Abstract
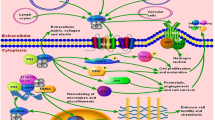
The fatality of cancer is mainly bestowed to the property of otherwise benign tumor cells to become malignant and invade surrounding tissues by circumventing normal tissue barriers through a process called metastasis. S100A4 which is a member of the S100 family of calcium-binding proteins has been shown to be able to activate and integrate pathways both intracellular and extracellular to generate a phenotypic response characteristic of cancer metastasis. A large number of studies have shown an increased expression level of S100A4 in various types of cancers. However, its implications in cancer metastasis in terms of whether an increased expression of S100A4 is a causal factor for metastasis or just another after effect of several other physiological and molecular changes in the body resulting from metastasis are not clear. Here we describe the emerging preclinical and clinical evidences implicating S100A4 protein, in both its forms (intracellular and extracellular) in the process of tumorigenesis and metastasis in humans. Based on studies utilizing S100A4 as a metastasis biomarker and molecular target for therapies such as gene therapy, we suggest that S100A4 has emerged as a promising molecule to be tested for anticancer drugs. This review provides an insight in the (1) molecular mechanisms through which S100A4 drives the tumorigenesis and metastasis and (2) developments made in the direction of evaluating S100A4 as a cancer biomarker and drug target.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moore, B. W. (1965). A soluble protein characteristic of the nervous system. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 19(6), 739–744.
Heizmann, C. W., & Cox, J. A. (1998). New perspectives on S100 proteins: a multifunctional Ca(2+)-, Zn(2+)- and Cu(2+)-binding protein family. BioMetals, 11(4), 383–397.
Otterbein, L. R., Kordowska, J., Witte-Hoffmann, C., Wang, C. L., & Dominguez, R. (2002). Crystal structures of S100A6 in the Ca(2+)-free and Ca(2+)-bound states: the calcium sensor mechanism of S100 proteins revealed at atomic resolution. Structure, 10(4), 557–567.
Drohat, A. C., Baldisseri, D. M., Rustandi, R. R., & Weber, D. J. (1998). Solution structure of calcium-bound rat S100B(betabeta) as determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry, 37(9), 2729–2740.
Wright, N. T., Varney, K. M., Ellis, K. C., Markowitz, J., Gitti, R. K., Zimmer, D. B., & Weber, D. J. (2005). The three-dimensional solution structure of Ca(2+)-bound S100A1 as determined by NMR spectroscopy. Journal of Molecular Biology, 353(2), 410–426.
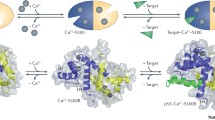
Garrett, S. C., Varney, K. M., Weber, D. J., & Bresnick, A. R. (2006). S100A4, a mediator of metastasis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281(2), 677–680.
Mazzucchelli, L. (2002). Protein S100A4: too long overlooked by pathologists? American Journal of Pathology, 160(1), 7–13.
Hernan, R., Fasheh, R., Calabrese, C., Frank, A. J., Maclean, K. H., Allard, D., Barraclough, R., & Gilbertson, R. J. (2003). ERBB2 up-regulates S100A4 and several other prometastatic genes in medulloblastoma. Cancer Research, 63(1), 140–148.
Tulchinsky, E. M., Georgiev, G. P., & Lukanidin, E. M. (1996). Novel AP-1 binding site created by DNA-methylation. Oncogene, 12(8), 1737–1745.
Cohn, M. A., Hjelmso, I., Wu, L. C., Guldberg, P., Lukanidin, E. M., & Tulchinsky, E. M. (2001). Characterization of Sp1, AP-1, CBF and KRC binding sites and minisatellite DNA as functional elements of the metastasis-associated mts1/S100A4 gene intronic enhancer. Nucleic Acids Research, 29(16), 3335–3346.
Li, Y., Liu, Z. L., Zhang, K. L., Chen, X. Y., Kong, Q. Y., Wu, M. L., Sun, Y., Liu, J., & Li, H. (2009). Methylation-associated silencing of S100A4 expression in human epidermal cancers. Experimental Dermatology, 18(10), 842–848.
Xie, R., Loose, D. S., Shipley, G. L., Xie, S., Bassett, R. L., Jr., & Broaddus, R. R. (2007). Hypomethylation-induced expression of S100A4 in endometrial carcinoma. Modern Pathology, 20(10), 1045–1054.
Rehman, I., Goodarzi, A., Cross, S. S., Leiblich, A., Catto, J. W., Phillips, J. T., & Hamdy, F. C. (2007). DNA methylation and immunohistochemical analysis of the S100A4 calcium binding protein in human prostate cancer. The Prostate, 67(4), 341–347.
Tarabykina, S., Griffiths, T. R., Tulchinsky, E., Mellon, J. K., Bronstein, I. B., & Kriajevska, M. (2007). Metastasis-associated protein S100A4: spotlight on its role in cell migration. Current Cancer Drug Targets, 7(3), 217–228.
Dukhanina, E. A., Dukhanin, A. S., Lomonosov, M. Y., Lukanidin, E. M., & Georgiev, G. P. (1997). Spectral studies on the calcium-binding properties of Mts1 protein and its interaction with target protein. FEBS Letters, 410(2–3), 403–406.
Takenaga, K., Nakanishi, H., Wada, K., Suzuki, M., Matsuzaki, O., Matsuura, A., & Endo, H. (1997). Increased expression of S100A4, a metastasis-associated gene, in human colorectal adenocarcinomas. Clinical Cancer Research, 3(12 Pt 1), 2309–2316.
Boni, R., Burg, G., Doguoglu, A., Ilg, E. C., Schafer, B. W., Muller, B., & Heizmann, C. W. (1997). Immunohistochemical localization of the Ca2+ binding S100 proteins in normal human skin and melanocytic lesions. British Journal of Dermatology, 137(1), 39–43.
Ilg, E. C., Schafer, B. W., & Heizmann, C. W. (1996). Expression pattern of S100 calcium-binding proteins in human tumors. International Journal of Cancer, 68(3), 325–332.
Duarte, W. R., Iimura, T., Takenaga, K., Ohya, K., Ishikawa, I., & Kasugai, S. (1999). Extracellular role of S100A4 calcium-binding protein in the periodontal ligament. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 255(2), 416–420.
Ambartsumian, N., Klingelhofer, J., Grigorian, M., Karlstrom, O., Sidenius, N., Georgiev, G., & Lukanidin, E. (1998). Tissue-specific posttranscriptional downregulation of expression of the S100A4(mts1) gene in transgenic animals. Invasion & Metastasis, 18(2), 96–104.
Gibbs, F. E., Barraclough, R., Platt-Higgins, A., Rudland, P. S., Wilkinson, M. C., & Parry, E. W. (1995). Immunocytochemical distribution of the calcium-binding protein p9Ka in normal rat tissues: variation in the cellular location in different tissues. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, 43(2), 169–180.
Klingelhofer, J., Ambartsumian, N. S., & Lukanidin, E. M. (1997). Expression of the metastasis-associated mts1 gene during mouse development. Developmental Dynamics, 210(2), 87–95.
Schneider, M., Hansen, J. L., & Sheikh, S. P. (2008). S100A4: a common mediator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, fibrosis and regeneration in diseases? Journal of Molecular Medicine, 86(5), 507–522.
Grigorian, M., Ambartsumian, N., & Lukanidin, E. (2008). Metastasis-inducing S100A4 protein: implication in non-malignant human pathologies. Current Molecular Medicine, 8(6), 492–496.
Goto, K., Endo, H., & Fujiyoshi, T. (1988). Cloning of the sequences expressed abundantly in established cell lines: identification of a cDNA clone highly homologous to S-100, a calcium binding protein. Journal of Biochemistry, 103(1), 48–53.
Ebralidze, A., Tulchinsky, E., Grigorian, M., Afanasyeva, A., Senin, V., Revazova, E., & Lukanidin, E. (1989). Isolation and characterization of a gene specifically expressed in different metastatic cells and whose deduced gene product has a high degree of homology to a Ca2+-binding protein family. Genes & Development, 3(7), 1086–1093.
Strutz, F., Okada, H., Lo, C. W., Danoff, T., Carone, R. L., Tomaszewski, J. E., & Neilson, E. G. (1995). Identification and characterization of a fibroblast marker: FSP1. The Journal of Cell Biology, 130(2), 393–405.
De Vouge, M. W., & Mukherjee, B. B. (1992). Transformation of normal rat kidney cells by v-K-ras enhances expression of transin 2 and an S-100-related calcium-binding protein. Oncogene, 7(1), 109–119.
Takenaga, K., Nakamura, Y., Endo, H., & Sakiyama, S. (1994). Involvement of S100-related calcium-binding protein pEL98 (or mts1) in cell motility and tumor cell invasion. Japanese Journal of Cancer Research, 85(8), 831–839.
Wang, Y. Y., Ye, Z. Y., Zhao, Z. S., Tao, H. Q., & Chu, Y. Q. (2010). High-level expression of S100A4 correlates with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Annals of Surgical Oncology, 17(1), 89–97.
Yonemura, Y., Endou, Y., Kimura, K., Fushida, S., Bandou, E., Taniguchi, K., Kinoshita, K., Ninomiya, I., Sugiyama, K., Heizmann, C. W., Schafer, B. W., & Sasaki, T. (2000). Inverse expression of S100A4 and E-cadherin is associated with metastatic potential in gastric cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, 6(11), 4234–4242.
Rosty, C., Ueki, T., Argani, P., Jansen, M., Yeo, C. J., Cameron, J. L., Hruban, R. H., & Goggins, M. (2002). Overexpression of S100A4 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas is associated with poor differentiation and DNA hypomethylation. American Journal of Pathology, 160(1), 45–50.
Ikenaga, N., Ohuchida, K., Mizumoto, K., Yu, J., Fujita, H., Nakata, K., Ueda, J., Sato, N., Nagai, E., & Tanaka, M. (2009). S100A4 mRNA is a diagnostic and prognostic marker in pancreatic carcinoma. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery, 13(10), 1852–1858.
Wang, H. Y., Zhang, J. Y., Cui, J. T., Tan, X. H., Li, W. M., Gu, J., & Lu, Y. Y. (2010). Expression status of S100A14 and S100A4 correlates with metastatic potential and clinical outcome in colorectal cancer after surgery. Oncology Reports, 23(1), 45–52.
Kim, J. H., Kim, C. N., Kim, S. Y., Lee, J. S., Cho, D., Kim, J. W., & Yoon, S. Y. (2009). Enhanced S100A4 protein expression is clinicopathologically significant to metastatic potential and p53 dysfunction in colorectal cancer. Oncology Reports, 22(1), 41–47.
Cho, Y. G., Kim, C. J., Nam, S. W., Yoon, S. H., Lee, S. H., Yoo, N. J., Lee, J. Y., & Park, W. S. (2005). Overexpression of S100A4 is closely associated with progression of colorectal cancer. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 11(31), 4852–4856.
Zou, M., Famulski, K. S., Parhar, R. S., Baitei, E., Al-Mohanna, F. A., Farid, N. R., & Shi, Y. (2004). Microarray analysis of metastasis-associated gene expression profiling in a murine model of thyroid carcinoma pulmonary metastasis: identification of S100A4 (Mts1) gene overexpression as a poor prognostic marker for thyroid carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 89(12), 6146–6154.
Zou, M., Al-Baradie, R. S., Al-Hindi, H., Farid, N. R., & Shi, Y. (2005). S100A4 (Mts1) gene overexpression is associated with invasion and metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma. British Journal of Cancer, 93(11), 1277–1284.
Moriyama-Kita, M., Endo, Y., Yonemura, Y., Heizmann, C. W., Miyamori, H., Sato, H., Yamamoto, E., & Sasaki, T. (2005). S100A4 regulates E-cadherin expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Letters, 230(2), 211–218.
Chen, X. L., Zhang, W. G., Chen, X. Y., Sun, Z. M., & Liu, S. H. (2006). Correlations of S100A4 protein expression to invasion and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. Ai Zheng, 25(9), 1134–1137.
Qi, R. X., & Xu, X. Y. (2007). Inverse correlation of S100A4 and E-cad protein expression and their clinical significance in non-small cell lung cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 29(9), 681–684.
Kimura, K., Endo, Y., Yonemura, Y., Heizmann, C. W., Schafer, B. W., Watanabe, Y., & Sasaki, T. (2000). Clinical significance of S100A4 and E-cadherin-related adhesion molecules in non-small cell lung cancer. International Journal of Oncology, 16(6), 1125–1131.
Gupta, S., Hussain, T., MacLennan, G. T., Fu, P., Patel, J., & Mukhtar, H. (2003). Differential expression of S100A2 and S100A4 during progression of human prostate adenocarcinoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 21(1), 106–112.
Bandiera, A., Melloni, G., Freschi, M., Giovanardi, M., Carretta, A., Borri, A., Ciriaco, P., & Zannini, P. (2009). Prognostic factors and analysis of S100a4 protein in resected pulmonary metastases from renal cell carcinoma. World Journal of Surgery, 33(7), 1414–1420.
Ismail, N. I., Kaur, G., Hashim, H., & Hassan, M. S. (2008). S100A4 overexpression proves to be independent marker for breast cancer progression. Cancer Cell International, 8, 12.
Pedersen, K. B., Nesland, J. M., Fodstad, O., & Maelandsmo, G. M. (2002). Expression of S100A4, E-cadherin, alpha- and beta-catenin in breast cancer biopsies. British Journal of Cancer, 87(11), 1281–1286.
Platt-Higgins, A. M., Renshaw, C. A., West, C. R., Winstanley, J. H., de Silva, R. S., Barraclough, R., & Rudland, P. S. (2000). Comparison of the metastasis-inducing protein S100A4 (p9ka) with other prognostic markers in human breast cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 89(2), 198–208.
Ambartsumian, N. S., Grigorian, M. S., Larsen, I. F., Karlstrom, O., Sidenius, N., Rygaard, J., Georgiev, G., & Lukanidin, E. (1996). Metastasis of mammary carcinomas in GRS/A hybrid mice transgenic for the mts1 gene. Oncogene, 13(8), 1621–1630.
Davies, M. P., Rudland, P. S., Robertson, L., Parry, E. W., Jolicoeur, P., & Barraclough, R. (1996). Expression of the calcium-binding protein S100A4 (p9Ka) in MMTV-neu transgenic mice induces metastasis of mammary tumours. Oncogene, 13(8), 1631–1637.
Maelandsmo, G. M., Hovig, E., Skrede, M., Engebraaten, O., Florenes, V. A., Myklebost, O., Grigorian, M., Lukanidin, E., Scanlon, K. J., & Fodstad, O. (1996). Reversal of the in vivo metastatic phenotype of human tumor cells by an anti-CAPL (mts1) ribozyme. Cancer Research, 56(23), 5490–5498.
Takenaga, K., Nakamura, Y., & Sakiyama, S. (1997). Expression of antisense RNA to S100A4 gene encoding an S100-related calcium-binding protein suppresses metastatic potential of high-metastatic Lewis lung carcinoma cells. Oncogene, 14(3), 331–337.
Saleem, M., Adhami, V. M., Ahmad, N., Gupta, S., & Mukhtar, H. (2005). Prognostic significance of metastasis-associated protein S100A4 (Mts1) in prostate cancer progression and chemoprevention regimens in an autochthonous mouse model. Clinical Cancer Research, 11(1), 147–153.
Rudland, P. S., Platt-Higgins, A., Renshaw, C., West, C. R., Winstanley, J. H., Robertson, L., & Barraclough, R. (2000). Prognostic significance of the metastasis-inducing protein S100A4 (p9Ka) in human breast cancer. Cancer Research, 60(6), 1595–1603.
Lee, W. Y., Su, W. C., Lin, P. W., Guo, H. R., Chang, T. W., & Chen, H. H. (2004). Expression of S100A4 and met: potential predictors for metastasis and survival in early-stage breast cancer. Oncology, 66(6), 429–438.
Kriajevska, M. V., Cardenas, M. N., Grigorian, M. S., Ambartsumian, N. S., Georgiev, G. P., & Lukanidin, E. M. (1994). Non-muscle myosin heavy chain as a possible target for protein encoded by metastasis-related mts-1 gene. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269(31), 19679–19682.
Helfman, D. M., Kim, E. J., Lukanidin, E., & Grigorian, M. (2005). The metastasis associated protein S100A4: role in tumour progression and metastasis. British Journal of Cancer, 92(11), 1955–1958.
Kriajevska, M., Fischer-Larsen, M., Moertz, E., Vorm, O., Tulchinsky, E., Grigorian, M., Ambartsumian, N., & Lukanidin, E. (2002). Liprin beta 1, a member of the family of LAR transmembrane tyrosine phosphatase-interacting proteins, is a new target for the metastasis-associated protein S100A4 (Mts1). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277(7), 5229–5235.
Endo, H., Takenaga, K., Kanno, T., Satoh, H., & Mori, S. (2002). Methionine aminopeptidase 2 is a new target for the metastasis-associated protein, S100A4. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277(29), 26396–26402.
Grigorian, M., Andresen, S., Tulchinsky, E., Kriajevska, M., Carlberg, C., Kruse, C., Cohn, M., Ambartsumian, N., Christensen, A., Selivanova, G., & Lukanidin, E. (2001). Tumor suppressor p53 protein is a new target for the metastasis-associated Mts1/S100A4 protein: functional consequences of their interaction. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276(25), 22699–22708.
Takenaga, K., Nakamura, Y., Sakiyama, S., Hasegawa, Y., Sato, K., & Endo, H. (1994). Binding of pEL98 protein, an S100-related calcium-binding protein, to nonmuscle tropomyosin. The Journal of Cell Biology, 124(5), 757–768.
Watanabe, Y., Usada, N., Minami, H., Morita, T., Tsugane, S., Ishikawa, R., Kohama, K., Tomida, Y., & Hidaka, H. (1993). Calvasculin, as a factor affecting the microfilament assemblies in rat fibroblasts transfected by src gene. FEBS Letters, 324(1), 51–55.
Li, Z. H., & Bresnick, A. R. (2006). The S100A4 metastasis factor regulates cellular motility via a direct interaction with myosin-IIA. Cancer Research, 66(10), 5173–5180.
Li, Z. H., Spektor, A., Varlamova, O., & Bresnick, A. R. (2003). Mts1 regulates the assembly of nonmuscle myosin-IIA. Biochemistry, 42(48), 14258–14266.
Kriajevska, M., Tarabykina, S., Bronstein, I., Maitland, N., Lomonosov, M., Hansen, K., Georgiev, G., & Lukanidin, E. (1998). Metastasis-associated Mts1 (S100A4) protein modulates protein kinase C phosphorylation of the heavy chain of nonmuscle myosin. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273(16), 9852–9856.
Dulyaninova, N. G., Malashkevich, V. N., Almo, S. C., & Bresnick, A. R. (2005). Regulation of myosin-IIA assembly and Mts1 binding by heavy chain phosphorylation. Biochemistry, 44(18), 6867–6876.
Berge, G., Costea, D. E., Berg, M., Rasmussen, H., Grotterod, I., Lothe, R. A., et al. (2010). Coexpression and nuclear colocalization of metastasis-promoting protein S100A4 and p53 without mutual regulation in colorectal carcinoma. Amino Acids, 42(4), 875–884.
Chen, H., Fernig, D. G., Rudland, P. S., Sparks, A., Wilkinson, M. C., & Barraclough, R. (2001). Binding to intracellular targets of the metastasis-inducing protein, S100A4 (p9Ka). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 286(5), 1212–1217.
Kim, E. J., & Helfman, D. M. (2003). Characterization of the metastasis-associated protein, S100A4. Roles of calcium binding and dimerization in cellular localization and interaction with myosin. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278(32), 30063–30073.
Tarabykina, S., Kriajevska, M., Scott, D. J., Hill, T. J., Lafitte, D., Derrick, P. J., Dodson, G. G., Lukanidin, E., & Bronstein, I. (2000). Heterocomplex formation between metastasis-related protein S100A4 (Mts1) and S100A1 as revealed by the yeast two-hybrid system. FEBS Letters, 475(3), 187–191.
Wang, G., Rudland, P. S., White, M. R., & Barraclough, R. (2000). Interaction in vivo and in vitro of the metastasis-inducing S100 protein, S100A4 (p9Ka) with S100A1. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275(15), 11141–11146.
Wang, G., Zhang, S., Fernig, D. G., Martin-Fernandez, M., Rudland, P. S., & Barraclough, R. (2005). Mutually antagonistic actions of S100A4 and S100A1 on normal and metastatic phenotypes. Oncogene, 24(8), 1445–1454.
Saleem, M., Kweon, M. H., Johnson, J. J., Adhami, V. M., Elcheva, I., Khan, N., Bin, H. B., Bhat, K. M., Sarfaraz, S., Reagan-Shaw, S., Spiegelman, V. S., Setaluri, V., & Mukhtar, H. (2006). S100A4 accelerates tumorigenesis and invasion of human prostate cancer through the transcriptional regulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(40), 14825–14830.
Bjornland, K., Winberg, J. O., Odegaard, O. T., Hovig, E., Loennechen, T., Aasen, A. O., Fodstad, O., & Maelandsmo, G. M. (1999). S100A4 involvement in metastasis: deregulation of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases in osteosarcoma cells transfected with an anti-S100A4 ribozyme. Cancer Research, 59(18), 4702–4708.
Adhami, V. M., Siddiqui, I. A., Ahmad, N., Gupta, S., & Mukhtar, H. (2004). Oral consumption of green tea polyphenols inhibits insulin-like growth factor-I-induced signaling in an autochthonous mouse model of prostate cancer. Cancer Research, 64(23), 8715–8722.
Schmidt-Hansen, B., Ornas, D., Grigorian, M., Klingelhofer, J., Tulchinsky, E., Lukanidin, E., & Ambartsumian, N. (2004). Extracellular S100A4(mts1) stimulates invasive growth of mouse endothelial cells and modulates MMP-13 matrix metalloproteinase activity. Oncogene, 23(32), 5487–5495.
Hofmann, M. A., Drury, S., Fu, C., Qu, W., Taguchi, A., Lu, Y., Avila, C., Kambham, N., Bierhaus, A., Nawroth, P., Neurath, M. F., Slattery, T., Beach, D., McClary, J., Nagashima, M., Morser, J., Stern, D., & Schmidt, A. M. (1999). RAGE mediates a novel proinflammatory axis: a central cell surface receptor for S100/calgranulin polypeptides. Cell, 97(7), 889–901.
Huttunen, H. J., Kuja-Panula, J., Sorci, G., Agneletti, A. L., Donato, R., & Rauvala, H. (2000). Coregulation of neurite outgrowth and cell survival by amphoterin and S100 proteins through receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) activation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275(51), 40096–40105.
Logsdon, C. D., Fuentes, M. K., Huang, E. H., & Arumugam, T. (2007). RAGE and RAGE ligands in cancer. Current Molecular Medicine, 7(8), 777–789.
Sauter, W., Rosenberger, A., Beckmann, L., Kropp, S., Mittelstrass, K., Timofeeva, M., Wolke, G., Steinwachs, A., Scheiner, D., Meese, E., Sybrecht, G., Kronenberg, F., Dienemann, H., Chang-Claude, J., Illig, T., Wichmann, H. E., Bickeboller, H., & Risch, A. (2008). Matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP1) is associated with early-onset lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 17(5), 1127–1135.
Basile, A., Biziato, D., Sherbet, G. V., Comi, P., & Cajone, F. (2008). Hyperthermia inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis: relative signaling status of P53, S100A4, and Notch in heat sensitive and resistant cell lines. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 103(1), 212–220.
Lindsey, J. C., Lusher, M. E., Anderton, J. A., Gilbertson, R. J., Ellison, D. W., & Clifford, S. C. (2007). Epigenetic deregulation of multiple S100 gene family members by differential hypomethylation and hypermethylation events in medulloblastoma. British Journal of Cancer, 97(2), 267–274.
Acknowledgments
The unpublished studies cited in the manuscript from the corresponding author’s laboratory are supported by The Hormel Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, S.K., Siddique, H.R. & Saleem, M. S100A4 calcium-binding protein is key player in tumor progression and metastasis: preclinical and clinical evidence. Cancer Metastasis Rev 31, 163–172 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-011-9338-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-011-9338-4