Abstract
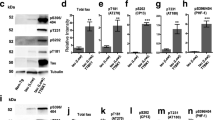
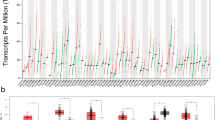
Tau-tubulin kinase 1 (TTBK1) is a CNS-specific, kinase that has been implicated in the pathological phosphorylation of tau in Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD). TTBK1 is a challenging therapeutic target because it shares a highly conserved catalytic domain with its homolog, TTBK2, a ubiquitously expressed kinase genetically linked to the disease spinocerebellar ataxia type 11. The present study attempts to elucidate the functional distinctions between the TTBK isoforms and increase our understanding of them as distinct targets for the treatment of neurodegenerative disease. We demonstrate that in cortical neurons, TTBK1, not TTBK2, is the isoform responsible for tau phosphorylation at epitopes enriched in tauopathies such as Serine 422. In addition, although our elucidation of the crystal structure of the TTBK2 kinase domain indicates almost identical structural similarity with TTBK1, biochemical and cellular assays demonstrate that the enzymatic activity of these two proteins is regulated by a combination of unique extra-catalytic sequences and autophosphorylation events. Finally, we have identified an unbiased list of neuronal interactors and phosphorylation substrates for TTBK1 and TTBK2 that highlight the unique cellular pathways and functional networks that each isoform is involved in. This data address an important gap in knowledge regarding the implications of targeting TTBK kinases and may prove valuable in the development of potential therapies for disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data and material described in this manuscript are available upon request. The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE [1] partner repository with the following dataset identifiers: “Identification of TTBK1 autophosphorylation sites in HEK293 cells” PXD017939. “TTBK1/TTBK2 Phosphoproteomics in mouse cortical neurons” PXD017938. “Identifying interactors through BioID2 in rat cortical neurons” PXD017937.
References
Almilaji A, Munoz C, Hosseinzadeh Z, Lang F (2013) Upregulation of Na+, Cl- coupled betaine/ γ-amino-butyric acid transporter BGT1 by tau tubulin kinase 2. Cell Physiol Biochem 32:334–343
Augustinack JC, Schneider A, Mandelkow EM, Hyman BT (2002) Specific tau phosphorylation sites correlate with severity of neuronal cytopathology in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 103(1):26–35
Biernat J, Mandelkow EM (1999) The development of cell processes induced by tau protein requires phosphorylation of serine 262 and 356 in the repeat domain and is inhibited by phosphorylation in the proline-rich domains. Mol Biol Cell 10(3):727–740. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.10.3.727
Bowie E, Norris R, Anderson KV, Goetz SC (2018) Spinocerebellar ataxia type 11-associated alleles of Ttbk2 dominantly interfere with ciliogenesis and cilium stability. PLoS Genet 14(12):e1007844
Bussière T, Hof PR, Mailliot C, Brown CD, Caillet-Boudin ML, Perl DP, Buée L, Delacourte A (1999) Phosphorylated serine422 on tau proteins is a pathological epitope found in several diseases with neurofibrillary degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 97(3):221–230
Čajánek L, Glatter T, Nigg EA (2015) The E3 ubiquitin ligase Mib1 regulates Plk4 and centriole biogenesis. J Cell Sci 128(9):1674–1682. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.166496
Čajánek L, Nigg EA (2014) Cep164 triggers ciliogenesis by recruiting Tau tubulin kinase 2 to the mother centriole. PNAS 111(28):2841–2850
Dillon GM, Henderson JL, Bao C, Joyce JA, Calhoun M, Amaral B, King KW, Bajrami B, Rabah D (2020) Acute inhibition of the CNS-specific kinase TTBK1 significantly lowers tau phosphorylation at several disease relevant sites. PLoS ONE 15:4
Fernius J, Starkenberg A, Pokrzywa M, Thor S (2017) Human TTBK1, TTBK2 and MARK1 kinase toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster is exacerbated by co-expression of human Tau. Biol Open 6(7):1013–1023
Flotow H, Graves PR, Wang AQ, Fiol CJ, Roeske RW, Roach PJ (1990) Phosphate groups as substrate determinants for casein kinase I action. J Biol Chem 265(24):14264–14269
Goetz SC, Liem KF Jr, Anderson KV (2012) The spinocerebellar ataxia-associated gene tau tubulin kinase 2 (TTBK2) controls the initiation of ciliogenesis. Cell 151(4):847–858
Guillozet-Bongaarts AL, Cahill ME, Cryns VL, Reynolds MR, Berry RW, Binder LI (2006) Pseudophosphorylation of tau at serine 422 inhibits caspase cleavage: in vitro evidence and implications for tangle formation in vivo. J Neurochem 97(4):1005–1014
Hasegawa M, Jakes R, Crowther RA, Lee VM, Ihara Y, Goedert M (1996) Characterization of mAb AP422, a novel phosphorylation-dependent monoclonal antibody against tau protein. FEBS Lett 384(1):25–30
Honnappa S, Gouveia SM, Weisbrich A, Damberger FF, Bhavesh NS, Jawhari H, Grigoriev I, van Rijssel FJ, Buey RM, Lawera A, Jelesarov I, Winkler FK, Wüthrich K, Akhmanova A, Steinmetz MO (2009) An EB1-binding motif acts as a microtubule tip localization signal. Cell 138(2):366–376
Houlden H, Johnson J, Gardner-Thorpe C, Lashley T, Hernandez D, Worth P, Singleton AB, Hilton DA, Holton J, Revesz T, Davis MB, Giunti P, Wood NW (2007) Mutations in TTBK2, encoding a kinase implicated in tau phosphorylation, segregate with spinocerebellar ataxia type 11. Nat Genet 39(12):1434–1436
Hu WT, Josephs KA, Knopman DS, Boeve BF, Dickson DW, Petersen RC, Parisi JE (2008) Temporal lobar predominance of TDP-43 neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions in Alzheimer disease. Acta Neuropathol 116(2):215–220
Ikezu S, Ikezu T (2014) Tau-tubulin kinase. Front Mol Neurosci 7:33
Iqbal K, Liu F, Gong CX, Grundke-Iqbal I (2010) Tau in Alzheimer disease and related tauopathies. Curr Alzheimer Res 7(8):656–664
Jiang K, Toedt G, Montenegro Gouveia S, Davey NE, Hua S, van der Vaart B, Grigoriev I, Larsen J, Pedersen LB, Bezstarosti K, Lince-Faria M, Demmers J, Steinmetz MO, Gibson TJ, Akhmanova A (2012) A Proteome-wide screen for mammalian SxIP motif-containing microtubule plus-end tracking proteins. Curr Biol 22(19):1800–1807
Kanaan NM, Cox K, Alvarez VE, Stein TD, Poncil S, McKee AC (2016) Characterization of early pathological tau conformations and phosphorylation in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 75(1):19–34
Kimura T, Ono T, Takamatsu J, Yamamoto H, Ikegami K, Kondo A, Hasegawa M, Ihara Y, Miyamoto E, Miyakawa T (1996) Sequential changes of tau-site-specific phosphorylation during development of paired helical filaments. Dementia 7(4):177–181
Koren SA, Hamm MJ, Meier SE, Weiss BE, Nation GK, Chishti EA, Arango JP, Chen J, Zhu H, Blalock EM, Abisambra JF (2019) Tau drives translational selectivity by interacting with ribosomal proteins. Acta Neuropathol 137(4):571–583
Kwong LK, Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2007) TDP-43 proteinopathy: the neuropathology underlying major forms of sporadic and familial frontotemporal lobar degeneration and motor neuron disease. Acta Neuropathol 114(1):63–70
Lee VM, Goedert M, Trojanowski JQ (2001) Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1121–1159
Liachko NF, McMillan PJ, Strovas TJ, Loomis E, Greenup L, Murrell JR, Ghetti B, Raskind MA, Montine TJ, Bird TD, Leverenz JB, Kraemer BC (2014) The tau tubulin kinases TTBK1/2 promote accumulation of pathological TDP-43. PLoS Genet 10(12):e1004803
Lund H, Cowburn RF, Gustafsson E, Strömberg K, Svensson A, Dahllund L, Malinowsky D, Sunnemark D (2013) Tau-tubulin kinase 1 expression, phosphorylation and co-localization with phospho-Ser422 tau in the Alzheimer's disease brain. Brain Pathol 23(4):378–389
Mandell JW, Banker GA (1996) A spatial gradient of tau protein phosphorylation in nascent axons. J Neurosci 16(18):5727–5740
McInnes J, Wierda K, Snellinx A, Bounti L, Wang Y, Stancu I, Apóstolo N, Gevaert K, Dewachter I, Spires-Jones TL, De Strooper B, De Wit J, Zhou L, Verstreken P (2018) Synaptogyrin-3 mediates presynaptic dysfunction induced by tau. Neuron 97(4):823–835
McKee AC, Gavett BE, Stern RA, Nowinski CJ, Cantu RC, Kowall NW, Perl DP, Hedley-Whyte ET, Price B, Sullivan C, Morin P, Lee HS, Kubilus CA, Daneshvar DH, Wulff M, Budson AE (2010) TDP-43 proteinopathy and motor neuron disease in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 69(9):918–929
Neddens J, Temmel M, Flunkert S, Kerschbaumer B, Hoeller C, Loeffler T, Niederkofler V, Daum G, Attems J, Hutter-Paier B (2018) Phosphorylation of different tau sites during progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 6(1):52
Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Micsenyi MC, Chou TT, Bruce J, Schuck T, Grossman M, Clark CM, McCluskey LF, Miller BL, Masliah E, Mackenzie IR, Feldman H, Feiden W, Kretzschmar HA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314(5796):130–133
Oda T, Chiba S, Nagai T, Mizuno K (2014) Binding to Cep164, but not EB1, is essential for centriolar localization of TTBK2 and its function in ciliogenesis. Genes Cells 19(12):927–940
Pascual G, Wadia JS, Zhu X, Keogh E, Kükrer B, van Ameijde J, Inganäs H, Siregar B, Perdok G, Diefenbach O, Nahar T, Sprengers I, Koldijk MH, der Linden EC, Peferoen LA, Zhang H, Yu W, Li X, Wagner M, Moreno V, Kim J, Costa M, West K, Fulton Z, Chammas L, Luckashenak N, Fletcher L, Holland T, Arnold C, Anthony Williamson R, Hoozemans JJ, Apetri A, Bard F, Wilson IA, Koudstaal W, Goudsmit J (2017) Immunological memory to hyperphosphorylated tau in asymptomatic individuals. Acta Neuropathol 133(5):767–783
Roux KJ, Kim DI, Raida M, Burke B (2012) A promiscuous biotin ligase fusion protein identifies proximal and interacting proteins in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol 196(6):801–810
Sato S, Cerny RL, Buescher JL, Ikezu T (2006) Tau-tubulin kinase 1 (TTBK1), a neuron-specific tau kinase candidate, is involved in tau phosphorylation and aggregation. J Neurosci 98(5):1573–1584
Sato S, Xu J, Okuyama S, Martinez LB, Walsh SM, Jacobsen MT, Swan RJ, Schlautman JD, Ciborowski P, Ikezu T (2008) Spatial learning impairment, enhanced CDK5/p35 activity, and downregulation of NMDA receptor expression in transgenic mice expressing tau-tubulin kinase 1. J Neurosci 28(53):14511–14521
Seo S, Baye LM, Schulz NP, Beck JS, Zhang Q, Slusarski DC, Sheffield VC (2010) BBS6, BBS10, and BBS12 form a complex with CCT/TRiC family chaperonins and mediate BBSome assembly. PNAS 107(4):1488–1493
Takahashi M, Tomizawa K, Sato K, Ohtake A, Omori A (1995) A novel tau-tubulin kinase from bovine brain. FEBS Lett 372(1):59–64
Taylor LM, McMillan PJ, Liachko NF, Strovas TJ, Ghetti B, Bird TD, Keene CD, Kraemer BC (2018) Pathological phosphorylation of tau and TDP-43 by TTBK1 and TTBK2 drives neurodegeneration. Mol Neurodegener 13(1):7
Tomizawa K, Omori A, Ohtake A, Sato K, Takahashi M (2001) Tau-tubulin kinase phosphorylates tau at Ser-208 and Ser-210, sites found in paired helical ¢lament-tau. FEBS Lett 492(3):221–227
Vana L, Kanaan NM, Ugwu IC, Wuu J, Mufson EJ, Binder LI (2011) Progression of tau pathology in cholinergic Basal forebrain neurons in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol 179(5):2533–2550
Vázquez-Higuera JL, Mateo I, Sánchez-Juan P, Rodríguez-Rodríguez E, Pozueta A, Calero M, Dobato JL, Frank-García A, Valdivieso F, Berciano J, Bullido MJ, Combarros O (2011) Genetic variation in the tau kinases pathway may modify the risk and age at onset of Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 27(2):291–297
Violet M, Delattre L, Tardivel M, Sultan A, Chauderlier A, Caillierez R, Talahari S, Nesslany F, Lefebvre B, Bonnefoy E, Buée L, Galas MC (2014) A major role for Tau in neuronal DNA and RNA protection in vivo under physiological and hyperthermic conditions. Front Cell Neurosci 8:84
Watanabe T, Kakeno M, Matsui T, Sugiyama I, Arimura N, Matsuzawa K, Shirahige A, Ishidate F, Nishioka T, Taya S, Hoshino M, Kaibuchi K (2015) TTBK2 with EB1/3 regulates microtubule dynamics in migrating cells through KIF2A phosphorylation. J Cell Biol 210(5):737–751
Xue Y, Wan PT, Hillertz P, Schweikart F, Zhao Y, Wissler L, Dekker N (2013) X-ray structural analysis of tau-tubulin kinase 1 and its interactions with small molecular inhibitors. ChemMedChem 11:1846–1854
Yu NN, Yu JT, Xiao JT, Zhang HW, Lu RC, Jiang H, Xing ZH, Tan L (2011) Tau-tubulin kinase-1 gene variants are associated with Alzheimer's disease in Han Chinese. Neurosci Lett 491(1):83–86
Zhang N, Gordon SL, Fritsch MJ, Esoof N, Campbell DG, Gourlay R, Velupillai S, Macartney T, Peggie M, van Aalten DM, Cousin MA, Alessi DR (2015) Phosphorylation of synaptic vesicle protein 2A at Thr84 by casein kinase 1 family kinases controls the specific retrieval of synaptotagmin-1. J Neurosci 35(6):2492–2507
Funding
Biogen provided support in the form of salaries for all authors, but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The specific roles of these authors are articulated in the ‘Author Contributions’ section.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Confirm that all authors listed adhere to requirements for authorship.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Employment at Biogen does not alter authors adherence to the journals policies on conflicts of interest or sharing data and materials.
Ethics Approval
All experiments were conducted in compliance with the rules set forth by the Biogen Institutional Animal Use and Care Committee under protocol number 881 and in accordance with the guidelines established in the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, C., Bajrami, B., Marcotte, D.J. et al. Mechanisms of Regulation and Diverse Activities of Tau-Tubulin Kinase (TTBK) Isoforms. Cell Mol Neurobiol 41, 669–685 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00875-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00875-6