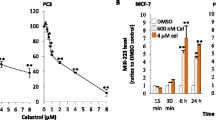
Silibinin is a natural polyphenol with high antioxidant and anticancer properties, which causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in most cancer cell types including breast cancer, but the in-line mechanisms, are still unknown. Silibinin significantly downregulated oncomiR miR-21 expression in breast cancer cells. Here the effect of anti-miR-21 on cell viability, apoptotic induction, cell cycle distribution, and the expression levels of downstream targets of miR-21 were investigated in MCF-7 and T47D cells. MiR-21 mimic transfection was also applied in silibinin treated samples to evaluate functional role of miR-21downregulation on silibinin effects. It was found that after anti-miR-21 transfection, no significant changes were detected in cell viability, apoptosis (except early apoptosis), and cell cycle in MCF-7 and T47D cells. Compared to silibinin, miR-21 mimic transfection in combination with silibinin caused a slight modulation in some of the examined silibinin effects including apoptosis, Bcl2 mRNA and PTEN mRNA and protein levels. Silibinin slightly changed luciferase activity from reporters containing the miR-21 recognition elements from PTEN-3′UTR and Bcl2-3′UTR in both cell lines. Together these data demonstrated negligible cancer-progression impact of miR-21 and limited roles of miR-21 downregulation in examined silibinin effects, and strengthened the anti-cancer pathways of silibinin other than miR-21downregulation in MCF-7 and T47D cells.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ERa+ :
-
Estrogen receptor alpha positive
- ERa− :
-
Estrogen receptor alpha negative
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- SNORD-47:
-
Small nucleolar RNA 47
- PDCD4:
-
Programmed cell death protein 4
- TM1:
-
Tropomyosine 1
- PMSF:
-
Phenyl methyl sulfonyl fluoride
References
Asad SF, Singh S, Ahmad A, Hadi SM (1998) Flavonoids: antioxidants in diet and potential anticancer agents. Med Sci Res 26:723–728
Bakhshandeh B, Soleimani M, Hafizi M, Ghaemi N (2012) A comparative study on nonviral genetic modifications in cord blood and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotechnology 64:523–540
Bartel D (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297
Chahar MK, Sharma N, Dobhal MP, Joshi YC (2011) Flavonoids: a versatile source of anticancer drugs. Pharmacogn Rev 5(9):1–12
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K, Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Guo X, Li Q, Li X, Wang W, Zhang Y, Wang J, Jiang X, Xiang Y, Xu C, Zheng P, Zhang J, Li R, Zhang H, Shang X, Gong T, Ning G, Wang J, Zen K, Zhang J, Zhang CY (2008) Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res 18(10):997–1006
Cheng CJ, Bahal R, Babar IA, Pincus Z, Barrera F, Liu C, Svoronos A, Braddock DT, Glazer PM, Engelman DM, Saltzman WM, Slack FJ (2015) MicroRNA silencing for cancer therapy targeted to the tumour microenvironment. Nature 518(7537):107–110
Deep G, Agarwal R (2007) Chemopreventive efficacy of silymarin in skin and prostate cancer. Integr Cancer Ther 6(2):130–145
Dong J, Zhao YP, Zhou L, Zhang TP, Chen G (2011) Bcl-2 upregulation induced by miR-21 via a direct interaction is associated with apoptosis and chemoresistance in MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells. Arch Med Res 42(1):8–14
Duan WJ, Li QS, Xia MY, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Ikejima T (2011) Silibinin activated p53 and induced autophagic death in human fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells via reactive oxygen species-p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathways. Biol Pharm Bull 34(1):47–53
Esau CC (2008) Inhibition of microRNA with antisense oligonucleotides. Methods 44(1):55–60
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M, Ménard S, Palazzo JP, Rosenberg A, Musiani P, Volinia S, Nenci I, Calin GA, Querzoli P, Negrini M, Croce CM (2005) MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 65(16):7065–7070
Jahanafrooz Z, Motamed N, Bakhshandeh B (2016) Comparative evaluation of silibinin on cell cycle and apoptosis in human breast cancer MCF-7 and T47D cell lines. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 17(5):2661–2665
Krützfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R, Rajeev KG, Tuschl T, Manoharan M, Stoffel M (2005) Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with ‘antagomirs’. Nature 438(7068):685–689
Lee YS, Dutta A (2009) MicroRNA in Cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 4:199–227
Li L, Gao Y, Zhang L, Zeng J, He D, Sun Y (2008) Silibinin inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis by caspase activation, down-regulating survivin and blocking EGFR-ERK activation in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett 272(1):61–69
Li LQ, Li XL, Wang L, Du WJ, Guo R, Liang HH, Liu X, Liang DS, Lu YJ, Shan HL, Jiang HC (2012) Matrine inhibits breast cancer growth via miR-21/PTEN/Akt pathway in MCF-7 cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 30(3):631–641
Ling H, Fabbri M, Calin GA (2013) MicroRNAs and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12(11):847–865
Mattie MD, Benz CC, Bowers J, Sensinger K, Wong L, Scott GK, Fedele V, Ginzinger D, Getts R, Haqq C (2006) Optimized high-throughput microRNA expression profiling provides novel biomarker assessment of clinical prostate and breast cancer biopsies. Mol Cancer 5:24
Mohammadi-Yeganeh S, Paryan M, Mirab Samiee S, Soleimani M, Arefian E, Azadmanesh K, Mostafavi E, Mahdian R, Karimipoor M (2013) Development of a robust, low cost stem-loop real-time quantification PCR technique for miRNA expression analysis. Mol Biol Rep 40(5):3665–3674
Mokhtari MJ, Motamed N, Shokrgozar MA (2008) Evaluation of silibinin on the viability, migration and adhesion of the human prostate adenocarcinoma (PC-3) cell line. Cell Biol Int 32(8):888–892
Naderi M, Abdul Tehrani H, Soleimani M, Shabani I, Hashemi SM (2015) A home-brew real-time PCR assay for reliable detection and quantification of mature miR-122. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 23(8):601–606
Osborne CK, Hobbs K, Trent JM (1987) Biological differences among MCF-7 human breast cancer cell lines from different laboratories. Breast Cancer Res Treat 9(2):111–121
Ranji N, Sadeghizadeh M, Shokrgozar MA, Bakhshandeh B, Karimipour M, Amanzadeh A, Azadmanesh K (2013) MiR-17-92 cluster: an apoptosis inducer or proliferation enhancer. Mol Cell Biochem 380(1–2):229–238
Riccardi C, Nicoletti I (2006) Analysis of apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. Nat Protoc 1(3):1458–1461
Roy S, Kaur M, Agarwal C, Tecklenburg M, Sclafani RA, Agarwal R (2007) p21 and p27 induction by silibinin is essential for its cell cycle arrest effect in prostate carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther 6(10):2696–2707
Sak K (2014) Cytotoxicity of dietary flavonoids on different human cancer types. Pharmacogn Rev 8(16):122–146
Sempere LF, Christensen M, Silahtaroglu A, Bak M, Heath CV, Schwartz G, Wells W, Kauppinen S, Cole CN (2007) Altered microRNA expression confined to specific epithelial cell subpopulations in breast cancer. Cancer Res 67(24):11612–11620
Sharma G, Singh RP, Chan DC, Agarwal R (2003) Silibinin induces growth inhibition and apoptotic cell death in human lung carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res 23(3B):2649–2655
Shenouda SK, Alahari SK (2009) MicroRNA function in cancer: oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer Metastasis Rev 28(3–4):369–378
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F, Mo YY (2007) miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene 26(19):2799–2803
Sicard F, Gayral M, Lulka H, Buscail L, Cordelie P (2013) Targeting miR-21 for the Therapy of Pancreatic Cancer. Mol Ther 21(5):986–994
Teng Y, Manavalan TT, Hu C, Medjakovic S, Jungbauer A, Klinge CM (2013) Endocrine disruptors fludioxonil and fenhexamid stimulate miR-21 expression in breast cancer cells. Toxicol Sci 131(1):71–83
Tiwari P, Kumar A, Balakrishnan S, Kushwaha HS, Mishra KP (2011) Silibinin-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 and T47D human breast carcinoma cells involves caspase-8 activation and mitochondrial pathway. Cancer Invest 29(1):12–20
Vasudevan S (2012) Posttranscriptional upregulation by microRNAs. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 3(3):311–330
Verschoyle RD, Greaves P, Patel K, Marsden DA, Brown K, Steward WP, Gescher AJ (2008) Evaluation of the cancer chemopreventive efficacy of silibinin in genetic mouse models of prostate and intestinal carcinogenesis: relationship with silibinin levels. Eur J Cancer 44(6):898–906
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, Prueitt RL, Yanaihara N, Lanza G, Scarpa A, Vecchione A, Negrini M, Harris CC, Croce CM (2006) A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(7):2257–2261
Weng L, Brown J, Eng C (2001) PTEN induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through phosphoinositol-3-kinase/Akt-dependent and -independent pathways. Hum Mol Genet 10(3):237–242
Wickramasinghe NS, Manavalan TT, Dougherty SM, Riggs KA, Li Y, Klinge CM (2009) Estradiol downregulates miR-21 expression and increases miR-21 target gene expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res 37(8):2584–2595
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng L, Wu QL, Zeng YX, Shao JY (2008) MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA 14(11):2348–2360
Zadeh MM, Ranji N, Motamed N (2015) Deregulation of miR-21 and miR-155 and their putative targets after silibinin treatment in T47D breast cancer cells. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 18(12):1209–1214
Zadeh MM, Motamed N, Ranji N, Majidi M, Falahi F (2016) Silibinin-induced apoptosis and downregulation of microRNA-21 and microRNA-155 in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Breast Cancer 19(1):45–52
Zhu S, Wu H, Wu F, Nie D, Sheng S, Mo YY (2008) MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and metastasis. Cell Res 18(3):350–359
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our thanks to Prof. Elaheh Elahi for providing psiCHECK™-2 vector, Dr. Ehsan Arefian, for providing dual-luciferase activity reporter assay kit, Mr Babak Saffari, PhD student for constructing psiCheck-2/PTEN-3′UTR and psiCheck-2/Bcl2-3′UTR vectors, Miss Mahfam Shariati, MSc student for vector extraction and Miss Mehraban Mirrahimi, MSc student for bacterial culture, in Tehran University which help us after manuscript revision.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. The authors greatly acknowledge the financial supports of Science and Technology Park, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jahanafrooz, Z., Motamed, N. & Bakhshandeh, B. Effects of miR-21 downregulation and silibinin treatment in breast cancer cell lines. Cytotechnology 69, 667–680 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-017-0076-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-017-0076-5