Abstract
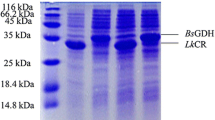
Carbonyl reductase, as biocatalyst, is very important to chiral alcohols production through asymmetric reduction of carbonyl compound. A novel thermal stable carbonyl reductase from Bacillus cereus (BcCR) dependant on NADPH was obtained through a new genome mining strategy proposed in this work. By analyzing its amino acid sequence and structure, the BcCR should be a thermal stability and wide pH tolerance carbonyl reductase. Its gene was cloned by PCR with B. cereus genomic DNA as template. Its heterologous expression system, E. coli BL21 (DE3) plysS/pET28a-bccr, was constructed, and BcCR was successfully expressed. Enzymatic properties show that at 57.5 °C and pH 7.0 it can reach maximum reaction rate. Its Km and Vmax to ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate is 1.85 mmol/L and 0.22 µmol/(min·mgprotein), respectively. It can catalyze the asymmetric reduction of the β-carbonyl compound, such as ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate to ethyl S-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyrate. This paper proposes a practical method for discovery of new carbonyl reductases, and provides a novel enzyme as biocatalyst for asymmetric reduction of β-carbonyl compound.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang Z-H, Luo L, Chang X, Zhou W, Chen G-H, Zhao Y, Wang Y-J (2012) J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39:835–841
Xu GC, Yu HL, Shang YP, Xu JH (2015) RSC Adv 46:22703–22711
Luo W, Deng XX, Huo J, Ruan T, Gong ZW, Yan JB, Yang Z-H, Quan C, Cui ZF (2018) Catal Lett 148:1714–1722
Yang Z-H, Zeng R, Yang G, Wang Y, Li LZ, Lv ZS, Yao M, Lai B (2008) J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:1047–1051
Wang YJ, Chen XP, Shen W, Liu ZQ, Zheng YG (2017) Biochem Eng J 128:54–62
Penning TM (2015) Chem-Biol Interact 234:236–246
Guo CX, Tang MH, Ni Y (2016) J Mol Catal B: Enzym 123:67–72
Wang YJ, Ying BB, Shen W, Zheng RC, Zheng YG (2017) Enzyme Microb Technol 107:32–40
Zhang YP, Wang HL, Chen LF, Wu K, Xie JL, Wei DZ (2016) J Mol Catal B: Enzym 134:51–60
Aggarwal N, Ananthathamula R, Kumar KV, Doble M, Chadha A (2018) Mol Catal 460:40–45
Ning CX, Su EZ, Wei DZ (2014) Arch Biochem Biophys 564:219–228
He YC, Zhang DP, Tao ZC, Zhang X, Yang ZX (2014) Bioresour Technol 172:342–348
Chen R, Liu X, Lin J, Wei D (2014) J Agric Chem Soc Japan 78:1350–1356
Guo R, Nie Y, Mu XQ, Xu Y, Xiao R (2014) J Mol Catal B: Enzym 105:66–73
Zaparucha A, de Berardinis V, Vaxelaire-Vergne C (2018) In: Williams G, Hall M (eds) Modern biocatalysis: advances towards synthetic biological systems. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Yu SZ, Li HX, Lu Y, Zheng GJ (2017) Appl Biochem Biotechnol 184:1319–1331
Yang Z-H, Ruan T, Luo W, Wu Y, Zuo ZY, Hou YL, Li LL (2018) Chinese patent 201810218384.2
Wilson K (2001) Curr Protoc Mol Biol 56:241–245
Cheng Y, Wei H, Sun R, Tian Z, Zheng X (2016) Anal Biochem 494:37–39
Kavanagh KL, Jornvall H, Persson B, Oppermann U (2008) Cell Mol Life Sci 65:3895–3906
Fukuda Y, Sakuraba H, Araki T, Ohshima T, Yoneda K (2016) Enzyme Microb Technol 91:17–25
Wang Q, Shen L, Ye T, Cao D, Chen R, Pei X, Xie T, Li Y, Gong W, Yin X (2012) Bioresour Technol 123:690–694
Wang LJ, Li CX, Ni Y, Zhang J, Liu X, Xu JH (2011) Bioresour Technol 102:7023–7028
Huang L, Xu JH, Yu HL (2015) J Biotechnol 203:54–61
Cao H, Mi L, Ye Q, Zang G, Yan M, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Li X, Xu L, Xiong J, Ouyang P, Ying H (2011) Bioresour Technol 102:1733–1739
Zhao FJ, Pei XQ, Ren ZQ, Wu Z-L (2016) Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:3567–3575
Wei P, Gao JX, Zheng GW, Wu H, Zong MH, Lou WY (2016) J Biotechnol 230:54–62
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge all the financial supports for this research by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21376184), the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars (State Education Ministry), Foundation from the Educational Commission of Hubei Province of China (Grant No. D20121108), the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2017YFF0205803), and the National Institute of Metrology of China (21-AKY1615).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest Statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, YL., Ruan, T., Hou, HS. et al. A Novel Thermal Stable Carbonyl Reductase from Bacillus cereus by Gene Mining as Biocatalyst for β-Carbonyl Ester Asymmetric Reduction Reaction. Catal Lett 149, 610–618 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-018-2645-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-018-2645-4