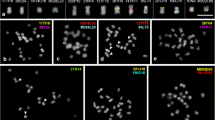
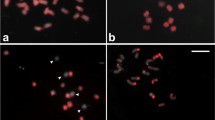
Abstract
Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) is an annual legume grown in tropical and subtropical regions, which is economically relevant due to high protein content in dried beans, green pods, and leaves. In this work, a comparative cytogenetic study between V. unguiculata and Phaseolus vulgaris (common bean) was conducted using BAC-FISH. Sequences previously mapped in P. vulgaris chromosomes (Pv) were used as probes in V. unguiculata chromosomes (Vu), contributing to the analysis of macrosynteny between both legumes. Thirty-seven clones from P. vulgaris ‘BAT93’ BAC library, corresponding to its 11 linkage groups, were hybridized in situ. Several chromosomal rearrangements were identified, such as translocations (between BACs from Pv1 and Pv8; Pv2 and Pv3; as well as Pv2 and Pv11), duplications (BAC from Pv3), as well as paracentric and pericentric inversions (BACs from Pv3, and Pv4, respectively). Two BACs (from Pv2 and Pv7), which hybridized at terminal regions in almost all P. vulgaris chromosomes, showed single-copy signal in Vu. Additionally, 17 BACs showed no signal in V. unguiculata chromosomes. The present results demonstrate the feasibility of using BAC libraries in comparative chromosomal mapping and karyotype evolution studies between Phaseolus and Vigna species, and revealed several macrosynteny and collinearity breaks among both legumes.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAC:
-
Bacterial artificial chromosome
- CABMV:
-
Cowpea aphid born mosaic virus
- CPSMV:
-
Cowpea severe mosaic virus
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- FISH:
-
Fluorescent in situ hybridization
- LG:
-
Linkage group
- Mya:
-
Million years ago
- rDNA:
-
Ribosomal DNA
- SSC:
-
Saline-sodium citrate
References
Almeida CCS, Pedrosa-Harand A (2013) High macro-collinearity between lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.) and the common bean (P. vulgaris L.) as revealed by comparative cytogenetic mapping. Theor Appl Genet 126:1909–1916
Amarillo FIE, Bass HW (2011) A transgenomic cytogenetic sorghum (Sorghum propinquum) bacterial artificial chromosome fluorescence in situ hybridization Map of maize (Zea mays L.) pachytene chromosome 9, evidence for regions of genome hyperexpansion. Genetics 177:1509–1526
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:208–218
Bonifácio EM, Fonsêca A, Almeida C, Santos KGB, Pedrosa-Harand A (2012) Comparative cytogenetic mapping between the lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.) and the common bean (P. vulgaris L.). Theor Appl Genet 124:1513–1520
Bordat A, Savois V, Nicolas M, Salse J, Chauveau A, Bourgeois M et al (2011) Translational genomics in legumes allowed placing in silico 5460 unigenes on the pea functional map and identified candidate genes in Pisum sativum L. G3 1: 93-103. y of Pernambuco
Bortoleti KCA, Benko-Iseppon AM, Melo NF, Brasileiro-Vidal AC (2012) Chromatin differentiation between Vigna radiata (L.) R. Wilczek and V. unguiculata (L.) Walp. (Fabaceae). Plant Syst Evol 298:689–693
Boutin SR, Young ND, Olson TC, Yu Z-H, Shoemaker RC, Vallejos CE (1995) Genome conservation among three legume genera detected with DNA markers. Genome 38:928–937
Carvalho CR, Saraiva LS (1993) An air drying technique for maize chromosomes without enzymatic maceration. Biotech Histochem 68:142–145
Choi H-K, Mun J-H, Kim D-J et al (2004) Estimating genome conservation between crop and model legume species. Agric Sci 101:15289–15294
Choi HW, Kim M-Y, Lee S-H, Sultana S, Bang J-W (2013) Molecular cytogenetic analysis of the Vigna species distributed in Korea. Genes Genom 35:257–264
David P, Chen NWG, Pedrosa-Harand A et al (2009) A nomadic subtelomeric disease resistance gene cluster in common bean. Plant Physiol 151:1048–1065
Delgado-Salinas A, Bibler R, Lavin M (2006) Phylogeny of the genus Phaseolus (Leguminosae): a recent diversification in an ancient landscape. Syst Bot 31:779–791
Delgado-Salinas A, Thulin M, Pasquet R, Weeden N, Lavin M (2011) Vigna (Leguminosae) sensu lato: the names and identities of the American segregate genera. Am J Bot 98:1694–1715
Figueroa DM, Davis JD, Strobel C et al (2011) The selection and Use of sorghum (sorghum propinquum) bacterial artificial chromosomes as cytogenetic FISH probes for maize (Zea mays L.). J Biomed Biotechnol 1:16
Findley SD, Cannon S, Varala K (2010) A fluorescence in situ hybridization system for karyotyping soybean. Genet 185:727–744
Fonsêca AFA (2010) Evolução cariotípica no gênero Phaseolus L.: mapeamento comparativo entre P. microcarpus Mart. e o feijão comum (P. vulgaris L.), MSc Thesis, Federal University of Pernambuco
Fonsêca AFA, Pedrosa-Harand A (2013) Karyotype stability in the genus Phaseolus evidenced by the comparative mapping of the wild species Phaseolus microcarpus. Genome 56:335–343
Fonsêca AFA, Ferreira J, Santos TRB et al (2010) Cytogenetic map of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Chromos Res 18:487–502
Freyre R, Skroch PW, Geffroy V et al (1998) Towards an integrated linkage map of common bean: 4. Development of a core linkage map and alignment of RFLP maps. Theor Appl Genet 97:847–856
Galasso I, Schmidt T, Pignone D, Heslop-Harrison JS (1995) The molecular cytogenetics of Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp: the physical organization and characterization of 18S-5,8S-25S rRNA genes, 5S rRNA genes, telomere-like sequences, and a family of centromeric repetitive DNA sequences. Theor Appl Genet 91:928–935
Guerra M, Kenton A, Bennett MD (1996) RDNA sites in mitotic and polytene chromosomes of Vigna unguiculata (L.) walp and Phaseolus coccineus L. Revealed by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Ann Bot 78:157–161
Hay AS, Pieper B, Cooke E et al (2014) Cardamine hirsuta: a versatile genetic system for comparative studies. Plant J 78:1–15
Heslop-Harrison JS, Schwarzacher T (2011) Organisation of the plant genome in chromosomes. Plant J 66:18–33
Heslop-Harrison JS, Schwazarcher T, Anamthawat-Jónsson K, Leitch AR, Shi M (1991) In situ hybridization with automated chromosome denaturation. Technique 3:109–115
Heslop-Harrison JS, Harrison GE, Leitch IJ (1992) Reprobing of DNA: DNA in situ hybridization preparations. Trends Genet 8:372–373
Hougaard BK, Madsen LH, Sandal N et al (2008) Legume anchor markers link syntenic regions between Phaseolus vulgaris, Lotus japonicus, Medicago truncatula and Arachis. Genetics 179:2299–2312
Huynh BL, Close TJ, Roberts PA et al (2013) Gene pools and the genetic architecture of domesticated cowpea. Plant Genome 6:2
Iwata A, Greenland CM, Jackson SA (2013) Cytogenetics of legumes in the phaseoloid clade. Plant Genome 6:3
Kang YJ, Kim SK, Kim MY et al (2014) Genome sequence of mungbean and insights into evolution within Vigna species. Nature 5:5443
Kido EA, Barbosa PK, Ferreira Neto JCR et al (2011) Identification of plant protein kinases in response to abiotic and biotic stresses using SuperSAGE. Curr Protein Pept Sci 12:643–656
Koumbaris GL, Bass HW (2003) A new single-locus cytogenetic mapping system for maize (Zea mays L.): overcoming FISH detection limits with marker-selected sorghum (S. propinquum L.) BAC clones. Plant J 35:647–659
Lavin M, Herendeen PS, Wojciechowski MF (2005) Evolutionary rates analysis of Leguminosae implicates a rapid diversification of lineages during the Tertiary. Syst Biol 54:575–594
Lisch D (2013) How important are transposons for plant evolution? Genetics 14:49–61
Lou Q, Iovene M, Spooner DM, Buell CR, Jiang J (2010) Evolution of chromosome 6 of Solanum species revealed by comparative fluorescence in situ hybridization mapping. Chromosoma 119:435–442
Lucas MR, Diop N-N, Wanamaker S, Ehlers JD, Roberts PA, Close TJ (2011) Cowpea–soybean synteny clarified through an improved genetic map. Plant Genome 4:218–225
Lysak MA, Mandáková T (2010) Lacombe b reciprocal and multi-species chromosome BAC painting in crucifers (brassicaceae). Cytogenet Genome Res 129:184–189
Lysak MA, Berr A, Pecinka A, Schmidt R, Mcbreen K, Schubert I (2006) Mechanisms of chromosome number reduction in Arabidopsis thaliana and related Brassicaceae species. Plant Biol 103:13
Ma L, Vu GTH, Schubert V et al (2010) Synteny between brachypodium distachyon and Hordeum vulgare as revealed by FISH. Chromosome Res 18:841–850
Mandáková T, Lysak MA (2008) Chromosomal phylogeny and karyotype evolution in x = 7 crucifer species (brassicaceae). Plant Cell 20:2559–2570
Maréchal R, Mascherpa JM, Stainier F (1978) Étude taxonomique d’un groupe complexe d’espèces de genres Phaseolus et Vigna (Papilionaceae) sur la base de donneés morphologiques et polliniques, traiteés par l’analyse informatique. Boissiera 28:1–273
McClean PE, Mamidi S, Mcconnell M, Chikara S, Lee R (2010) Synteny mapping between common bean and soybean reveals extensive blocks of shared loci. Genomics 11:184
McConnell M, Mamidi S, Lee R et al (2010) Syntenic relationships among legumes revealed using a gene-based genetic linkage map of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor Appl Genet 121:1103–1116
Mendes S, Moraes AP, Mirkov TE, Pedrosa-Harand A (2011) Chromosome homeologies and high variation in heterochromatin distribution between Citrus L. and Poncirus Raf. as evidenced by comparative cytogenetic mapping. Chromosome Res 19:521–530
Menéndez CM, Hall AE, Gepts P (1997) A genetic linkage map of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) developed from a cross between two inbred domesticated lines. Theor Appl Genet 95:1210–1217
Muchero W, Diop NN, Bhat PR et al (2009) A consensus genetic map of cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp] and synteny based on EST-derived SNPs. Agric Sci 106:43
Murray J, Larsen J, Michaels TE, Schaafsma A, Vallejos CE, Pauls KP (2002) Identification of putative genes in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) genomic (Bng) RFLP clones and their conversion to STSs. Genome 45:1013–1024
Ouédraogo JT, Gowda BS, Jean M, Close TJ, Ehlers JD (2002) An improved genetic linkage map for cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) combining AFLP, RFLP, RAPD, biochemical markers, and biological resistance traits. Genome 45:175–188
Pedrosa A, Sandal N, Stougaard J, Schweizer D, Bachmair A (2002) Chromosomal map of the model legume Lotus japonicus. Genetics 161:1661–1672
Pedrosa-Harand A, Kami J, Geffroy V, Gepts P, Schweizer D (2009) Cytogenetic mapping of common bean chromosomes reveals a less compartmentalized small-genome plant species. Chromos Res 17:405–417
Ribeiro T, Santos KGB, Fonsêca AFA, Pedrosa-Harand A (2011) Isolation and characterization of a new repetitive DNA family recently amplified in the Mesoamerican gene pool of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L., Fabaceae). Genetica 139:1135–1142
Richard MMS, Chen NG, Hareau V et al (2013) The subtelomeric khipu satellite repeat from Phaseolus vulgaris: lessons learned from the genome analysis of the Andean genotype G19833. Plant Genet Genomic 4:109
Sato S, Isobe S, Tabata S (2010) Structural analyses of the genomes in legumes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:1–7
Schmutz J, Cannon SB, Schlueter J et al (2010) Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature 463:178–183
Schmutz J, McClean PE, Mamidi S et al (2014) A reference genome for common bean and genome-wide analysis of dual domestications. Nature 46:707–713
Schrire BD (2005) Tribe Phaseoleae. In: Lewis GP, Schrire B, Mackinder B, Lock M (eds) Legumes of the world. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, UK, pp 393–431
Schubert I (2007) Chromosome evolution. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:109–115
Schwarzacher T, Heslop-Harrison P (2000) Practical in situ hybridization, 1st edn. BIOS Scientific, Oxford
Shirasawa K, Bertioli DJ, Varshney RK et al (2013) Integrated consensus Map of cultivated peanut and wild relatives reveals structures of the a and B genomes of arachis and divergence of the legume genomes. DNA Res 20:173–184
Soares-Cavalcanti NM, Pandolfi V, Kido EA, Belarmino LC, Houllou-Kido LM, Benko-Iseppon AM (2011) Perfil geral de expressão associado à tolerância à salinidade e seca em feijão caupi (Vigna unguiculata). In: Trabalhos apresentados no Simpósio sobre Tolerância à Deficiência Hídrica em Plantas: Adaptando as culturas ao clima do futuro, ISSN 1678-9644, Goiânia, Embrapa Documentos. 265: 65-75.
Stefanovic S, Pfeil BE, Palmer JD, Doyle JJ (2009) Relationships among phaseoloid legumes based on sequences from eight chloroplast regions. Syst Bot 34:115–128
Szinay D, Wijnker E, Van Den Berg R, Visser RGF, de Jong H, Bai Y (2012) Chromosome evolution in Solanum traced by cross-species BAC-FISH. New Phytol 195:688–698
Vallejos CE, Sakiyama NS, Chase CD (1992) A molecular marker-based linkage map of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Genetics 131:733–740
Varshney RK, Chen W, Li Y et al (2012) Draft genome sequence of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan), an orphan legume crop of resource-poor farmers. Nat Biotechnol 30:83–89
Varshney RK, Song C, Saxena RK et al (2013) Draft genome sequence of chickpea (Cicer arietinum) provides a resource for trait improvement. Nat Biotechnol 31:240–246
Yang H, Tao Y, Zheng Z et al (2013) Draft genome sequence, and a sequence-defined genetic linkage map of the legume crop species Lupinus angustifolius L. PLoS One 8:e64799–e64799
Young ND, Bharti AK (2012) Genome-enabled insights into legume biology. Annu Rev Plant Biol 63:14.1–14.23
Young ND, Debellé F, Oldroyd GED, Geurts R, Cannon SB, Udvardi MK et al (2011) The Medicago genome provides insight into the evolution of rhizobial symbioses. Nature 480:520–524
Zwick MS, Hanson RR, Mcknight TD et al (1997) A rapid procedure for the isolation of C0t-1 DNA from plants. Genome 40:138–142
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Embrapa Meio-Norte (Teresina, Brazil) and Embrapa Arroz e Feijão (Santo Antônio de Goiás, Brazil) for supplying seeds, and also CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico), CAPES (Coordenação de Pessoal de Nível Superior) and FACEPE (Fundação de Amparo à Ciência e Tecnologia do Estado de Pernambuco) for financial support and fellowships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Jiming Jiang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasconcelos, E.V., de Andrade Fonsêca, A.F., Pedrosa-Harand, A. et al. Intra- and interchromosomal rearrangements between cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.] and common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) revealed by BAC-FISH. Chromosome Res 23, 253–266 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-014-9464-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-014-9464-2