Abstract
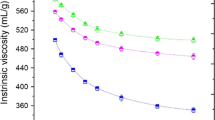
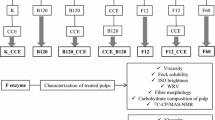
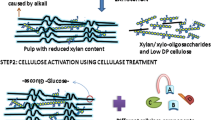
Cellulase treatment for decreasing viscosity of cellulose (dissolving pulp) is a promising approach to reduce the use of toxic chemicals, such as hypochlorite in the dissolving pulp manufacturing process. In this study, the use of an endoglucanase-rich cellulase to replace the hypochlorite for this purpose and its improvements of the Fock reactivity were investigated. The results showed that at a given viscosity level, the replacement of hypochlorite treatment with a cellulase treatment in the bleach plant under otherwise the same conditions led to a higher Fock reactivity (72.0 vs 46.7 %). These results were due to the enzymatic peeling/etching mechanism, which partially peeled the primary wall of the fibers, thus improving the accessibility of fibers. The improved accessibility of the enzymatic treated pulp was supported by the positive fiber morphological changes determined, based on the SEM, BET and WRV methods. The alkali solubility results further supported the conclusion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambjörnsson HA, Östberg L, Schenzel K, Larsson PT, Germgård U (2014) Enzyme pretreatment of dissolving pulp as a way to improve the following dissolution in NaOH/ZnO. Holzforschung 68(4):385–391
Biermann CJ (1996) Handbook of pulping and papermaking. Academic press, New York
Cao Y, Tan H (2002) Effects of cellulase on the modification of cellulose. Carbohydr Res 337(4):1291–1296
Chiriac AI, Pastor FIJ, Popa VI, Aflori M, Ciolacu D (2014) Changes of supramolecular cellulose structure and accessibility induced by the processive endoglucanase Cel9B from Paenibacillus barcinonensis. Cellulose 21(1):203–219
Christoffersson KE, Sjöström M, Edlund U, Lindgren Å, Dolk M (2002) Reactivity of dissolving pulp: characterisation using chemical properties, NMR spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis. Cellulose 9(2):159–170
Clarke K, Li X, Li K (2011) The mechanism of fiber cutting during enzymatic hydrolysis of wood biomass. Biomass Bioenergy 35(9):3943–3950
Duan C, Long Y, Li J, Ma X, Ni Y (2015) Changes of cellulose accessibility to cellulase due to fiber hornification and its impact on enzymatic viscosity control of dissolving pulp. Cellulose 22(4):2729–2736
Engstrom A-C, Ek M, Henriksson G (2006) Improved accessibility and reactivity of dissolving pulp for the viscose process: pretreatment with monocomponent endoglucanase. Biomacromolecules 7:2027–2031
Gehmayr V, Sixta H (2011) Dissolving pulps from enzyme treated kraft pulps for viscose application. Lenzing Ber 89:152–160
Gehmayr V, Sixta H (2012) Pulp properties and their influence on enzymatic degradability. Biomacromolecules 13(3):645–651
Gehmayr V, Schild G, Sixta H (2011) A precise study on the feasibility of enzyme treatments of a kraft pulp for viscose application. Cellulose 18(2):479–491
Grönqvist S et al (2014) Fibre porosity development of dissolving pulp during mechanical and enzymatic processing. Cellulose 21(5):3667–3676
Henriksson G, Christiernin M, Agnemo R (2005) Monocomponent endoglucanase treatment increases the reactivity of softwood sulphite dissolving pulp. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 32(5):211–214
Ibarra D, Köpcke V, Ek M (2010a) Behavior of different monocomponent endoglucanases on the accessibility and reactivity of dissolving-grade pulps for viscose process. Enzyme Microb Technol 47(7):355–362
Ibarra D, Kopcke V, Larsson PT, Jaaskelainen AS, Ek M (2010b) Combination of alkaline and enzymatic treatments as a process for upgrading sisal paper-grade pulp to dissolving-grade pulp. Bioresour Technol 101(19):7416–7423
Le Moigne N, Jardeby K, Navard P (2010) Structural changes and alkaline solubility of wood cellulose fibers after enzymatic peeling treatment. Carbohydr Polym 79(2):325–332
Li J, Liu Y, Duan C, Zhang H, Ni Y (2015a) Mechanical pretreatment improving hemicelluloses removal from cellulosic fibers during cold caustic extraction. Bioresour Technol 192:501–506
Li R, Wang S, Lu A, Zhang L (2015b) Dissolution of cellulose from different sources in an NaOH/urea aqueous system at low temperature. Cellulose 22(1):339–349
Miao Q, Chen L, Huang L, Tian C, Zheng L, Ni Y (2014a) A process for enhancing the accessibility and reactivity of hardwood kraft-based dissolving pulp for viscose rayon production by cellulase treatment. Bioresour Technol 154:109–113
Miao Q, Tian C, Chen L, Huang L, Zheng L, Ni Y (2014b) Combined mechanical and enzymatic treatments for improving the Fock reactivity of hardwood kraft-based dissolving pulp. Cellulose 22(1):803–809
Penttilä PA et al (2010) Changes in submicrometer structure of enzymatically hydrolyzed microcrystalline cellulose. Biomacromolecules 11(4):1111–1117
Quintana E, Valls C, Vidal T, Roncero MB (2013) An enzyme-catalysed bleaching treatment to meet dissolving pulp characteristics for cellulose derivatives applications. Bioresour Technol 148:1–8
Sixta H (2006) Pulp bleaching. Handbook of pulp. Wiley-VCH Verlag GMbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, pp 609–932
Sixta H et al (2013) Novel concepts of dissolving pulp production. Cellulose 20(4):1547–1561
Strunk P, Lindgren Å, AGNEMO BER, Eliasson B (2012) Chemical changes of cellulose pulps in the processing to viscose dope. Cellul Chem Technol 46(9):559–569
Thygesen LG, Hidayat BJ, Johansen KS, Felby C (2011) Role of supramolecular cellulose structures in enzymatic hydrolysis of plant cell walls. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38(8):975–983
Tian C, Zheng L, Miao Q, Nash C, Cao C, Ni Y (2013) Improvement in the Fock test for determining the reactivity of dissolving pulp. Tappi J 12(11):21–26
Tian C, Zheng LQ, Miao QX, Cao CY, Ni YH (2014) Improving the reactivity of kraft-based dissolving pulp for viscose rayon production by mechanical treatments. Cellulose 21(5):3647–3654
Trygg J, Fardim P (2011) Enhancement of cellulose dissolution in water-based solvent via ethanol–hydrochloric acid pretreatment. Cellulose 18(4):987–994
Wang L, Zhang Y, Gao P, Shi D, Liu H, Gao H (2006) Changes in the structural properties and rate of hydrolysis of cotton fibers during extended enzymatic hydrolysis. Biotechnol Bioeng 93(3):443–456
Wang Q, Liu S, Yang G, Chen J, Ni Y (2015) Cationic polyacrylamide enhancing cellulase treatment efficiency of hardwood kraft-based dissolving pulp. Bioresour Technol 183:42–46
Zhang Z-J, Chen Y-Z, Hu H-R, Sang Y-Z (2013) The beatability-aiding effect of Aspergillus niger crude cellulase on bleached Simao pine kraft pulp and its mechanism of action. BioResources 8(4):5861–5870
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Canada Research Chairs and NSERC CRD program, and the Tianjin Municipal Science and Technology Commission (Grant No. 12ZCZDGX01100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, C., Verma, S.K., Li, J. et al. Viscosity control and reactivity improvements of cellulose fibers by cellulase treatment. Cellulose 23, 269–276 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0822-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0822-9