Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study is to evaluate the clinical significance of S100A4 mRNA expression in pancreatic cancer.
Materials and Methods
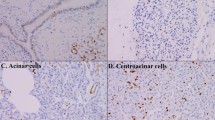
We obtained invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) cells from ten lesions, intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) cells from 20 lesions, and normal ductal cells from 20 normal pancreatic tissues by laser microdissection of frozen tissues. S100A4 expression was examined in the microdissected cells and in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples of 87 pancreatic cancers by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.
Results
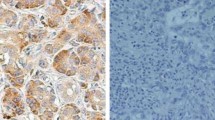
IDC cells expressed higher levels of S100A4 than IPMN cells (P = 0.002) and normal ductal cells (P < 0.001), although the difference between IPMN cells and normal ductal cells was not statistically significant (P = 0.070). Analysis of FFPE samples revealed that high S100A4 expression was significantly associated with a shorter overall survival (P = 0.023). In immunohistochemical analysis, the extent of S100A4 mRNA expression was significantly correlated with the expression of S100A4 protein (P = 0.028).
Conclusion
S100A4 could be a marker for malignancy in pancreatic tumors and for poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eskelinen MJ, Haglund UH. Prognosis of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma: review of clinical and histopathological variables and possible uses of new molecular methods. Eur J Surg 1999;165:292–306.
Yeo TP, Hruban RH, Leach SD, Wilentz RE, Sohn TA, Kern SE, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Maitra A, Goggins M, Canto MI, Abrams RA, Laheru D et al. Pancreatic cancer. Curr Probl Cancer 2002;26:176–275.
Sener SF, Fremgen A, Menck HR, Winchester DP. Pancreatic cancer: a report of treatment and survival trends for 100,313 patients diagnosed from 1985–1995, using the National Cancer Database. J Am Coll Surg 1999;189:1–7.
American gastroenterological association medical position statement: epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 1999;117:1463–1484.
Adsay NV, Conlon KC, Zee SY, Brennan MF, Klimstra DS. Intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: an analysis of in situ and invasive carcinomas in 28 patients. Cancer 2002;94:62–77.
Garcea G, Neal CP, Pattenden CJ, Steward WP, Berry DP. Molecular prognostic markers in pancreatic cancer: a systematic review. Eur J Cancer 2005;41:2213–2236.
Sinicrope FA, Evans DB, Leach SD, Cleary KR, Fenoglio CJ, Lee JJ, Abbruzzese JL. bcl-2 and p53 expression in resectable pancreatic adenocarcinomas: association with clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res 1996;2:2015–2022.
Friess H, Lu Z, Andren-Sandberg A, Berberat P, Zimmermann A, Adler G, Schmid R, Buchler MW. Moderate activation of the apoptosis inhibitor bcl-xL worsens the prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg 1998;228:780–787.
Nio Y, Dong M, Iguchi C, Yamasawa K, Toga T, Itakura M, Tamura K. Expression of Bcl-2 and p53 protein in resectable invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas: effects on clinical outcome and efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy. J Surg Oncol 2001;76:188–196.
Yamamoto H, Itoh F, Iku S, Adachi Y, Fukushima H, Sasaki S, Mukaiya M, Hirata K, Imai K. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in human pancreatic adenocarcinomas: clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of matrilysin expression. J Clin Oncol 2001;19:1118–1127.
Joo YE, Rew JS, Park CS, Kim SJ. Expression of E-cadherin, alpha- and beta-catenins in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreatology 2002;2:129–137.
Seo Y, Baba H, Fukuda T, Takashima M, Sugimachi K. High expression of vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with liver metastasis and a poor prognosis for patients with ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2000;88:2239–2245.
Niedergethmann M, Hildenbrand R, Wostbrock B, Hartel M, Sturm JW, Richter A, Post S. High expression of vascular endothelial growth factor predicts early recurrence and poor prognosis after curative resection for ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Pancreas 2002;25:122–129.
Ikeda N, Adachi M, Taki T, Huang C, Hashida H, Takabayashi A, Sho M, Nakajima Y, Kanehiro H, Hisanaga M, Nakano H, Miyake M. Prognostic significance of angiogenesis in human pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer 1999;79:1553–1563.
Kuwahara K, Sasaki T, Kuwada Y, Murakami M, Yamasaki S, Chayama K. Expressions of angiogenic factors in pancreatic ductal carcinoma: a correlative study with clinicopathologic parameters and patient survival. Pancreas 2003;26:344–349.
Giovannetti E, Del Tacca M, Mey V, Funel N, Nannizzi S, Ricci S, Orlandini C, Boggi U, Campani D, Del Chiaro M, Iannopollo M, Bevilacqua G et al. Transcription analysis of human equilibrative nucleoside transporter-1 predicts survival in pancreas cancer patients treated with gemcitabine. Cancer Res 2006;66:3928–3935.
Donato R. S100: a multigenic family of calcium-modulated proteins of the EF-hand type with intracellular and extracellular functional roles. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2001;33:637–668.
Tarabykina S, Kriajevska M, Scott DJ, Hill TJ, Lafitte D, Derrick PJ, Dodson GG, Lukanidin E, Bronstein I. Heterocomplex formation between metastasis-related protein S100A4 (Mts1) and S100A1 as revealed by the yeast two-hybrid system. FEBS Lett 2000;475:187–191.
Rudland PS, Platt-Higgins A, Renshaw C, West CR, Winstanley JH, Robertson L, Barraclough R. Prognostic significance of the metastasis-inducing protein S100A4 (p9Ka) in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 2000;60:1595–1603.
Yonemura Y, Endou Y, Kimura K, Fushida S, Bandou E, Taniguchi K, Kinoshita K, Ninomiya I, Sugiyama K, Heizmann CW, Schafer BW, Sasaki T. Inverse expression of S100A4 and E-cadherin is associated with metastatic potential in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2000;6:4234–4242.
Takenaga K, Nakamura Y, Sakiyama S. Expression of antisense RNA to S100A4 gene encoding an S100-related calcium-binding protein suppresses metastatic potential of high-metastatic Lewis lung carcinoma cells. Oncogene 1997;14:331–337.
Strutz F, Okada H, Lo CW, Danoff T, Carone RL, Tomaszewski JE, Neilson EG. Identification and characterization of a fibroblast marker: FSP1. J Cell Biol 1995;130:393–405.
Grigorian M, Ambartsumian N, Lykkesfeldt AE, Bastholm L, Elling F, Georgiev G, Lukanidin E. Effect of mts1 (S100A4) expression on the progression of human breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer 1996;67:831–841.
Lloyd BH, Platt-Higgins A, Rudland PS, Barraclough R. Human S100A4 (p9Ka) induces the metastatic phenotype upon benign tumour cells. Oncogene 1998;17:465–473.
Maelandsmo GM, Hovig E, Skrede M, Engebraaten O, Florenes VA, Myklebost O, Grigorian M, Lukanidin E, Scanlon KJ, Fodstad O. Reversal of the in vivo metastatic phenotype of human tumor cells by an anti-CAPL (mts1) ribozyme. Cancer Res 1996;56:5490–5498.
Bjornland K, Winberg JO, Odegaard OT, Hovig E, Loennechen T, Aasen AO, Fodstad O, Maelandsmo GM. S100A4 involvement in metastasis: deregulation of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases in osteosarcoma cells transfected with an anti-S100A4 ribozyme. Cancer Res 1999;59:4702–4708.
Miyamori H, Hasegawa K, Kim KR, Sato H. Expression of metastasis-associated mts1 gene is co-induced with membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) during oncogenic transformation and tubular formation of Madin Darby canine kidney (MDCK) epithelial cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 2000;18:51–56.
Schmidt-Hansen B, Klingelhofer J, Grum-Schwensen B, Christensen A, Andresen S, Kruse C, Hansen T, Ambartsumian N, Lukanidin E, Grigorian M. Functional significance of metastasis-inducing S100A4(Mts1) in tumor-stroma interplay. J Biol Chem 2004;279:24498–24504.
Semov A, Moreno MJ, Onichtchenko A, Abulrob A, Ball M, Ekiel I, Pietrzynski G, Stanimirovic D, Alakhov V. Metastasis-associated protein S100A4 induces angiogenesis through interaction with Annexin II and accelerated plasmin formation. J Biol Chem 2005;280:20833–20841.
arrett SC, Varney KM, Weber DJ, Bresnick AR. S100A4, a mediator of metastasis. J Biol Chem 2006;281:677–680.
Ninomiya I, Ohta T, Fushida S, Endo Y, Hashimoto T, Yagi M, Fujimura T, Nishimura G, Tani T, Shimizu K, Yonemura Y, Heizmann CW et al. Increased expression of S100A4 and its prognostic significance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol 2001;18:715–720.
Kimura K, Endo Y, Yonemura Y, Heizmann CW, Schafer BW, Watanabe Y, Sasaki T. Clinical significance of S100A4 and E-cadherin-related adhesion molecules in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol 2000;16:1125–1131.
Davies BR, O’Donnell M, Durkan GC, Rudland PS, Barraclough R, Neal DE, Mellon JK. Expression of S100A4 protein is associated with metastasis and reduced survival in human bladder cancer. J Pathol 2002;196:292–299.
Rosty C, Ueki T, Argani P, Jansen M, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Hruban RH, Goggins M. Overexpression of S100A4 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas is associated with poor differentiation and DNA hypomethylation. Am J Pathol 2002;160:45–50.
Ai KX, Lu LY, Huang XY, Chen W, Zhang HZ. Prognostic significance of S100A4 and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2008;14:1931–1935.
Oida Y, Yamazaki H, Tobita K, Mukai M, Ohtani Y, Miyazaki N, Abe Y, Imaizumi T, Makuuchi H, Ueyama Y, Nakamura M. Increased S100A4 expression combined with decreased E-cadherin expression predicts a poor outcome of patients with pancreatic cancer. Oncol Rep 2006;16:457–463.
Mahon PC, Baril P, Bhakta V, Chelala C, Caulee K, Harada T, Lemoine NR. S100A4 contributes to the suppression of BNIP3 expression, chemoresistance, and inhibition of apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 2007;67:6786–6795.
Hamilton SR and Aaltonen LA. (eds): World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Digestive System. Lyon: IARC Press, 2000.
Tachikawa T, Irie T. A new molecular biology approach in morphology: basic method and application of laser microdissection. Med Electron Microsc 2004;37:82–88.
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Miyasaka Y, Yu J, Cui L, Yamaguchi H, Toma H, Takahata S, Sato N, Nagai E, Yamaguchi K, Tsuneyoshi M et al. Over-expression of S100A2 in pancreatic cancer correlates with progression and poor prognosis. J Pathol 2007;213:275–282.
Godfrey TE, Kim SH, Chavira M, Ruff DW, Warren RS, Gray JW, Jensen RH. Quantitative mRNA expression analysis from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues using 5′ nuclease quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. J Mol Diagnostics 2000;2:84–91.
Abrahamsen HN, Steiniche T, Nexo E, Hamilton-Dutoit SJ, Sorensen BS. Towards quantitative mRNA analysis in paraffin-embedded tissues using real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction: a methodological study on lymph nodes from melanoma patients. J Mol Diagnostics 2003;5:34–41.
Hoffmann AC, Mori R, Vallbohmer D, Brabender J, Klein E, Drebber U, Baldus SE, Cooc J, Azuma M, Metzger R, Hoelscher AH, Danenberg KD et al. High expression of HIF1a is a predictor of clinical outcome in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas and correlated to PDGFA, VEGF, and bFGF. Neoplasia 2008;10:674–679.
McCarthy DM, Maitra A, Argani P, Rader AE, Faigel DO, Van Heek NT, Hruban RH, Wilentz RE. Novel markers of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in fine-needle aspiration: mesothelin and prostate stem cell antigen labeling increases accuracy in cytologically borderline cases. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2003;11:238–243.
Khalid A, Pal R, Sasatomi E, Swalsky P, Slivka A, Whitcomb D, Finkelstein S. Use of microsatellite marker loss of heterozygosity in accurate diagnosis of pancreaticobiliary malignancy from brush cytology samples. Gut 2004;53:1860–1865.
Govil H, Reddy V, Kluskens L, Treaba D, Massarani-Wafai R, Selvaggi S, Gattuso P. Brush cytology of the biliary tract: retrospective study of 278 cases with histopathologic correlation. Diagn Cytopathol 2002;26:273–277.
Selvaggi SM. Biliary brushing cytology. Cytopathology 2004;15:74–79.
Buchholz M, Kestler H, Gress TM. Differential diagnosis of pancreatic tumors by molecular analysis of clinical specimens. Pancreatology 2008;8:551–557.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and grants from the Takeda Science Foundation, Pancreas Research Foundation of Japan, and Nakajima Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikenaga, N., Ohuchida, K., Mizumoto, K. et al. S100A4 mRNA is a Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker in Pancreatic Carcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg 13, 1852–1858 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-009-0978-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-009-0978-4