Abstract
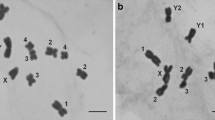
The cane toad (Bufo marinus) is one of the most notorious animal pests encountered in Australia. Members of the genus Bufo historically have been regarded as having genotypic sex determination with male homogamety/female heterogamety. Nevertheless, as with many toads, karyotypic analyses of the cane toad have so far failed to identify heteromorphics sex chromosomes. In this study, we used comparative genomic hybridization, reverse fluorescence staining, C-banding, and morphometric analyses of chromosomes to characterize sex chromosome dimorphism in B. marinus. We found that females consistently had a length dimorphism associated with a nucleolus organizer region (NOR) on one of the chromosome 7 pair. A strong signal over the longer NOR in females, and the absence of a signal in males indicated sex-specific DNA sequences. All females were heterozygous and all males homozygous, indicating a ZZ/ZW sex chromosomal system. Our study confirms the existence of sex chromosomes in this species. The ability to reliably identify genotypic sex of cane toads will be of value in monitoring and control efforts in Australia and abroad.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- NOR:
-
Nucleolus organizer region
- GSD:
-
Genotypic sex determination
- CGH:
-
Comparative genomic hybridization
- SSC:
-
Standard saline citrate
- CMA3:
-
Chromomycin A3
- dDNA:
-
Genomic deoxyribonucleic acid
- rDNA:
-
Ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid
- dUTP:
-
2′-Deoxyuridine 5′-Triphosphate
References
Baldissera FA, Batistik RF, Haddad CFB (1999) Cytotaxonomic considerations with the description of two new NOR locations for South American toads, genus Bufo (Anura: Bufonidae). Amphib-Reptil 20:413–420
Bergero R, Charlesworth D (2009) The evolution of restricted recombination in sex chromosomes. Trends Ecol Evol 24:94–102
Bogart JP (1972) Karyotypes. In: Blair WF (ed) Evolution in the genus Bufo. University of Texas Press, Austin
Born GG, Bertollo LA (2000) An XX/XY sex chromosome system in a fish species, Hoplias malabaricus, with a polymorphic NOR-bearing X chromosome. Chromosome Res 8:111–118
Boron A, Porycka K, Ito D, Abe S, Kirtiklis L (2009) Comparative molecular cytogenetic analysis of three Leuciscus species (Pisces, Cyprinidae) using chromosome banding and FISH with rDNA. Genetica 135:199–207
Charlesworth B, Langley CH, Stephan W (1986) The evolution of restricted recombination and the accumulation of repeated DNA sequences. Genetics 112:947–962
Cole CJ, Lowe CH, Wright JW (1968) Karyotypes of eight species of toads (genus Bufo) in North America. Copeia 1968:96–100
Cotton S, Wedekind C (2007) Control of introduced species using Trojan sex chromosomes. Trends Ecol Evol 22:441–443
Duellman WE, Trueb L (1994) Biology of amphibians. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, Maryland
Easteal S (1981) The history of introductions of Bufo marinus (Amphibia: Anura); a natural experiment in evolution. Biol J Linn Soc 16:93–113
Eggert C (2004) Sex determination: the amphibian models. Reprod Nutr Dev 44:539–549
Ezaz T, Quinn AE, Miura I, Sarre SD, Georges A, Marshall Graves JA (2005) The dragon lizard Pogona vitticeps has ZZ/ZW micro-sex chromosomes. Chromosome Res 13:763–776
Ezaz T, Valenzuela N, Grutzner F, Miura I, Georges A, Burke RL, Graves JA (2006) An XX/XY sex microchromosome system in a freshwater turtle, Chelodina longicollis (Testudines: Chelidae) with genetic sex determination. Chromosome Res 14:139–150
Gall JG (1968) Differential synthesis of the genes for ribosomal RNA during amphibian oogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 60:553–560
Goodpasture C, Bloom SE (1975) Visualization of nucleolar organizer regions im mammalian chromosomes using silver staining. Chromosoma 53:37–50
Green DM (1988) Cytogenetics of the New Zealand frog, Leiopelma hochstetteri; extraordinary supernumerary chromosome variation and a unique sex-chromosome system. Chromosoma 97:55–70
Gutierrez JB, Teem JL (2006) A model describing the effect of sex-reversed YY fish in an established wild population: the use of a Trojan Y chromosome to cause extinction of an introduced exotic species. J Theor Biol 241:333–341
Hayes TB (1998) Sex determination and primary sex differentiation in amphibians: genetic and developmental mechanisms. J Exp Zool 281:373–399
Hillis DM, Green DM (1990) Evolutionary changes of heterogametic sex in the phylogenetic history of amphibians. J Evol Biol 3:49–64
Kawai A, Nishida-Umehara C, Ishijima J, Tsuda Y, Ota H, Matsuda Y (2007) Different origins of bird and reptile sex chromosomes inferred from comparative mapping of chicken Z-linked genes. Cytogenet Genome Res 117:92–102
King M, Contreras N, Honeycutt RL (1990) Variation within and between nucleolar organizer regions in Australian hylid frogs (Anura) shown by 18S + 28S in-situ hybridization. Genetica 80:17–29
Loeber J, Pan FC, Pieler T (2009) Generation of transgenic frogs. Methods Mol Biol 561:65–72
Miller L, Brown DD (1969) Variation in the activity of nucleolar organizers and their ribosomal gene content. Chromosoma 28:430–444
Miura I (2007) An evolutionary witness: the frog Rana rugosa underwent change of heterogametic sex from XY male to ZW female. Sex Dev 1:323–331
Miura I, Ohtani H, Nakamura M, Ichikawa Y, Saitoh K (1998) The origin and differentiation of the heteromorphic sex chromosomes Z, W, X, and Y in the frog Rana rugosa, inferred from the sequences of a sex-linked gene, ADP/ATP translocase. Mol Biol Evol 15:1612–1619
Nakamura M (2009) Sex determination in amphibians. Semin Cell Dev Biol 20:271–282
Ogata M, Hasegawa Y, Ohtani H, Mineyama M, Miura I (2008) The ZZ/ZW sex-determining mechanism originated twice and independently during evolution of the frog, Rana rugosa. Heredity 100:92–99
Reed KM, Phillips RB (1997) Polymorphism of the nucleolus organizer region (NOR) on the putative sex chromosomes of Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus) is not sex-related. Chromosome Res 5:221–227
Schmid M (1978) Chromosome banding in Amphibia I. Constitutive heterochromatin and nucleolus organizer regions in Bufo and Hyla. Chromosoma 66:361–388
Schmid M (1980) Chromosome banding in amphibia. IV. Differentiation of GC- and AT-rich chromosome regions in Anura. Chromosoma 77:83–103
Schmid M (1982) Chromosome banding in amphibia. VII. Analysis of the Structure of NORs in Anura. Chromosoma 87:327–344
Schmid M, de Almeida CG (1988) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. XII. Restriction endonuclease banding. Chromosoma 96:283–290
Schmid M, Steinlein C (2001) Sex chromosomes, sex-linked genes, and sex determination in the vertebrate class amphibia. EXS 91:143–76
Schmid M, Steinlein C (2003) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. XXIX. The primitive XY/XX sex chromosomes of Hyla femoralis (Anura, Hylidae). Cytogenet Genome Res 101:74–79
Schmid M, Haaf T, Geile B, Sims S (1983) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. VIII. An unusual XY/XX-sex chromosome system in Gastrotheca riobambae (Anura, Hylidae). Chromosoma 88:69–82
Schmid M, Ohta S, Steinlein C, Guttenbach M (1993) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. XIX. Primitive ZW/ZZ sex chromosomes in Buergeria buergeri (Anura, Rhacophoridae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 62:238–246
Schweizer D (1976) Reverse fluorescent chromosome banding with chromomycin and DAPI. Chromosoma 58:307–324
Traut W, Sahara K, Otto TD, Marec F (1999) Molecular differentiation of sex chromosomes probed by comparative genomic hybridization. Chromosoma 108:173–180
Ueda Y, Kondoh H, Mizuno N (2005) Generation of transgenic newt Cynops pyrrhogaster for regeneration study. Genesis 41:87–98
Ullerich FH (1967) Weitere untersuchungen über chromosomen verhältnisse und DNS-gehalt bei Anuran (Amphibia). Chromosoma 8:345–368
Uno Y, Nishida C, Yoshimoto S, Ito M, Oshima Y, Yokoyama S, Nakamura M, Matsuda Y (2008) Diversity in the origins of sex chromosomes in anurans inferred from comparative mapping of sexual differentiation genes for three species of the Raninae and Xenopodinae. Chromosome Res 16:999–1011
Urban MC, Phillips BL, Skelly DK, Shine R (2007) The cane toad's (Chaunus [Bufo] marinus) increasing ability to invade Australia is revealed by a dynamically updated range model. Proc Biol Sci 274:1413–1419
Valenzuela N (2008) Sexual development and the evolution of sex determination. Sex Dev 2:64–72
Verma RS, Babu A (1995) Human chromosomes: principles and techniques. McGraw-Hill, Inc., New York
Volpe EP, Gebhardt BM (1968) Somatic chromosomes of the marine toad, Bufo marinus (Linnae). Copeia 1968:570–576
Wallace H, Badawy GM, Wallace BM (1999) Amphibian sex determination and sex reversal. Cell Mol Life Sci 55:901–909
Watson JM, Meyne J, Graves JA (1996) Ordered tandem arrangement of chromosomes in the sperm heads of monotreme mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10200–10205
Wiley JE (2003) Replication banding and FISH analysis reveal the origin of the Hyla femoralis karyotype and XY/XX sex chromosomes. Cytogenet Genome Res 101:80–83
Acknowledgments
We thank Chris Hardy from CSIRO Entomology for cane toad tissue and blood samples, Cate Browne for assistance with blood culture techniques, Ikuo Miura for discussion of preliminary results, and members of the Koopman and Graves laboratories for insightful discussions on technical aspects of the research. Finally we thank the two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments on this manuscript. This work was funded by the Invasive Animals Cooperative Research Center, the Queensland State Government, and the Australian Research Council. Peter Koopman is a Federation Fellow of the ARC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Herbert Macgregor
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 213 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abramyan, J., Ezaz, T., Graves, J.A.M. et al. Z and W sex chromosomes in the cane toad (Bufo marinus). Chromosome Res 17, 1015–1024 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-009-9095-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-009-9095-1