Abstract
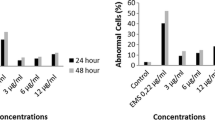
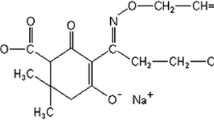
The organophosphorous insecticide acephate was tested for its ability to induce in vitro cytogenetic effect in human peripheral lymphocytes by using the chromosomal aberrations (CAs), sister chromatid exchange (SCE) and micronuclei (MN) assay. The level of nuclear DNA damage of acephate was evaluated by using the comet assay. Concentrations of 12.5, 25, 50, 100 and 200 μg mL−1 of acephate were used. All concentrations of acephate induced significant increase in the frequency of CAs and in the formation of MN dose dependently (r = 0.92 at 24 h, r = 0.95 at 48 h for CAs, r = 0.87 for MN). A significant increase was observed in induction of SCE at 50, 100 and 200 μg mL−1 concentrations during 24 h treatment and at all concentrations (except 12.5 μg mL−1) during 48 h treatment period in a dose-dependent manner (r = 0.84 at 24 h, r = 0.88 at 48 h). Acephate did not affect the replicative index and cytokinesis-block proliferation index (CBPI). However, it significantly decreased the mitotic index at all three highest concentrations (50, 100, 200 μg mL−1) for 24 h treatment and at all concentrations (except 12.5 μg mL−1) for 48 h treatment, dose-dependently (r = 0.94 at 24 h, r = 0.92 at 48 h). A significant increase in mean comet tail length was observed at 100 and 200 μg mL−1 concentrations compared with negative control in a concentration-dependent manner (r = 0.94). The mean comet tail intensity was significantly increased at only 200 μg mL−1 concentration. The present results indicate that acephate is a clastogenic, cytotoxic agent and it causes DNA damage at high concentrations in human lymphocytes in culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando M, Wakamatsu K (1982) Inhibitory effect of acephate (N-acetyl O, S-dimethyl thiophospamide) on serum cholinesterase. J Toxicol Sci 7:185–192
Behera BC, Bhunya SP (1989) Studies on the genotoxicity of asataf (acephate) an organophosphate insecticide, in a mammalian in vivo system. Mutat Res 223:287–293. doi:10.1016/0165-1218(89)90121-3
Breau AP, Mitchell WM, Swinson J, Field L (1985) Mutagenetic and cell transformation activities of representative phophorothiate esters in vitro. J Toxicol Environ Health 16:403–413
Carver JH, Bootman J, Cimino MC, Esber HJ, Kirby P, Kirkhart B, Wong ZA, MacGregor JA (1985) Genotoxic potential of acephate technical: in vitro and in vivo effects. Toxicology 35:125–142. doi:10.1016/0300-483X(85)90027-7
Çelik M, Ünal F, Yüzbaşıoğlu D, Ergün MA, Arslan O, Kasap R (2004) In vitro effect of karathane LC (dinocap) on human lymphocytes. Mutagenesis 20:101–104. doi:10.1093/mutage/gei013
Chantelli-Forti G, Paolini M, Hrelia P (1993) Multiple end point procedure to evaluate risk from pesticides. Environ Health Perspect 101:15–20. doi:10.2307/3431693
Chaudhuri K, Selvaraj S, Pal AK (1999) Studies on the genotoxicity of endosulfan in bacterial systems. Mutat Res 439:63–67
Chen WL, Sheets JJ, Nolan RJ, Mattsson JL (1999) Human red blood cell acetyl cholinesterase inhibition as the appropriate and conservative surrogate endpoint for establishing chloropyrifos reference concentration. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 29:15–22. doi:10.1006/rtph.1998.1256
Das PG, Shaik AP, Jamil K (2006) Estimation of apoptosis and necrosis caused by pesticides invVitro on human lymphocytes using DNA diffusion assay. Drug Chem Toxicol 29:147–156. doi:10.1080/01480540600561387
Donaldson D, Kiely T, Grube A (2002) Pesticide industry sales and usage: 1998 and 1999 market estimates. USEPA, Washington, DC
Epel D (1963) The effects of carbon monoxide inhibition of ATP level and the date of mitosis in sea urching egg. J Cell Biol 17:315–319. doi:10.1083/jcb.17.2.315
Eto M, Ohkawa H (1970) Alkylation reaction of organophosphorus pesticides: its chemical and biochemical significance. In: O’Brien RD, Yamamoto I (eds) Biochemical toxicology of insecticides. Academic Press, New York Inc., p p 93
Garrett NE, Stack HF, Waters MD (1986) Evaluation of the genetic activity profiles of 65 pesticides. Mutat Res 168:301–325
Hidalgo A, Gonzalez-Reyes JA, Navas P, Garcia-Herdugo G (1989) Abnormal mitosis and growth inhibition in allium cepa roots induced by propham and chlorpropham. Cytobios 57:7–14
Hour TC, Chin L, Lin JK (1998) Comparative investigation on the mutagenicities of organophosphate, phthalimide, pyrethroid and carbamate insecticides by the ames and lactam tests. Mutagenesis 13:157–166. doi:10.1093/mutage/13.2.157
Jain AK, Andsorbhoy RK (1988) Cytogenetical studies on the effects of some chlorinated pesticides. III. Concluding remarks. Cytologia (Tokyo) 53:427–436
Jena GB, Bhunya SP (1994) Mutagenicity of an organophosphate insecticide acephate-an in vivo study in chicks. Mutagenesis 9:319–324. doi:10.1093/mutage/9.4.319
Jones DCL, Simmons VF, Mortelman’s KE, Mitchell AD, Evans EL, Jones MM, Riccio ES, Robinson DE, Kirkland BA (1984) In vitro and in vivo Mutagenicity Studies of Environmental Chemicals, US EPA-600/1-84-003, Office of Research and Development, Health effects Research Laboratory, Research Triangle Park NC NTIS Report No. PB84-138973
Karabay NU, Oğuz MG (2005) Cytogenetic and genotoxic effects of the insecticides, imidacloprid and methamidophos. Genet Mol Res 4(4):653–662
Lin MF, Wu CL, Wang TC (1987) Pesticide clastogenicity in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mutat Res 188:241–250. doi:10.1016/0165-1218(87)90095-4
Liou SH, Chen YH, Loh CH, Yang T, Wu TN, Chen CJ, Hsieh LL (2002) The association between frequencies of mitomycin C-induced sister chromatid exchange and cancer risk in arseniasis. Toxicol Lett 129:237–243. doi:10.1016/S0378-4274(02)00017-6
Mahajna M, Quistad BG, Casida JE (1997) Acephate insecticide toxicity: safety conferred by inhibition of the bioactivating carboxyamidase by the metabolite methamidophos. Chem Res Toxicol 10:64–69. doi:10.1021/tx9601420
Palus J, Rydzynski K, Dziubaltowska E, Wyszynska K, Natarajan AT, Nilsson R (2003) Genotoxic effects of occupational exposure to lead and cadmium. Mutat Res 540:19–28
Poovala VS, Kanji VK, Tachikawa H, Salahudeen AK (1998) Role of oxidant stress and antioxidant protection in acephate ınduced renal tubular cytotoxicty. Toxicol Sci 46:403–409
Rahman MF, Mahboob M, Danadevi K, Banu BS, Grover P (2002) Assessment of genotoxic effects of chloropyriphos and acephate by the comet assay in mice leucocytes. Mutat Res 516:139–147
Rixian L, Huasheng H, Xinhong W, Keijian W, Chunguang W (2005) The genotoxic effects of benzo[a]pyrene and methamidophos on black porgy evaluated by comet assay. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 23(4):455–460
Saleha BB, Danadevi K, Rahman MF, Ahuja YR, Kaiser J (2001) Genotoxic effect of monocrotophos to sentinel species using comet assay. Food Chem Toxicol 39:361–366. doi:10.1016/S0278-6915(00)00141-1
Simmon VF, Poole DC, Mitchell AD, Robinson DE (1978) In vitro Microbiological Mutagenicity and unscheduled DNA Synthesis Studies of 18 Pesticides, Final report SRI Project LSU-3493-NS, Contract No. 68-01-2458, US Environmental Protection Agency, p 156
Singh AK (1984) Improved analysis of acephate and methamidophos in biological samples by selective ion monitoring gas chromotography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr 301:465–469. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(01)89221-9
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low level of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 17:184–187. doi:10.1016/0014-4827(88)90265-0
Speit G, Houpter S (1985) On the mechanism of differential Giemsa staining of bromodeoxyuridine substitute chromosomes. II. Differences between the demonstration of sister chromatid differentiation and replication patterns. Hum Genet 70:126–129. doi:10.1007/BF00273070
Surrales J, Xamena N, Creus A, Catalan J, Norppa H, Marcos R (1995) Induction of micronuclei by five pyrethroid insecticides in whole blood and isolated human lymphocytes cultures. Mutat Res 341:169–184. doi:10.1016/0165-1218(95)90007-1
Tomlin CDS (ed) (2003) The pesticide manual, 13th edn. BCPC, Alton
Van’t Hof J (1968) The action of IAA and kinetin on the mitotic cycle of proliferative and stationary phase excised root meristem. Exp Cell Res 51:167–176. doi:10.1016/0014-4827(68)90167-5
Waters MD, Sandhu SS, Simmon VF, Mortelmans KE, Mitchell AD, Jorgenson TA, Jones DCL, Valencia R, Garrett NE (1982) Study of pesticide genotoxicity. In: Fleck RA, Hollaender A (eds) Genetic toxicology—an agricultural perspective. Plenum Press, New York, pp 275–326
Wild D (1975) Mutagenicity studies on organophosphorus insecticides. Mutat Res 32:133–150
Wildemauve C, Lontie JP, Schoofs L, Van Lavebeke N (1983) The mutagenicity in procaryotes of insecticides, acaricides and nematicides. Residue Rev 89:129–178
Yılmaz S, Aksoy H, Ünal F, Çelik M, Yüzbaşıoğlu D (2008) Genotoxic action of fungicide conan 5FL (hexaconazole) on mammalian cells in vivo and in vitro. Russ J Genet 44(3):273–278
Yüzbaşıoğlu D, Çelik M, Yılmaz S, Ünal F, Aksoy H (2006) Clastogenicity of the fungicide afugan in cultured human lymphocytes. Mutat Res 604:53–59
Yüzbaşıoğlu D, Ünal F, Yılmaz S, Aksoy H, Çelik M (2008) Genotoxicity testing of fluconazole in vivo and in vitro. Mutat Res 649:155–160
Zakharov AF, Egolina NA (1972) Differential spiralization along mammalian mitotic chromosomes. Part I. BudRrevealed differentiation in Chinese hamster chromosomes. Chromosoma 38:341–355. doi:10.1007/BF00320156
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by Gazi University Research Projects under grant no: FEF 05/2006-23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özkan, D., Yüzbaşıoğlu, D., Ünal, F. et al. Evaluation of the cytogenetic damage induced by the organophosphorous insecticide acephate. Cytotechnology 59, 73–80 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-009-9195-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-009-9195-y