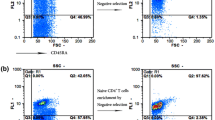
Abstract
Study of the non-coding RNA roles in the regulation of adaptive immune responses through T cells could be the basis of novel therapeutic applications. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of short non-coding RNAs that control the cell’s functions and destination. To investigate the role of miRNAs in T cell activation, herein the expressions of miR-17-92 cluster and its paralogs were studied in naïve CD4+T cells that were activated by anti-CD2, -CD3, -CD28 microbeads and induced with or without IL-2. Proliferation and apoptosis rate of the cultured cells were determined by BrdU incorporation assay (ELISA) and propidium iodide staining, respectively. In continuation the expressions of eight miRNAs of the mentioned clusters were analyzed quantitatively. In addition their potential targets were predicted using multiple algorithms; as a confirmation, the transcription of PIK3R3 (a putative target of modulated miRNAs) was evaluated. Stimulation index (SI) of activated cells was decreased on day 6; whereas, the IL-2 induced cells showed increase in SI in the assay time. Evaluation of eight members of the aforementioned cluster showed upregulation of miR-92a-2* (~15 times) in IL-2 un-induced (activated) cells relative to the IL-2 induced cells. In silico investigations revealed that the suggested miRNAs targeted genes that were involved in cell proliferation, survival, and apoptosis. Transcriptional analysis of PIK3R3 illustrated decrease in activated cells relative to IL-2 induced cells. According to our findings, it seems that multiple members of miR-17-92 families in activated CD4+T cells inhibited negative regulators of IL-2 such as DUSP, PTPN, and SOCS families after IL-2 induction. According to our findings, it seems that multiple genes of cell proliferation-related families such as MAPK, E2F, AKT, STAT, and JAK as well as PIK3R3 are inhibited by miR-17-92 cluster in activated cells. As FASL is a putative target of over-expressed miRNAs in activated cell, antigen-induced cell death (AICD) might be occurred in FASL-independent manner. Altogether this study suggested that clonal expansion through IL-2 signaling pathway does not depend on the members of miR-17-92 family; while, it appears that AICD in activated CD4+T cells without IL-2 induction is affected by these miRNA clusters.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xue Q, Guo ZY, Li W, Wen WH, Meng YL, Jia LT, Wang J, Yao LB, Jin BQ, Wang T, Yang AG (2011) Human activated CD4(+) T lymphocytes increase IL-2 expression by downregulating microRNA-181c. Mol Immunol 48:592–599. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2010.10.021
Michel F, Attal-Bonnefoy G, Mangino G, Mise-Omata S, Acuto O (2001) CD28 as a molecular amplifier extending TCR ligation and signaling capabilities. Immunity 15:935–945. doi:S1074-7613(01)00244-8
Liwski RS, Chase JC, Baldridge WH, Sadek I, Rowden G, West KA (2006) Prolonged costimulation is required for naive T cell activation. Immunol Lett 106:135–143. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2006.05.003
Garcon F, Patton DT, Emery JL, Hirsch E, Rottapel R, Sasaki T, Okkenhaug K (2008) CD28 provides T-cell costimulation and enhances PI3K activity at the immune synapse independently of its capacity to interact with the p85/p110 heterodimer. Blood 111:1464–1471. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-08-108050
Eder AM, Dominguez L, Franke TF, Ashwell JD (1998) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulation of T cell receptor-mediated interleukin-2 gene expression in normal T cells. J Biol Chem 273:28025–28031
Curtale G, Citarella F, Carissimi C, Goldoni M, Carucci N, Fulci V, Franceschini D, Meloni F, Barnaba V, Macino G (2010) An emerging player in the adaptive immune response: microRNA-146a is a modulator of IL-2 expression and activation-induced cell death in T lymphocytes. Blood 115:265–273. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-06-225987
Fung MM, Rohwer F, McGuire KL (2003) IL-2 activation of a PI3K-dependent STAT3 serine phosphorylation pathway in primary human T cells. Cell Signal 15:625–636. doi:S0898656803000032
Jaleco S, Swainson L, Dardalhon V, Burjanadze M, Kinet S, Taylor N (2003) Homeostasis of naive and memory CD4+T cells: IL-2 and IL-7 differentially regulate the balance between proliferation and Fas-mediated apoptosis. J Immunol 171:61–68
Zhang S, Zhang H, Zhao J (2009) The role of CD4 T cell help for CD8 CTL activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 384:405–408. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.04.134
Lai YP, Lin CC, Liao WJ, Tang CY, Chen SC (2009) CD4+T cell-derived IL-2 signals during early priming advances primary CD8+T cell responses. PLoS ONE 4:e7766. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007766
Sereti I, Anthony KB, Martinez-Wilson H, Lempicki R, Adelsberger J, Metcalf JA, Hallahan CW, Follmann D, Davey RT, Kovacs JA, Lane HC (2004) IL-2-induced CD4+T-cell expansion in HIV-infected patients is associated with long-term decreases in T-cell proliferation. Blood 104:775–780. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-12-4355
Yang JC, Sherry RM, Steinberg SM, Topalian SL, Schwartzentruber DJ, Hwu P, Seipp CA, Rogers-Freezer L, Morton KE, White DE, Liewehr DJ, Merino MJ, Rosenberg SA (2003) Randomized study of high-dose and low-dose interleukin-2 in patients with metastatic renal cancer. J Clin Oncol 21:3127–3132. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.02.122
Markowitz N, Bebchuk JD, Abrams DI (2003) Nadir CD4+T cell count predicts response to subcutaneous recombinant interleukin-2. Clin Infect Dis 37:e115–e120. doi:10.1086/378293
Lodish HF, Zhou B, Liu G, Chen CZ (2008) Micromanagement of the immune system by microRNAs. Nat Rev Immunol 8:120–130. doi:10.1038/nri2252
Kanellopoulou C, Monticelli S (2008) A role for microRNAs in the development of the immune system and in the pathogenesis of cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 18:79–88. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.01.002
Sonkoly E, Stahle M, Pivarcsi A (2008) MicroRNAs and immunity: novel players in the regulation of normal immune function and inflammation. Semin Cancer Biol 18:131–140. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.01.005
Lindsay MA (2008) MicroRNAs and the immune response. Trends Immunol 29:343–351. doi:10.1016/j.it.2008.04.004
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:259–269. doi:10.1038/nrc1840
Bakhshandeh B, Hafizi M, Ghaemi N, Soleimani M (2012) Down-regulation of miRNA-221 triggers osteogenic differentiation in human stem cells. Biotechnol Lett 34:1579–1587. doi:10.1007/s10529-012-0934-3
Sasaki K, Kohanbash G, Hoji A, Ueda R, McDonald HA, Reinhart TA, Martinson J, Lotze MT, Marincola FM, Wang E, Fujita M, Okada H (2010) miR-17-92 expression in differentiated T cells—implications for cancer immunotherapy. J Transl Med 8:17. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-8-17
Cho WC (2007) OncomiRs: the discovery and progress of microRNAs in cancers. Mol Cancer 6:60. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-6-60
Diosdado B, van de Wiel MA, Terhaar Sive Droste JS, Mongera S, Postma C, Meijerink WJ, Carvalho B, Meijer GA (2009) MiR-17-92 cluster is associated with 13q gain and c-myc expression during colorectal adenoma to adenocarcinoma progression. Br J Cancer 101:707–714. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605037
Olive V, Jiang I, He L (2010) mir-17-92, a cluster of miRNAs in the midst of the cancer network. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42:1348–1354. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2010.03.004
Shu L, Yin W, Zhuang H, Hua Z (2006) Comparison of gene expression profiles in mouse primary T cells under normal and prolonged activation. Blood Cells Mol Dis 37:64–75. doi:10.1016/j.bcmd.2006.04.002
Rajewsky N (2006) microRNA target predictions in animals. Nat Genet 38(Suppl):S8–S13. doi:10.1038/ng1798
Bakhshandeh B, Soleimani M, Hafizi M, Paylakhi SH, Ghaemi N (2012) microRNA signature associated with osteogenic lineage commitment. Mol Biol Rep 39:7569–7581. doi:10.1007/s11033-012-1591-2
Bakhshandeh B, Soleimani M, Paylakhi SH, Ghaemi N (2012) A microRNA signature associated with chondrogenic lineage commitment. J Genet 91:171–182
Chang X, Liu F, Wang X, Lin A, Zhao H, Su B (2011) The kinases MEKK2 and MEKK3 regulate transforming growth factor-beta-mediated helper T cell differentiation. Immunity 34:201–212. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2011.01.017
Kane LP, Lin J, Weiss A (2002) It’s all Rel-ative: NF-kappaB and CD28 costimulation of T-cell activation. Trends Immunol 23:413–420
Juntilla MM, Wofford JA, Birnbaum MJ, Rathmell JC, Koretzky GA (2007) Akt1 and Akt2 are required for alphabeta thymocyte survival and differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:12105–12110. doi:10.1073/pnas.0705285104
Oda K, Asao H, Higuchi M, Tanaka N, Moffatt S, Nakamura M, Tabayashi K, Sugamura K (1997) Induction of IL-1 beta-converting enzyme-independent apoptosis by IL-2 in human T cell lines. Int Immunol 9:1303–1310
Kovanen PE, Young L, Al-Shami A, Rovella V, Pise-Masison CA, Radonovich MF, Powell J, Fu J, Brady JN, Munson PJ, Leonard WJ (2005) Global analysis of IL-2 target genes: identification of chromosomal clusters of expressed genes. Int Immunol 17:1009–1021. doi:10.1093/intimm/dxh283
Liao W, Lin JX, Leonard WJ (2011) IL-2 family cytokines: new insights into the complex roles of IL-2 as a broad regulator of T helper cell differentiation. Curr Opin Immunol 23:598–604. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2011.08.003
Crispin JC, Apostolidis SA, Finnell MI, Tsokos GC (2011) Induction of PP2A Bbeta, a regulator of IL-2 deprivation-induced T-cell apoptosis, is deficient in systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:12443–12448. doi:10.1073/pnas.1103915108
Hieronymus T, Blank N, Gruenke M, Winkler S, Haas JP, Kalden JR, Lorenz HM (2000) CD 95-independent mechanisms of IL-2 deprivation-induced apoptosis in activated human lymphocytes. Cell Death Differ 7:538–547. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400684
Devireddy LR, Green MR (2003) Transcriptional program of apoptosis induction following interleukin 2 deprivation: identification of RC3, a calcium/calmodulin binding protein, as a novel proapoptotic factor. Mol Cell Biol 23:4532–4541
Fleischer A, Duhamel M, Lopez-Fernandez LA, Munoz M, Rebollo MP, Alvarez-Franco F, Rebollo A (2007) Cascade of transcriptional induction and repression during IL-2 deprivation-induced apoptosis. Immunol Lett 112:9–29. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2007.06.004
Razumilava N, Bronk SF, Smoot RL, Fingas CD, Werneburg NW, Roberts LR, Mott JL (2012) miR-25 targets TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) death receptor-4 and promotes apoptosis resistance in cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 55:465–475. doi:10.1002/hep.24698
Petrocca F, Vecchione A, Croce CM (2008) Emerging role of miR-106b-25/miR-17-92 clusters in the control of transforming growth factor beta signaling. Cancer Res 68:8191–8194. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1768
Cloonan N, Brown MK, Steptoe AL, Wani S, Chan WL, Forrest AR, Kolle G, Gabrielli B, Grimmond SM (2008) The miR-17-5p microRNA is a key regulator of the G1/S phase cell cycle transition. Genome Biol 9:R127. doi:10.1186/gb-2008-9-8-r127
Jiang S, Li C, Olive V, Lykken E, Feng F, Sevilla J, Wan Y, He L, Li QJ (2011) Molecular dissection of the miR-17-92 cluster’s critical dual roles in promoting Th1 responses and preventing inducible Treg differentiation. Blood 118:5487–5497. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-05-355644
O’Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT (2005) c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature 435:839–843. doi:10.1038/nature03677
Woods K, Thomson JM, Hammond SM (2007) Direct regulation of an oncogenic micro-RNA cluster by E2F transcription factors. J Biol Chem 282:2130–2134. doi:10.1074/jbc.C600252200
Yu XF, Zou J, Bao ZJ, Dong J (2011) miR-93 suppresses proliferation and colony formation of human colon cancer stem cells. World J Gastroenterol 17:4711–4717. doi:10.3748/wjg.v17.i42.4711
Boyerinas B, Park SM, Hau A, Murmann AE, Peter ME (2010) The role of let-7 in cell differentiation and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 17:F19–F36. doi:10.1677/ERC-09-0184
Fang L, Zhang HB, Li H, Fu Y, Yang GS (2012) miR-548c-5p inhibits proliferation and migration and promotes apoptosis in CD90(+) HepG2 cells. Radiol Oncol 46:233–241. doi:10.2478/v10019-012-0025-z
Beadling C, Smith KA (2002) DNA array analysis of interleukin-2-regulated immediate/early genes. Med Immunol 1:2
Deane JA, Trifilo MJ, Yballe CM, Choi S, Lane TE, Fruman DA (2004) Enhanced T cell proliferation in mice lacking the p85beta subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. J Immunol 172:6615–6625
Kok K, Geering B, Vanhaesebroeck B (2009) Regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase expression in health and disease. Trends Biochem Sci 34:115–127. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2009.01.003
Fletcher J, Starr R (2005) The role of suppressors of cytokine signaling in thymopoiesis and T cell activation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:1774–1786. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2005.04.005
Sporri B, Kovanen PE, Sasaki A, Yoshimura A, Leonard WJ (2001) JAB/SOCS1/SSI-1 is an interleukin-2-induced inhibitor of IL-2 signaling. Blood 97:221–226
Xiao C, Rajewsky K (2009) microRNA control in the immune system: basic principles. Cell 136:26–36. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.027
Acknowledgments
Hereby, we thank Iran national science foundation for providing the project costs. Also, we thank College of cell bank of Pasteur Institute of Iran. We appreciate the cooperation and advice of Dr. Mehdi Mahdavi, Arash Zaminy, Dr. Kambiz Arasteh, Dr. Hana Hanaee Ahwazi, Rohollah Nakhaee Sistani, Mohammad Dezfoulinegad, and Dr. Ehsan Mostafavi.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranji, N., Sadeghizadeh, M., Shokrgozar, M.A. et al. miR-17-92 cluster: an apoptosis inducer or proliferation enhancer. Mol Cell Biochem 380, 229–238 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1678-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1678-7