Abstract
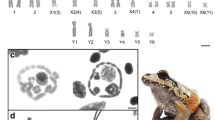
Amphibians employ genetic sex determination systems with male and female heterogamety. The ancestral state of sex determination in amphibians has been suggested to be female heterogamety; however, the origins of the sex chromosomes and the sex-determining genes are still unknown. In Xenopus laevis, chromosome 3 with a candidate for the sex- (ovary-) determining gene (DM-W) was recently identified as the W sex chromosome. This study conducted comparative genomic hybridization for X. laevis and Xenopus tropicalis and FISH mapping of eight sexual differentiation genes for X. laevis, X. tropicalis, and Rana rugosa. Three sex-linked genes of R. rugosa—AR, SF-1/Ad4BP, and Sox3—are all localized to chromosome 10 of X. tropicalis, whereas AR and SF-1/Ad4BP are mapped to chromosome 14 and Sox3 to chromosome 11 in X. laevis. These results suggest that the W sex chromosome was independently acquired in the lineage of X. laevis, and the origins of the ZW sex chromosomes are different between X. laevis and R. rugosa. Cyp17, Cyp19, Dmrt1, Sox9, and WT1 were localized to autosomes in X. laevis and R. rugosa, suggesting that these five genes probably are not candidates for the sex-determining genes in the two anuran species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abinawanto, Shimada K, Yoshida K, Saito N (1996) Effects of aromatase inhibitor on sex differentiation and levels of P450 (17alpha) and P450 arom messenger ribonucleic acid of gonads in chicken embryos. Gen Comp Endocrinol 102: 241–246.
Akatsuka N, Komatsuzaki E, Ishikawa A, Suzuki I, Yamane N, Miyata S (2005) Expression of the gonadal p450 aromatase gene of Xenopus and characterization of the 5′-flanking region of the aromatase gene. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 96: 45–50.
Aoyama S, Shibata K, Tokunaga S, Takase M, Matsui K, Nakamura M (2003) Expression of Dmrt1 protein in developing and in sex-reversed gonads of amphibians. Cytogenet Genome Res 101: 295–301.
Arakawa Y, Nishida-Umehara C, Matsuda Y, Sutou S, Suzuki H (2002) X-chromosomal localization of mammalian Y-linked genes in two XO species of the Ryukyu spiny rat. Cytogenet Genome Res 99: 303–309.
Belterman RHR, de Boer LEM (1984) A karyological study of 55 species of birds, including karyotypes of 39 species new to cytology. Genetica 65: 39–82.
Bisbee CA, Baker MA, Wilson AC, Haji-Azumi I, Fischberg M (1977) Albumin phylogeny for clawed frogs (Xenopus). Science 195: 785–787.
Chang CY, Witschi E (1956) Genic control and hormonal reversal of sex differentiation in Xenopus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 93: 140–144.
Crews D (2003) Sex determination: where environment and genetics meet. Evol Dev 5: 50–55.
Elinson RP (1983) Inheritance and expression of a sex-linked enzyme in the frog, Rana clamitans. Biochem Genet 21: 435–442.
Evans BJ, Kelley DB, Tinsley RC, Melnick DJ, Cannatella DC (2004) A mitochondrial DNA phylogeny of African clawed frogs: phylogeography and implications for polyploid evolution. Mol Phylogenet Evol 33: 197–213.
Evans BJ, Kelley DB, Melnick DJ, Cannatella DC (2005) Evolution of RAG-1 in polyploid clawed frogs. Mol Biol Evol 22: 1193–1207.
Fischer L, Catz D, Kelley D (1993) An androgen receptor mRNA isoform associated with hormone-induced cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90: 8254–8258.
Graf JD (1993) Linkage map of Xenopus laevis. In: O’Brien, S.J., ed. Genetic Maps: Locus Maps of Complex Genomes. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, pp. 4330–4331.
Guan G, Kobayashi T, Nagahama Y (2000) Sexually dimorphic expression of two types of DM (Doublesex/Mab-3)-domain genes in a teleost fish, the Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 272: 662–666.
Hayes TB (1998) Sex determination and primary sex differentiation in amphibians: genetic and developmental mechanisms. J Exp Zool 281: 373–399.
Hillis DM, Green DM (1990) Evolutionary changes of heterogametic sex in the phylogenetic history of amphibians. J Evol Biol 3: 49–64.
Honda T, Suzuki H, Itoh M (1977) An unusual sex chromosome constitution found in the Amami spinous country-rat, Tokudaia osimensis osimensis. Jpn J Genet 52: 247–249.
Iwade R, Maruo K, Okada G, Nakamura M (2008) Elevated expression of P450c17 (CYP17) during testicular formation in the frog. Gen Comp Endocrinol 155: 79–87.
Jeffreys A, Wilson V, Wood D, Simons JP, Kay RM, Williams JG (1980) Linkage of adult alpha- and beta-globin genes in X. laevis and gene duplication by tetraploidization. Cell 21: 555–564.
Kawai A, Nishida-Umehara C, Ishijima J, Tsuda Y, Ota H, Matsuda Y (2007) Different origins of bird and reptile sex chromosomes inferred from comparative mapping of chicken Z-linked genes. Cytogenet Genome Res 117: 92–102.
Kawano K, Miura I, Morohashi K, Takase M, Nakamura M (1998) Molecular cloning and expression of the SF-1/Ad4BP gene in the frog, Rana rugosa. Gene 222: 169–176.
Kawano K, Furusawa S, Matsuda H, Takase M, Nakamura M (2001) Expression of steroidogenic factor-1 in frog embryo and developing gonad. Gen Comp Endocrinol 123: 13–22.
Kettlewell JR, Raymond CS, Zarkower D (2000) Temperature-dependent expression of turtle Dmrt1 prior to sexual differentiation. Genesis 26: 174–178.
Kochan KJ, Wright DA, Schroeder LJ, Shen J, Morizot DC (2003) Genetic linkage maps of the West African clawed frog Xenopus tropicalis. Dev Dyn 226: 99–102.
Kolomiets OL, Vorontsov NN, Lyapunova EA, Mazurova TF (1991) Ultrastructure, meiotic behavior, and evolution of sex chromosomes of the genus Ellobius. Genetica 84: 179–189.
Koyano S, Ito M, Takamatsu N, Takiguchi S, Shiba T (1997) The Xenopus Sox3 gene expressed in oocytes of early stages. Gene 188: 101–107.
Kumar S, Hedges SB (1998) A molecular timescale for vertebrate evolution. Nature 392: 917–920.
Lutz LB, Cole LM, Gupta MK, Kwist KW, Auchus RJ, Hammes SR (2001) Evidence that androgens are the primary steroids produced by Xenopus laevis ovaries and may signal through the classical androgen receptor to promote oocyte maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98: 13728–13733.
Marchand O, Govoroun M, D’Cotta H et al. (2000) DMRT1 expression during gonadal differentiation and spermatogenesis in the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Biochim Biophys Acta 1493: 180–187.
Matsubara K, Tarui H, Toriba M et al. (2006) Evidence for different origin of sex chromosomes in snakes, birds, and mammals and step-wise differentiation of snake sex chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103: 18190–18195.
Matsuda Y, Chapman VM (1995) Application of fluorescence in situ hybridization in genome analysis of the mouse. Electrophoresis 16: 261–272.
Matsuda Y, Nishida-Umehara C, Tarui H et al. (2005) Highly conserved linkage homology between birds and turtles: bird and turtle chromosomes are precise counterparts of each other. Chromosome Res 13: 601–615.
Morrish BC, Sinclair AH (2002) Vertebrate sex determination: many means to an end. Reproduction 124: 447–457.
Muller WP (1974) The lampbrush chromosomes of Xenopus laevis (Daudin). Chromosoma 47: 283–296.
Nakajima T, Takase M, Miura I, Nakamura M (2000) Two isoforms of FTZ-F1 messenger RNA: molecular cloning and their expression in the frog testis. Gene 248: 203–212.
Nanda I, Shan Z, Schartl M et al. (1999) 300 million years of conserved synteny between chicken Z and human chromosome 9. Nat Genet 21: 258–259.
Nanda I, Zend-Ajusch E, Shan Z et al. (2000) Conserved synteny between the chicken Z sex chromosome and human chromosome 9 includes the male regulatory gene DMRT1: a comparative (re)view on avian sex determination. Cytogenet Cell Genet 89: 67–78.
Nishioka M, Sumida M (1994) The position of sex-determining genes in the chromosomes of Rana nigromaculata and Rana brevioda. Sci Rep Lab Amphibian Biol Hiroshima Univ 13: 51–97.
Ohtani H, Miura I, Ichikawa Y (2003) Role of aromatase and androgen receptor expression in gonadal sex differentiation of ZW/ZZ-type frogs, Rana rugosa. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 134: 215–225.
Olmo E, Signorino G (2005) Chromorep: a reptile chromosomes database. (http://193.206.118.100/professori/chromorep.pdf).
Osawa N, Oshima Y, Nakamura M (2005) Molecular cloning of Dmrt1 and its expression in the gonad of Xenopus. Zool Sci 22: 681–687.
Oshima Y, Kato T, Wang D et al. (2006) Promoter activity and chromosomal location of the Rana rugosa P450 aromatase (CYP19) gene. Zool Sci 23: 79–85.
Sakurai N, Maruo K, Haraguchi S et al. (2008) Immunohistochemical detection and biological activities of CYP17 (P450c17) in the indifferent gonad of the frog Rana rugosa. JSteroid Biochem Mol Biol. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2008.07.002.
Schmid M, Steinlein C (1991) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. XVI. High-resolution replication banding patterns in Xenopus laevis. Chromosoma 101: 123–132.
Schmid M, Steinlein C (2001) Sex chromosomes, sex-linked genes, and sex determination in the vertebrate class Amphibia. In: Scherer G, Schmid M, eds., Genes and Mechanisms in Vertebrate Sex Determination. Basel: Birkhäuser Verlag, pp. 143–176.
Schmid M, Haaf T, Geile B, Sims S (1983) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. VIII. An unusual XY/XX-sex chromosome system in Gastrotheca riobambae (Anura, Hylidae). Chromosoma 88: 69–82.
Schmid M, Ohta S, Steinlein C, Guttenbach M (1993) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. XIX. Primitive ZW/ZZ sex chromosomes in Buergeria buergeri (Anura, Rhacophoridae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 62: 238–246.
Semba K, Saito-Ueno R, Takayama G, Kondo M (1996) cDNA cloning and its pronephros-specific expression of the Wilms’ tumor suppressor gene, WT1, from Xenopus laevis. Gene 175: 167–172.
Shan Z, Nanda I, Wang Y, Schmid M, Vortkamp A, Haaf T (2000) Sex-specific expression of an evolutionarily conserved male regulatory gene, DMRT1, in birds. Cytogenet Cell Genet 89: 252–257.
Shetty S, Kirby P, Zarkower D, Graves JA (2002) DMRT1 in a ratite bird: evidence for a role in sex determination and discovery of a putative regulatory element. Cytogenet Genome Res 99: 245–251.
Shibata K, Takase M, Nakamura M (2002) The Dmrt1 expression in sex-reversed gonads of amphibians. Gen Comp Endocrinol 127: 232–241.
Smith CA, Sinclair AH (2004) Sex determination: insights from the chicken. Bioessays 26: 120–132.
Smith CA, McClive PJ, Western PS, Reed KJ, Sinclair AH (1999) Conservation of a sex-determining gene. Nature 402: 601–602.
Sugita J, Takase M, Nakamura M (2001) Expression of Dax-1 during gonadal development of the frog. Gene 280: 67–74.
Sumida M, Nishioka M (2000) Sex-linked genes and linkage maps in amphibians. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 126: 257–270.
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res 75: 304–306.
Sutou S, Mitsui Y, Tsuchiya K (2001) Sex determination without the Y chromosome in two Japanese rodents Tokudaia osimensis osimensis and Tokudaia osimensis spp. Mamm Genome 12: 17–21.
Takagi N, Sasaki M (1974) A phylogenetic study of bird karyotypes. Chromosoma 46: 91–120.
Takase M, Noguchi S, Nakamura M (2000) Two Sox9 messenger RNA isoforms: isolation of cDNAs and their expression during gonadal development in the frog Rana rugosa. FEBS Lett 466: 249–254.
Tymowska J (1973) Karyotype analysis of Xenopus tropicalis Gray, Pipidae. Cytogenet Cell Genet 12: 297–304.
Tymowska J (1991) Polyploidy and cytogenetic variation in frogs of the genus Xenopus. In: Green DS and Sessions SK, eds., Amphibian Cytogenetics and Evolution. San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 259–297.
Tymowska J, Fischberg M (1973) Chromosome complements of the Genus Xenopus. Chromosoma 44: 335–342.
Tymowska J, Fischberg M (1982) A comparison of the karyotype, constitutive heterochromatin, and nucleolar organizer regions of the new tetraploid species Xenopus epitropicalis Fischberg and Picard with those of Xenopus tropicalis Gray (Anura, Pipidae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 34: 149–157.
Uehara M, Haramoto Y, Sekizaki H, Takahashi S, Asashima M (2002) Chromosome mapping of Xenopus tropicalis using the G- and Ag-bands: tandem duplication and polyploidization of larvae heads. Dev Growth Differ 44: 427–436.
Uno Y, Nishida C, Oshima Y et al. (2008) Comparative chromosome mapping of sex-linked genes and identification of sex chromosomal rearrangements in the Japanese wrinkled frog (Rana rugosa, Ranidae) with ZW and XY sex chromosome systems. Chromosome Res 16: 637–647.
Vorontsov NN, Lyapunova EA, Borissov YM, Dovgal VE (1980) Variability of sex chromosomes in mammals. Genetica 52/53: 361–372.
Wiley JE (2003) Replication banding and FISH analysis reveal the origin of the Hyla femoralis karyotype and XY/XX sex chromosome. Cytogenet Genome Res 101: 80–83.
Wright DA, Richards CM (1983) Two sex-linked loci in the leopard frog, Rana pipiens. Genetics 103: 249–261.
Yamamura Y, Aoyama S, Oshima Y, Kato T, Osawa N, Nakamura M (2005) Molecular cloning and expression in gonad of Rana rugosa WT1 and Fgf9. Zool Sci 22: 1045–1050.
Yoshimoto S, Okada E, Oishi T et al. (2006) Expression and promoter analysis of Xenopus DMRT1 and functional characterization of the transactivation property of its protein. Dev Growth Differ 48: 597–603.
Yoshimoto S, Okada E, Umemoto H et al. (2008) A W-linked DM-domain gene, DM-W, participates in primary ovary development in Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105: 2469–2474.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uno, Y., Nishida, C., Yoshimoto, S. et al. Diversity in the origins of sex chromosomes in anurans inferred from comparative mapping of sexual differentiation genes for three species of the Raninae and Xenopodinae. Chromosome Res 16, 999–1011 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-008-1257-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-008-1257-z