Abstract
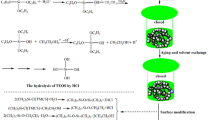
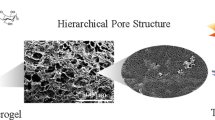
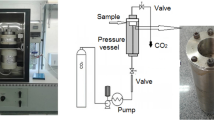
A thermally stable and hydrophobic cellulose nanofibril (CNF)–silica composite aerogel was prepared by simply immersing the CNF aerogel into the silica sol with different tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) concentration and shaping it by means of low-risk ambient pressure drying. After the introduction of the mesoporous silica particles into the cellulose network structure, the BET surface area was found to have sharply increased from 11.3 to 497.8 m2 g−1. All composite aerogels displayed good thermal stability and super-hydrophobicity compared with pure cellulose aerogel. The onset temperature of pyrolysis rose from 317 to 348 °C, and the contact angle reached 152.1°. The TEOS concentration was found to have a great influence on the silica content and the dispersion of silica particles in the cellulose scaffold. Good chemical compatibility at the nanoscale level was present, which indicates that a continuous and homogeneous CNF–silica interface would yield great improvement in thermal properties and water resistance. The results show that a composite aerogel prepared at 2.5 mol L−1 TEOS concentration has better comprehensive performance with only a slightly decrease in mechanical properties compared to CNF aerogel. Thus, this study details a new direction for the synthesis of a cellulose–silica composite aerogel with tailored properties achieved by controlling the silica content and silica dispersion in the cellulose scaffold. Thermally stable, water-resistant, and environmentally friendly cellulose–silica composite aerogels may provide a promising development for designing new functional aerogels that can be applied in various fields.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zou J, Liu J, Karakoti AS, Kumar A, Joung D, Li Q, Khondaker SI, Seal S, Zhai L (2010) Ultralight multiwalled carbon nanotube aerogel. ACS Nano 4:7293–7302
Hoepfner S, Ratke L, Milow B (2008) Synthesis and characterisation of nanofibrillar cellulose aerogels. Cellulose 15:121–129
Khare VP, Greenberg AR, Kelley SS, Pilath H, Juhn Roh I, Tyber J (2007) Synthesis and characterization of dense and porous cellulose films. J Appl Polym Sci 105:1228–1236
Heath L, Thielemans W (2010) Cellulose nanowhisker aerogels. Green Chem 12:1448–1453
Chin SF, Binti Romainor AN, Pang SC (2014) Fabrication of hydrophobic and magnetic cellulose aerogel with high oil absorption capacity. Mater Lett 115:241–243
He X, Cheng L, Wang Y, Zhao J, Zhang W, Lu C (2014) Aerogels from quaternary ammonium-functionalized cellulose nanofibers for rapid removal of Cr(VI) from water. Carbohydr Polym 111:683–687
Haimer E, Wendland M, Schlufter K, Frankenfeld K, Miethe P, Potthast A, Rosenau T, Liebner F (2010) Loading of bacterial cellulose aerogels with bioactive compounds by antisolvent precipitation with supercritical carbon dioxide. Macromol Symp 294:64–74
Zaborowska M, Bodin A, Bäckdahl H, Popp J, Goldstein A, Gatenholm P (2010) Microporous bacterial cellulose as a potential scaffold for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater 6:2540–2547
Kobayashi Y, Saito T, Isogai A (2014) Aerogels with 3D ordered nanofiber skeletons of liquid-crystalline nanocellulose derivatives as tough and transparent insulators. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:10394–10397
Sehaqui H (2011) Nanofiber networks, aerogels and biocomposites based on nanofibrillated cellulose from wood. Ph.D. dissertation, KTH School of Chemical Science and Engineering
Yang C, Chen C, Pan Y, Li S, Wang F, Li J, Li N, Li X, Zhang Y, Li D (2015) Flexible highly specific capacitance aerogel electrodes based on cellulose nanofibers, carbon nanotubes and polyaniline. Electrochim Acta 182:264–271
Nemoto J, Saito T, Isogai A (2015) Simple freeze-drying procedure for producing nanocellulose aerogel-containing, high-performance air filters. ACS Appl Mater Int 7:19809–19815
Wang M, Anoshkin IV, Nasibulin AG, Rha R, Nonappa Laine J, Kauppinen EI, Ikkala O (2016) Electrical behaviour of native cellulose nanofibril/carbon nanotube hybrid aerogels under cyclic compression. RSC Adv 6:89051–89056
Wan C, Li J (2015) Embedding ZnO nanorods into porous cellulose aerogels via a facile one-step low-temperature hydrothermal method. Mater Des 83:620–625
Ostrikov K (2005) Reactive plasmas as a versatile nanofabrication tool. Rev Mod Phys 77:489–511
Cervin NT, Aulin C, Larsson PT, Wågberg L (2012) Ultra porous nanocellulose aerogels as separation medium for mixtures of oil/water liquids. Cellulose 19:401–410
Korhonen JT, Hiekkataipale P, Malm J, Karppinen M, Ikkala O, Ras RHA (2011) Inorganic hollow nanotube aerogels by atomic layer deposition onto native nanocellulose templates. ACS Nano 5:1967–1974
Russler A, Wieland M, Bacher M, Henniges U, Miethe P, Liebner F, Potthast A, Rosenau T (2012) AKD-modification of bacterial cellulose aerogels in supercritical CO2. Cellulose 19:1337–1349
Liu S, Yan Q, Tao D, Yu T, Liu X (2012) Highly flexible magnetic composite aerogels prepared by using cellulose nanofibril networks as templates. Carbohydr Polym 89:551–557
Xia YD, Mokaya R (2004) Ordered mesoporous carbon hollow spheres nanocast using mesoporous silica via chemical vapor deposition. Adv Mater 16:886–891
Cai J, Liu S, Feng J, Kimura S, Wada M, Kuga S, Zhang L (2012) Cellulose–silica nanocomposite aerogels by in-situ formation of silica in cellulose gel. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:2076–2079
Meng Y, Wu Q, Young TM, Huang B, Wang S, Li Y (2017) Analyzing three-dimensional structure and geometrical shape of individual cellulose nanocrystal from switchgrass. Polym Compos 38:2368–2377. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.23819
Meng Y, Young TM, Liu P, Contescu CI, Huang B, Wang S (2015) Ultralight carbon aerogel from nanocellulose as a highly selective oil absorption material. Cellulose 22:435–447
Fu J, Wang S, He C, Lu Z, Huang J, Chen Z (2016) Facilitated fabrication of high strength silica aerogels using cellulose nanofibrils as scaffold. Carbohydr Polym 147:89–96
Hüsing N, Schubert U, Mezei R, Fratzl P, Riegel B, Kiefer W, Kohler D, Mader W (1999) Formation and structure of gel networks from Si(OEt)4/(MeO)3Si(CH2)3NR′2 mixtures (NR′2 = NH2 or NHCH2CH2NH2). Chem Mater 11:451–457
Gibson LJ, Ashby MF (1997) Cellular solids: structure and properties. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Fu J, He C, Huang J, Chen Z, Wang S (2016) Cellulose nanofibril reinforced silica aerogels: optimization of the preparation process evaluated by a response surface methodology. RSC Adv 6:100326–100333
Ashori A, Sheykhnazari S, Tabarsa T, Shakeri A, Golalipour M (2012) Bacterial cellulose/silica nanocomposites: preparation and characterization. Carbohydr Polym 90:413–418
Lu T, Jiang M, Jiang Z, Hui D, Wang Z, Zhou Z (2013) Effect of surface modification of bamboo cellulose fibers on mechanical properties of cellulose/epoxy composites. Compos B Eng 51:28–34
Shi J, Lu L, Guo W, Zhang J, Cao Y (2013) Heat insulation performance, mechanics and hydrophobic modification of cellulose–SiO2 composite aerogels. Carbohydr Polym 98:282–289
Zhang W, Zhang Y, Lu C, Deng Y (2012) Aerogels from crosslinked cellulose nano/micro-fibrils and their fast shape recovery property in water. J Mater Chem 22:11642–11650
Sinha E, Rout SK (2008) Influence of fibre-surface treatment on structural, thermal and mechanical properties of jute. J Mater Sci 43:2590–2601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2478-4
Guzun AS, Stroescu M, Jinga SI, Voicu G, Grumezescu AM, Holban AM (2014) Plackett–Burman experimental design for bacterial cellulose–silica composites synthesis. Mater Sci Eng C 42:280–288
Wei T, Chang T, Lu S, Chang Y (2007) Preparation of monolithic silica aerogel of low thermal conductivity by ambient pressure drying. J Am Ceram Soc 90:2003–2007
Liu S, Yu T, Hu N, Liu R, Liu X (2013) High strength cellulose aerogels prepared by spatially confined synthesis of silica in bioscaffolds. Colloids Surf A 439:159–166
He P, Gao X, Li X, Jiang Z, Yang Z, Wang C, Gu Z (2014) Highly transparent silica aerogel thick films with hierarchical porosity from water glass via ambient pressure drying. Mater Chem Phys 147:65–74
He F, Chao S, Gao Y, He X, Li M (2014) Fabrication of hydrophobic silica–cellulose aerogels by using dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as solvent. Mater Lett 137:167–169
Javadi A, Zheng Q, Payen F, Javadi A, Altin Y, Cai Z, Sabo R, Gong S (2013) Polyvinyl alcohol-cellulose nanofibrils-graphene oxide hybrid organic aerogels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:5969–5975
Okita Y, Saito T, Isogai A (2010) Entire surface oxidation of various cellulose microfibrils by TEMPO-mediated oxidation. Biomacromolecules 11:1696–1700
Tonoli GHD, Teixeira EM, Corrêa AC, Marconcini JM, Caixeta LA, Pereira-da-Silva MA, Mattoso LHC (2012) Cellulose micro/nanofibres from Eucalyptus kraft pulp: preparation and properties. Carbohydr Polym 89:80–88
Wan C, Lu Y, Jiao Y, Cao J, Sun Q, Li J (2015) Preparation of mechanically strong and lightweight cellulose aerogels from cellulose-NaOH/PEG solution. J Sol–Gel Sci Techn 74:256–259
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Special Fund for Forest Scientific Research in the Public Welfare Grant (No. 201504603), the 2014 UTIA Innovation Grant, and Tennessee Experimental Station Project (#TEN00510).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, J., He, C., Wang, S. et al. A thermally stable and hydrophobic composite aerogel made from cellulose nanofibril aerogel impregnated with silica particles. J Mater Sci 53, 7072–7082 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2034-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2034-9