Abstract
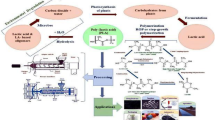
This study fabricated polylactic acid (PLA)/kenaf cellulose fiber biocomposite filaments via melt-extrusion process. Kenaf cellulose fibers (KF) were chemically extracted from locally grown kenaf plants and used as reinforcement. Moreover, the KF was then treated with tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), so-called KFs, to improve the compatibility between the fibers and PLA matrix. Also, the plasticizers (polyethylene glycol) were incorporated to enhance the flowability and processability of the biocomposites. The melt viscosities of the biocomposites increased as the solid KF and KFs were loaded. However, they were significantly decreased with the addition of plasticizers. The combined use of the plasticizers and TEOS treatment improved tensile strength, Young’s modulus and elongation of the biocomposites compared to the neat PLA. The obtained PLA/KFs biocomposite materials are proved to be a mechanical-improved material that could offer the opportunity for rapid production of 3D fully degradable biocomposite prototypes for applications in sustainable textiles and apparel, personalized prostheses and some medical devices that require high strength and elongation.
Graphic abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM D638-14 (2014) Standard test method for tensile properties of plastics. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA. www.astm.org
Aumnate C, Pongwisuthiruchte A, Pattananuwat P, Potiyaraj P (2018) Fabrication of ABS/graphene oxide composite filament for fused filament fabrication (FFF) 3D printing. Adv Mater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2830437
Aumnate C, Limpanart S, Soatthiyanon N, Khunton S (2019) PP/organoclay nanocomposites for fused filament fabrication (FFF) 3D printing. Express Polym Lett 13:898–909. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2019.78
Aumnate C, Potiyaraj P, Saengow C, Giacomin AJ (2021) Reinforcing polypropylene with graphene-polylactic acid microcapsules for fused-filament fabrication. Mater Des 198:109329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.109329
Azizi H, Ghasemi I (2009) Investigation on the dynamic melt rheological properties of polypropylene/wood flour composites. Polym Compos. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.20573
Bhasney SM, Kumar A, Katiyar V (2020) Microcrystalline cellulose, polylactic acid and polypropylene biocomposites and its morphological, mechanical, thermal and rheological properties. Compos Part B 184:107717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107717
Boruvka M, Behalek L, Lenfeld P, Ngaowthong C (2019) Structure-related properties of bionanocomposites based on poly (lactic acid), cellulose nanocrystals and organic impact modifier. Mater Technol 34:143–156. https://doi.org/10.1080/10667857.2018.1540332
Chan CH, Chia CH, Zakaria S et al (2013) Production and characterisation of cellulose and nano- crystalline cellulose from kenaf core wood. Bio Resour 8:785–794. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.8.1.785-794
Chang Y, Chen Y, Ning J et al (2019) No such thing as trash: a 3D-printable polymer composite composed of oil-extracted spent coffee grounds and polylactic acid with enhanced impact toughness. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:15304–15310. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02527
Ding W, Jahani D, Chang E et al (2016) Development of PLA/cellulosic fiber composite foams using injection molding: crystallization and foaming behaviors. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 83:130–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.10.003
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Frone AN, Berlioz S, Chailan J-F, Panaitescu DM (2013) Morphology and thermal properties of PLA–cellulose nanofibers composites. Carbohydr Polym 91:377–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.08.054
Fu J, He C, Wang S, Chen Y (2018) A thermally stable and hydrophobic composite aerogel made from cellulose nanofibril aerogel impregnated with silica particles. J Mater Sci 53:7072–7082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2034-9
Gemmeke N, Feldmann M, Heim HP (2019) Processing and characterization of engineering biocomposites based on polybutylenterephthalat (PBT) and polytrimethylentherephthalat (PTT) with regenerated cellulose fibers modified with maleic anhydride grafted polyethylene as a processing agent. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 118:327–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.01.007
Hamad K, Kaseem M, Yang HW et al (2015) Properties and medical applications of polylactic acid: a review. Express Polym Lett 9:435–455. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2015.42
Immonen K, Lahtinen P, Pere J (2017) Effects of surfactants on the preparation of nanocellulose-PLA composites. Bioengineering. 4(4):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering4040091
Jiang G, Yang T, Xu J et al (2020) Investigation into hydroxypropyl-methylcellulose-reinforced polylactide composites for fused deposition modelling. Ind Crops Prod 146:112174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112174
Jonoobi M, Harun J, Shakeri A et al (2009) Chemical composition, crystallinity, and thermal degradation of bleached and unbleached kenaf bast (Hibiscus cannabinus) pulp and nanofibers. Bio Resour 4:626–639. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.4.2.626-639
Kargarzadeh H, Ahmad I, Abdullah I et al (2012) Effects of hydrolysis conditions on the morphology, crystallinity, and thermal stability of cellulose nanocrystals extracted from kenaf bast fibers. Cellulose 19:855–866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9684-6
Liu J, Sun L, Xu W et al (2019) Current advances and future perspectives of 3D printing natural-derived biopolymers. Carbohydr Polym 207:297–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.11.077
Manoharan S, Suresha B, Ramadoss G, Bharath B (2014) Effect of short fiber reinforcement on mechanical properties of hybrid phenolic composites. J Mater 2014:478549. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/478549
Mokhena TC, Sefadi JS, Sadiku ER et al (2018) Thermoplastic processing of PLA/cellulose nanomaterials composites. Polym Basel. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121363
Murphy CA, Collins MN (2018) Microcrystalline cellulose reinforced polylactic acid biocomposite filaments for 3D printing. Polym Compos 39:1311–1320. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.24069
Osswald TA, Menges G, Manges G (2013) Materials science of polymers for engineers, 3rd edn. Hanser Publishers, Munich Vienna New York
Pinto AM, Cabral J, Tanaka DAP et al (2013) Effect of incorporation of graphene oxide and graphene nanoplatelets on mechanical and gas permeability properties of poly(lactic acid) films. Polym Int 62:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.4290
Scaffaro R, Botta L, Lopresti F et al (2017) Polysaccharide nanocrystals as fillers for PLA based nanocomposites. Cellulose 24:447–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1143-3
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE, Conrad CM (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29:786–794. https://doi.org/10.1177/004051755902901003
Sharma S, Singh AA, Majumdar A, Butola BS (2020) Harnessing the ductility of polylactic acid/halloysite nanocomposites by synergistic effects of impact modifier and plasticiser. Compos Part B 188:107845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.107845
Soatthiyanon N, Aumnate C, Srikulkit K (2020) Rheological, tensile, and thermal properties of poly(butylene succinate) composites filled with two types of cellulose (kenaf cellulose fiber and commercial cellulose). Polym Compos. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25575
Song Y, Jiang W, Zhang Y et al (2018) Isolation and characterization of cellulosic fibers from kenaf bast using steam explosion and fenton oxidation treatment. Cellulose 25:4979–4992. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1916-y
Spicker C, Rudolph N, Kühnert I, Aumnate C (2019) The use of rheological behavior to monitor the processing and service life properties of recycled polypropylene. Food Packag Shelf Life 19:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2019.01.002
Tekinalp HL, Meng X, Lu Y et al (2019) High modulus biocomposites via additive manufacturing: cellulose nanofibril networks as “microsponges.” Compos Part B 173:106817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.05.028
Thakur KM, Gupta KR, Thakur KV (2014) Surface modification of cellulose using silane coupling agent. Carbohydr Polym 111:849–855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.05.041
Walha F, Lamnawar K, Maazouz A, Jaziri M (2016) Rheological, morphological and mechanical studies of sustainably sourced polymer blends based on poly(lactic acid) and polyamide 11. Polym Basel. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8030061
Wang L, Gardner DJ (2017) Effect of fused layer modeling (FLM) processing parameters on impact strength of cellular polypropylene. Polym U K 113:74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2017.02.055
Wang XF, Zhang ZX, Le LJ et al (2015) Largely improved fracture toughness of an immiscible poly(L-lactide)/ethylene-co-vinyl acetate blend achieved by adding carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv 5:69522–69533. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra11192g
Wang X, Jiang M, Zhou Z et al (2017) 3D printing of polymer matrix composites: a review and prospective. Compos Part B 110:442–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.11.034
Wang Q, Ji C, Sun L et al (2020) Cellulose nanofibrils filled poly(lactic acid) biocomposite filament for FDM 3D printing. Molecules 25(10):2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102319
Xie A, Cui J, Chen Y et al (2019) Surface & coatings technology one-step facile fabrication of sustainable cellulose membrane with superhydrophobicity via a sol-gel strategy for efficient oil/water separation. Surf Coat Technol 361:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.01.040
Xu W, Pranovich A, Uppstu P et al (2018) Novel biorenewable composite of wood polysaccharide and polylactic acid for three dimensional printing. Carbohydr Polym 187:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.01.069
Zhang L, Zhang Q, Yu J et al (2019) Strengthened cellulosic gels by the chemical gelation of cellulose via crosslinking with TEOS. Cellulose 26:9819–9829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02765-7
Zhou L, He H, Li M et al (2018) Enhancing mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid) through its in-situ crosslinking with maleic anhydride-modified cellulose nanocrystals from cottonseed hulls. Ind Crop Prod 112:449–459
Acknowledgments
The authors thankfully acknowledge the support from National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT5-TRG63001-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CA Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing- Original draft preparation, Writing-Reviewing and Editing. NS Methodology, Investigation, Writing-Reviewing and Editing. TM Methodology, Investigation, Writing-Reviewing and Editing. PP Resources, Validation, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
The authors certify that this manuscript is original and has not been published and will not be submitted elsewhere for publication while being considered by Cellulose. The study is not split up into several parts to increase the quantity of submissions and submitted to various journals or to one journal over time. No data have been fabricated or manipulated (including images) to support your conclusions. No data, text, or theories by others are presented as if they were the authors’ own.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with Animal studies or human participants involvement performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aumnate, C., Soatthiyanon, N., Makmoon, T. et al. Polylactic acid/kenaf cellulose biocomposite filaments for melt extrusion based-3D printing. Cellulose 28, 8509–8525 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04069-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04069-1