Abstract
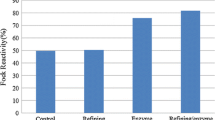
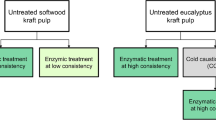
The development of efficient process steps to convert paper-grade to dissolving pulps was investigated as part of the work programme to improve the process economics. The challenge of pulp refinement comprises the selective removal of hemicelluloses and the precise adjustment of the pulp viscosity, while maintaining the reactivity of the pulp as required for viscose application. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of various enzyme treatments on a commercial oxygen-delignified Eucalyptus globulus paper-grade kraft pulp in the course of a total chlorine free bleaching sequence in combination with refining techniques following the principle of Modified Kraft Cooking (Sixta et al. 2007). The objectives were to assess its applicability as viscose pulp besides the reduction of chemical consumption in alkaline and ozone bleaching steps by means of xylanase pre-treatment and the controlled adjustment of final pulp viscosity utilizing endoglucanase post-treatment. Xylanase pre-treatment combined with cold caustic extraction at reduced alkalinity efficiently removed the hemicelluloses from the pulp and clearly increased the pulp brightness by extensive removal of hexenuronic acid side chains. The xylanase pre-treated pulp showed increased reactivity towards xanthation and high viscose dope quality in terms of particle content. The dependence of cellulose chain scission on the applied endoglucanase concentration was analyzed in detail, and this allowed precise viscosity reduction as well as reactivity increase. The differently treated pulps, with and without xylanase pre-treatment, were of very narrow molecular weight distribution and the quality of the spun fibers were very similar to those viscose fibers from commercial dissolving pulps.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- [η]:
-
Intrinsic viscosity
- A:
-
Acid bleaching
- AC:
-
Alkali cellulose
- AXU:
-
Active xylanase unit
- B:
-
Brightness
- CCE:
-
Cold caustic extraction
- DP:
-
Degree of polymerization
- ECF:
-
Elemental chlorine free
- ECU:
-
Endoglucanase unit
- EG:
-
Endoglucanase
- FV:
-
Filter clogging value
- HexA:
-
Hexenuronic acid
- MWD:
-
Molecular weight distribution
- n.d.:
-
Not determined
- O:
-
Oxygen bleaching
- odp:
-
Oven dried pulp
- P:
-
Peroxide bleaching
- PHK:
-
Pre-hydrolysis kraft pulp
- SEC:
-
Size exclusion chromatography
- TCF:
-
Total chlorine free
- WRV:
-
Water retention value
- X:
-
Xylanase
- Z:
-
Ozone bleaching
References
Allison RW, Clark TA (1994) Effect of enzyme pretreatment on ozone bleaching. Tappi J 77:127–134
Annergren G, Backlund Å, Richter J, Rydholm S (1965) Continuous prehydrolysis-kraft cooking. Tappi J 48:52–56
Atalla RH (1979) Conformational effects in the hydrolysis of cellulose. In: Brown RD Jr, Jurasek L (eds) Hydrolysis of cellulose: mechanisms of enzymatic and acid catalysis, 1st edn. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 55–69
Ates S, Ni Y, Atik C (2009) Effects of the endoxylanase treatment on fiber characteristics, brightness stability and strength properties of bleached wheat straw pulp. Cellul Chem Technol 43:17–23
Bajpai P, Bajpai PK (2001) Development of a process for the production of dissolving kraft pulp using xylanase enzyme. Appita J 54:381–384
Bertaud F, Laurent A, Garnier N, Vorion S, Sacon VM, Petit-Conil M (2008) Impact of xylanase pre-treatment of eucalyptus wood chips on kraft pulping and pulp bleachability. In: The 10th EWLP, KTH Stockholm, Sweden, Aug 25–28
Bhat MK (2000) Cellulases and related enzymes in biotechnology. Biotechnol Adv 18:355–383
Brown J, Cheek MC, Jameel H, Joyce TW (1994) Medium-consistency ozone bleaching with enzyme pretreatment. Tappi J 77:105–109
Cao Y, Tan H (2006) Improvement of alkali solubility of cellulose with enzymatic treatment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70:176–182
DIN standard (1977) 54355, Bestimmung der Beständigkeit von Zellstoff gegen Natronlauge (Alkaliresistenz)
DIN standard (1981) 54370, Bestimmung des Glührückstandes
El-Din NMS, El-Megeid FFA (1994) The effect of cold alkali pretreatment on the reactivity of some cellulosic pulps towards acetylation. Holzforschung 48:496–500
Engström A-C, Ek M, Henriksson G (2006) Improved accessibility and reactivity of dissolving pulp for the viscose process: pretreatment with monocomponent endoglucanase. Biomacromol 7:2027–2031
Gellerstedt G, Li J (1996) An HPLC method for the quantitative determination of hexeneuronic acid groups in chemical pulps. Carbohydr Res 294:41–51
Grassl M, Michal G, Rexer B (1987) Catalytic activity of enzymes. In: Gerhartz W, Yamamoto YS, Kaudy L, Rounsavill JF, Schulz G (eds) Ullmann’s encyclopedia of industrial chemistry, 5th edn edn. Weinheim, New York, pp 352–363
Henriksson G, Christiernin M, Agnemo R (2005) Monocomponent endoglucanase treatment increases the reactivity of softwood sulphite dissolving pulp. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 32:211–214
Hilden L, Väljamäe P, Johansson G (2005) Surface character of pulp fibres studied using endoglucanases. J Biotechnol 118:386–397
Hinck JF, Casebier RL, Hamilton JK (1985) Dissolving pulp manufacture. In: Kocurek MJ, Ingruber OV, Al-Wong PE (eds) Sulfite science & technology, 3rd edn. TAPPI, CPPA, Atlanta, pp 213–243
Ibarra D, Köpcke V, Larsson PT, Jääskeläinen A-S, Ek M (2010) Combination of alkaline and enzymatic treatments as a process for upgrading sisal paper-grade pulp to dissolving-grade pulp. Bioresour Technol 101:7416–7423
ISO standard (2009) 2470-1, Paper, board and pulps—measurement of diffuse blue reflectance factor—Part 1: indoor daylight conditions (ISO brightness)
Jackson LS, Heitmann JA Jr, Joyce TW (1998) Production of dissolving pulp from recovered paper using enzymes. Tappi J 81:171–178
Jayme G, Roffael E (1969) Einfluss von Natriumhyroxidlösungen verschiedener Konzentration auf die Feinstruktur und die Reaktivität der Cellulose. Das Papier 23:405–412
Jayme G, Schenck U (1949) Die Auswirkung verschiedener alkalischer Veredelungsbedingungen auf das Verhalten von Zellstoffen bei der Acetylierung. Das Papier 3:469–476
Jeffries TW, Davis M, Rosin B, Landucci LL (1998) Mechanisms for kappa reduction and color removal by xylanases. In: 7th international conference on biotechnology in the pulp and paper industry, Vancouver, Canada, June 16–19
Jiang Z-H, Van Lierop B, Berry R (2000) Hexenuronic acid groups in pulping and bleaching chemistry. Tappi J 83:167–175
Kleinert TN (1975) Kalt-alkalische Zellstoffreinigung und Celluloseaktivität im Viskoseprozeß. Holzforschung 29:134–135
Köpcke V, Ibarra D, Ek M (2008) Increasing accessibility and reactivity of paper grade pulp by enzymatic treatment for use as dissolving pulp. Nordic Pulp Pap Res J 23:363–368
Köpcke V, Ibarra D, Larsson PT, Ek M (2010) Optimization of treatment sequences for the production of dissolving pulp from birch kraft pulp. Nordic Pulp Pap Res J 25:31–38
Krässig HA (1984) Struktur und Reaktivität von Cellulosefasern. Das Papier 38:571–582
Krässig HA (1993a) Accessibility in intercrystalline reactions. In: Krässig HA (ed) Cellulose: structure, accessibility and reactivity, 1st edn. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, Amsterdam, pp 187–214
Krässig HA (1993b) Methods of activation. In: Krässig HA (ed) Cellulose: structure, accessibility and reactivity, 1st edn. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, Amsterdam, pp 215–276
Krässig HA (1993c) The fiber structure. In: Krässig HA (ed) Cellulose: structure, accessibility and reactivity, 1st edn. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, Amsterdam, pp 6–12
Kvarnlöf N, Jönnson LJ, Söderlung C-A, Germgard U (2008) Enzyme pretreatment to improve the cellulose reactivity in the viscose process In: The 10th EWLP, KTH Stockholm, Sweden, Aug 25–28
Kyrklund B, Sihtola H (1963) On structural changes in pulp fibres due to cold alkali treatment. Papper och Trä 4:131–134
Leschinsky M, Zuckerstätter G, Weber HK, Patt R, Sixta H (2008a) Effect of autohydrolysis of Eucalyptus globulus wood on lignin structure. Part 2: influence of autohydrolysis intensity. Holzforschung 62:653–658
Leschinsky M, Zuckerstätter G, Weber HK, Patt R, Sixta H (2008b) Effect of autohydrolysis of Eucalyptus globulus wood on lignin structure. Part 1: comparison of different lignin fractions formed during water prehydrolysis. Holzforschung 62:645–652
Li J, Gellerstedt G (1997) The contribution to kappa number from hexeneuronic acid groups in pulp xylan. Carbohydr Res 302:213–218
Li J, Gellerstedt G (2002) Oxymercuration-demercuration kappa number: an accurate estimation of the lignin content in chemical pulps. Nordic Pulp Pap Res J 17:410–414
Luo M (2009) Enzymatic treatment of pulp for lyocell manufacture. Weyerhaeuser-Company. Patent PCT/US2008/086367
Marx-Figini M (1978) Significance of the intrinsic viscosity ratio of unsubstituted and nitrated cellulose in different solvents. Angew Makromol Chemie 72:161–171
Medve J, Karlsson J, Lee D, Tjerneld F (1998) Hydrolysis of microcrystalline cellulose by cellobiohydrolase I and endoglucanase II from Trichoderma reesei: adsorption, sugar production pattern, and synergism of the enzymes. Biotechnol Bioeng 59:621–634
Oksanen T, Buchert J, Viikari L (1997) The role of hemicelluloses in the hornification of bleached kraft pulps. Holzforschung 51:355–360
Philipp B, Rehder W, Lang H (1965) Zur Carboxylbestimmung in Chemiezellstoffen. Das Papier 19:1–9
Puls J, Janzon R, Saake B (2006) Comparative removal of hemicelluloses from paper pulps using nitren, cuen, NaOH, and KOH. Lenzinger Berichte 86:63–70
Rahkamo L, Viikari L, Buchert J, Paakkari T, Suortti T (1998) Enzymatic and alkaline treatments of hardwood dissolving pulp. Cellulose 5:79–88
Röder T, Moosbauer J, Fasching M, Bohn A, Fink H-P, Baldinger T, Sixta H (2006) Crystallinity determination of native cellulose—comparison of analytical methods. Lenzinger Berichte 86:85–89
Roncero MB, Torres AL, Colom JF, Vidal T (2005) The effect of xylanase on lignocellulosic components during the bleaching of wood pulps. Bioresour Technol 96:21–30
Ruland W (1961) X-ray determination of crystallinity and diffuse disorder scattering. Acta Crystallogr 14:1180–1185
Rydholm SA (1965) Carbohydrate-removing methods. In: Rydholm SA (ed) Pulping processes, 1st edn. Robert E. Krieger Publishing Company Inc., Malabar, pp 992–1024
SCAN-CM standard (1999) 15:99, Viscosity in cupriethylenediamine solution
Schelosky N, Röder T, Baldinger T (1999) Molmassenverteilung cellulosischer Produkte mittels Größenausschlußchromatographie in DMAC/LiCl. Das Papier 53:728–738
Schild G, Sixta H, Gehmayr V (2010) Production of a novel generation of sulphur-free dissolving pulps In: Zellcheming cellulose-symposium. Wiesbaden, Germany, June 29–30
Sears KD, Hinck JF, Sewell CG (1982) Highly reactive wood pulps for cellulose acetate production. J Appl Polym Sci 27:4599–4610
Shatalov AA, Pereira H (2008a) Effect of xylanases on peroxide bleachability of eucalypt (E. globulus) kraft pulp. Biochem Eng J 40:19–26
Shatalov AA, Pereira H (2008b) The hexenuronic acid nature of xylanase-assisted direct brightening effect. In: The 10th EWLP, KTH Stockholm, Sweden, Aug 25–28
Sixta H (2006a) Pulp properties and applications. In: Sixta H (ed) Handbook of pulp, vol 2, 1st edn. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, pp 1009–1069
Sixta H (2006b) Pulp purification. In: Sixta H (ed) Handbook of pulp, vol 2, 1st edn. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, pp 933–966
Sixta H, Schelosky N, Milacher W, Baldinger T, Röder T (2001) Characterization of alkali-soluble pulp fractions by chromatography. In: The 11th ISWPC, Nice, France, June 11–14
Sixta H, Potthast A, Krotschek AW (2006) Chemical pulping processes. In: Sixta H (ed) Handbook of pulp, vol 1, 1st edn. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, pp 109–509
Sixta H, Promberger A, Borgards A, Möslinger R (2007) Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Zellstoffes. Lenzing-Aktiengesellschaft. Patent PCT/AT2007/000225
Spence K, Tucker J, Hart PW (2009) Comparison of various hardwood kraft pulp pre-bleaching techniques. Tappi J April: 10–14
Strey G, Wesley-Smith J, Wolfaardt F (2009) The influence of mannanase and endoglucanase treatment on the fibre stability of spruce CTMP. Holzforschung 63:521–527
TAPPI standard (1993a) T 203 om-93, Alpha-, beta and gamma-cellulose in pulp
TAPPI standard (1993b) T 236 cm-85, Kappa number of pulp
TAPPI standard (2004) T 227 om-04, Freeness of pulp (Canadian standard method)
Treiber E, Rehnström J, Ameen C, Kolos F (1962) Über eine Laboratoriums-Viskose-Kleinstanlage zur Testung von Chemiefaserzellstoffen. Das Papier 16:85–94
Valchev J, Tsekova P (2008) Xylanase post-treatment as a progress in bleaching processes In: The 10th EWLP, KTH Stockholm, Sweden, Aug 25–28
Vuorinen T, Fagerstroem P, Buchert J, Tenkanen M, Teleman A (1999) Selective hydrolysis of hexenuronic acid groups and its application in ECF and TCF bleaching of kraft pulps. J Pulp Pap Sci 25:155–162
Wallis AFA, Wearne RH (1990) Chemical cellulose from radiata pine kraft pulp. Appita 43:355–357, 366
Wizani W, Krotscheck A, Schuster J, Lackner K (1994) Verfahren zur Herstellung von Viskosezellstoffen. Voestalpine-Industrieanlagen-GmbH, Lenzing-Aktiengesellschaft. Patent PCT/AT93/00183
Wollboldt RP, Zuckerstätter G, Weber HK, Sixta H (2009) Influence of xylan in E. globulus on accessibility, reactivity and supramolecular structure. In: The 15th ISWFPC, Oslo, Norway, June 15–18
Yang JL, Sacon VM, Law SE, Eriksson KE (1993) Bleaching of eucalyptus kraft pulp with the EnZone process. Tappi J 76:91–96
Zellcheming (1957) Merkblatt IV/33/57, Bestimmung des Wasserrückhaltevermögens (Quellwertes) von Zellstoffen
Acknowledgments
Financial support was provided by the Austrian government, the provinces of lower Austria, upper Austria, and Carinthia as well as by Lenzing AG. We also express our gratitude to the Johannes Kepler University, Linz, the University of Natural Resources and Applied Life Sciences, Vienna, and Lenzing AG for their in-kind contribution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gehmayr, V., Schild, G. & Sixta, H. A precise study on the feasibility of enzyme treatments of a kraft pulp for viscose application. Cellulose 18, 479–491 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-010-9483-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-010-9483-x