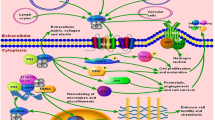
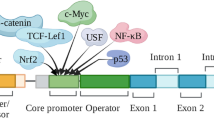
Abstract
Multiple reports have focused on S100A4’s role in cancer progression, specifically its ability to enhance metastasis. However, recent studies have linked S100A4 to several diseases besides cancer, including kidney fibrosis, cirrhosis, pulmonary disease, cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis, arthritis and neuronal injuries. Common to all these diseases is the involvement of fibrotic and inflammatory processes, i.e. processes greatly dependent on tissue remodelling, cell motility and epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Therefore, the basic biological mechanisms behind S100A4’s effects are emerging. S100A4 belongs to the S100 family of proteins that contain two Ca2+-binding sites including a canonical EF-hand motif. S100A4 is involved in the regulation of a wide range of biological effects including cell motility, survival, differentiation and contractility. S100A4 has both intracellular and extracellular effects. Hence, S100A4 interacts with cytoskeletal proteins and enhances metastasis of several types of cancer cells. In addition, S100A4 is secreted by unknown mechanisms, thus, paracrinely stimulating a variety of cellular responses, including angiogenesis and neuronal growth. Although many cellular effects of S100A4 are well described, the molecular mechanisms whereby S100A4 elicits these responses remain largely unknown. However, it is likely that the intracellular and the extracellular effects involve distinct mechanisms. In this review, we explore the possible roles of S100A4 in non-cancer diseases and employ this knowledge to describe underlying biological mechanisms including a change in cellular phenotype towards less tightly adherent cells and activation of fibrotic processes that may explain this protein’s involvement in multiple pathologies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iwano M, Plieth D, Danoff TM, Xue C, Okada H, Neilson EG (2002) Evidence that fibroblasts derive from epithelium during tissue fibrosis. J Clin Invest 110:341–350
Nishitani Y, Iwano M, Yamaguchi Y, Harada K, Nakatani K, Akai Y, Nishino T, Shiiki H, Kanauchi M, Saito Y, Neilson EG (2005) Fibroblast-specific protein 1 is a specific prognostic marker for renal survival in patients with IgAN. Kidney Int 68:1078–1085
Zeisberg M, Hanai J, Sugimoto H, Mammoto T, Charytan D, Strutz F, Kalluri R (2003) BMP-7 counteracts TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and reverses chronic renal injury. Nat Med 9:964–968
Rivard CJ, Brown LM, Almeida NE, Maunsbach AB, Pihakaski-Maunsbach K, Andres-Hernando A, Capasso JM, Berl T (2007) Expression of the calcium-binding protein S100A4 is markedly up-regulated by osmotic stress and is involved in the renal osmoadaptive response. J Biol Chem 282:6644–6652
Zeisberg M, Yang C, Martino M, Duncan M, Rieder F, Tanjore H, Kalluri R (2007) Fibroblasts derive from hepatocytes in liver fibrosis via epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem 282:23337–23347
Robertson H, Kirby JA, Yip WW, Jones DE, Burt AD (2007) Biliary epithelial–mesenchymal transition in posttransplantation recurrence of primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 45:977–981
Greenway S, van Suylen RJ, Du Marchie Sarvaas G, Kwan E, Ambartsumian N, Lukanidin E, Rabinovitch M (2004) S100A4/Mts1 produces murine pulmonary artery changes resembling plexogenic arteriopathy and is increased in human plexogenic arteriopathy. Am J Pathol 164:253–262
Kwapiszewska G, Wilhelm J, Wolff S, Laumanns I, Koenig IR, Ziegler A, Seeger W, Bohle RM, Weissmann N, Fink L (2005) Expression profiling of laser-microdissected intrapulmonary arteries in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Respir Res 6:109
Lawson WE, Polosukhin VV, Zoia O, Stathopoulos GT, Han W, Plieth D, Loyd JE, Neilson EG, Blackwell TS (2005) Characterization of fibroblast-specific protein 1 in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 171:899–907
Inamoto S, Murao S, Yokoyama M, Kitazawa S, Maeda S (2000) Isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury resulting in altered S100A4 and S100A11 protein expression in the rat. Pathol Int 50:480–485
Schneider M, Kostin S, Strom CC, Aplin M, Lyngbaek S, Theilade J, Grigorian M, Andersen CB, Lukanidin E, Lerche Hansen J, Sheikh SP (2007) S100A4 is upregulated in injured myocardium and promotes growth and survival of cardiac myocytes. Cardiovasc Res 75:40–50
Zeisberg EM, Tarnavski O, Zeisberg M, Dorfman AL, McMullen JR, Gustafsson E, Chandraker A, Yuan X, Pu WT, Roberts AB, Neilson EG, Sayegh MH, Izumo S, Kalluri R (2007) Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition contributes to cardiac fibrosis. Nat Med 13:952–961
Klingelhofer J, Senolt L, Baslund B, Nielsen GH, Skibshoj I, Pavelka K, Neidhart M, Gay S, Ambartsumian N, Hansen BS, Petersen J, Lukanidin E, Grigorian M (2007) Up-regulation of metastasis-promoting S100A4 (Mts-1) in rheumatoid arthritis: putative involvement in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 56:779–789
Masuda K, Masuda R, Neidhart M, Simmen BR, Michel BA, Muller-Ladner U, Gay RE, Gay S (2002) Molecular profile of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis depends on the stage of proliferation. Arthritis Res 4:R8
Senolt L, Grigorian M, Lukanidin E, Michel BA, Gay RE, Gay S, Pavelka K, Neidhart M (2006) S100A4 (Mts1): is there any relation to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis? Autoimmun Rev 5:129–131
Senolt L, Grigorian M, Lukanidin E, Simmen B, Michel BA, Pavelka K, Gay RE, Gay S, Neidhart M (2006) S100A4 is expressed at site of invasion in rheumatoid arthritis synovium and modulates production of matrix metalloproteinases. Ann Rheum Dis 65:1645–1648
Yammani RR, Carlson CS, Bresnick AR, Loeser RF (2006) Increase in production of matrix metalloproteinase 13 by human articular chondrocytes due to stimulation with S100A4: Role of the receptor for advanced glycation end products. Arthritis Rheum 54:2901–2911
Kozlova EN, Lukanidin E (2002) Mts1 protein expression in the central nervous system after injury. Glia 37:337–348
Kozlova EN, Lukanidin E (1999) Metastasis-associated mts1 (S100A4) protein is selectively expressed in white matter astrocytes and is up-regulated after peripheral nerve or dorsal root injury. Glia 27:249–258
Sandelin M, Zabihi S, Liu L, Wicher G, Kozlova EN (2004) Metastasis-associated S100A4 (Mts1) protein is expressed in subpopulations of sensory and autonomic neurons and in Schwann cells of the adult rat. J Comp Neurol 473:233–243
Ambartsumian NS, Grigorian MS, Larsen IF, Karlstrom O, Sidenius N, Rygaard J, Georgiev G, Lukanidin E (1996) Metastasis of mammary carcinomas in GRS/A hybrid mice transgenic for the mts1 gene. Oncogene 13:1621–1630
Davies MP, Rudland PS, Robertson L, Parry EW, Jolicoeur P, Barraclough R (1996) Expression of the calcium-binding protein S100A4 (p9Ka) in MMTV-neu transgenic mice induces metastasis of mammary tumours. Oncogene 13:1631–1637
Grigorian M, Ambartsumian N, Lykkesfeldt AE, Bastholm L, Elling F, Georgiev G, Lukanidin E (1996) Effect of mts1 (S100A4) expression on the progression of human breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer 67:831–841
Lloyd BH, Platt-Higgins A, Rudland PS, Barraclough R (1998) Human S100A4 (p9Ka) induces the metastatic phenotype upon benign tumour cells. Oncogene 17:465–473
Maelandsmo GM, Hovig E, Skrede M, Engebraaten O, Florenes VA, Myklebost O, Grigorian M, Lukanidin E, Scanlon KJ, Fodstad O (1996) Reversal of the in vivo metastatic phenotype of human tumor cells by an anti-CAPL (mts1) ribozyme. Cancer Res 56:5490–5498
Takenaga K, Nakamura Y, Sakiyama S (1997) Expression of antisense RNA to S100A4 gene encoding an S100-related calcium-binding protein suppresses metastatic potential of high-metastatic Lewis lung carcinoma cells. Oncogene 14:331–337
Tarabykina S, Griffiths TR, Tulchinsky E, Mellon JK, Bronstein IB, Kriajevska M (2007) Metastasis-associated protein S100A4: spotlight on its role in cell migration. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 7:217–228
Donato R (2001) S100: a multigenic family of calcium-modulated proteins of the EF-hand type with intracellular and extracellular functional roles. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 33:637–668
Santamaria-Kisiel L, Rintala-Dempsey AC, Shaw GS (2006) Calcium-dependent and -independent interactions of the S100 protein family. Biochem J 396:201–214
Tarabykina S, Kriajevska M, Scott DJ, Hill TJ, Lafitte D, Derrick PJ, Dodson GG, Lukanidin E, Bronstein I (2000) Heterocomplex formation between metastasis-related protein S100A4 (Mts1) and S100A1 as revealed by the yeast two-hybrid system. FEBS Lett 475:187–191
Dulyaninova NG, Malashkevich VN, Almo SC, Bresnick AR (2005) Regulation of myosin-IIA assembly and Mts1 binding by heavy chain phosphorylation. Biochemistry 44:6867–6876
Kriajevska M, Bronstein IB, Scott DJ, Tarabykina S, Fischer-Larsen M, Issinger O, Lukanidin E (2000) Metastasis-associated protein Mts1 (S100A4) inhibits CK2-mediated phosphorylation and self-assembly of the heavy chain of nonmuscle myosin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1498:252–263
Kriajevska M, Tarabykina S, Bronstein I, Maitland N, Lomonosov M, Hansen K, Georgiev G, Lukanidin E (1998) Metastasis-associated Mts1 (S100A4) protein modulates protein kinase C phosphorylation of the heavy chain of nonmuscle myosin. J Biol Chem 273:9852–9856
Li ZH, Spektor A, Varlamova O, Bresnick AR (2003) Mts1 regulates the assembly of nonmuscle myosin-IIA. Biochemistry 42:14258–14266
Ford HL, Silver DL, Kachar B, Sellers JR, Zain SB (1997) Effect of Mts1 on the structure and activity of nonmuscle myosin II. Biochemistry 36:16321–16327
Kriajevska M, Fischer-Larsen M, Moertz E, Vorm O, Tulchinsky E, Grigorian M, Ambartsumian N, Lukanidin E (2002) Liprin beta 1, a member of the family of LAR transmembrane tyrosine phosphatase-interacting proteins, is a new target for the metastasis-associated protein S100A4 (Mts1). J Biol Chem 277:5229–5235
Chen H, Fernig DG, Rudland PS, Sparks A, Wilkinson MC, Barraclough R (2001) Binding to intracellular targets of the metastasis-inducing protein, S100A4 (p9Ka). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 286:1212–1217
Fernandez-Fernandez MR, Veprintsev DB, Fersht AR (2005) Proteins of the S100 family regulate the oligomerization of p53 tumor suppressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:4735–4740
Grigorian M, Andresen S, Tulchinsky E, Kriajevska M, Carlberg C, Kruse C, Cohn M, Ambartsumian N, Christensen A, Selivanova G, Lukanidin E (2001) Tumor suppressor p53 protein is a new target for the metastasis-associated Mts1/S100A4 protein: functional consequences of their interaction. J Biol Chem 276:22699–22708
Novitskaya V, Grigorian M, Kriajevska M, Tarabykina S, Bronstein I, Berezin V, Bock E, Lukanidin E (2000) Oligomeric forms of the metastasis-related Mts1 (S100A4) protein stimulate neuronal differentiation in cultures of rat hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem 275:41278–41286
Wang G, Rudland PS, White MR, Barraclough R (2000) Interaction in vivo and in vitro of the metastasis-inducing S100 protein, S100A4 (p9Ka) with S100A1. J Biol Chem 275:11141–11146
Wang G, Zhang S, Fernig DG, Martin-Fernandez M, Rudland PS, Barraclough R (2005) Mutually antagonistic actions of S100A4 and S100A1 on normal and metastatic phenotypes. Oncogene 24:1445–1454
Helfman DM, Kim EJ, Lukanidin E, Grigorian M (2005) The metastasis associated protein S100A4: role in tumour progression and metastasis. Br J Cancer 92:1955–1958
Belot N, Pochet R, Heizmann CW, Kiss R, Decaestecker C (2002) Extracellular S100A4 stimulates the migration rate of astrocytic tumor cells by modifying the organization of their actin cytoskeleton. Biochim Biophys Acta 1600:74–83
Schmidt-Hansen B, Klingelhofer J, Grum-Schwensen B, Christensen A, Andresen S, Kruse C, Hansen T, Ambartsumian N, Lukanidin E, Grigorian M (2004) Functional significance of metastasis-inducing S100A4(Mts1) in tumor-stroma interplay. J Biol Chem 279:24498–24504
Ambartsumian N, Klingelhofer J, Grigorian M, Christensen C, Kriajevska M, Tulchinsky E, Georgiev G, Berezin V, Bock E, Rygaard J, Cao R, Cao Y, Lukanidin E (2001) The metastasis-associated Mts1(S100A4) protein could act as an angiogenic factor. Oncogene 20:4685–4695
Schmidt-Hansen B, Ornas D, Grigorian M, Klingelhofer J, Tulchinsky E, Lukanidin E, Ambartsumian N (2004) Extracellular S100A4(mts1) stimulates invasive growth of mouse endothelial cells and modulates MMP-13 matrix metalloproteinase activity. Oncogene 23:5487–5495
Kikuchi N, Horiuchi A, Osada R, Imai T, Wang C, Chen X, Konishi I (2006) Nuclear expression of S100A4 is associated with aggressive behavior of epithelial ovarian carcinoma: an important autocrine/paracrine factor in tumor progression. Cancer Sci 97:1061–1069
Lawrie A, Spiekerkoetter E, Martinez EC, Ambartsumian N, Sheward WJ, Maclean MR, Harmar AJ, Schmidt AM, Lukanidin E, Rabinovitch M (2005) Interdependent serotonin transporter and receptor pathways regulate S100A4/Mts1, a gene associated with pulmonary vascular disease. Circ Res 97:227–235
Fang Z, Forslund N, Takenaga K, Lukanidin E, Kozlova EN (2006) Sensory neurite outgrowth on white matter astrocytes is influenced by intracellular and extracellular S100A4 protein. J Neurosci Res 83:619–626
Kiryushko D, Novitskaya V, Soroka V, Klingelhofer J, Lukanidin E, Berezin V, Bock E (2006) Molecular mechanisms of Ca(2+) signaling in neurons induced by the S100A4 protein. Mol Cell Biol 26:3625–3638
Stary M, Schneider M, Sheikh SP, Weitzer G (2006) Parietal endoderm secreted S100A4 promotes early cardiomyogenesis in embryoid bodies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 343:555–563
Pedersen MV, Kohler LB, Grigorian M, Novitskaya V, Bock E, Lukanidin E, Berezin V (2004) The Mts1/S100A4 protein is a neuroprotectant. J Neurosci Res 77:777–786
Semov A, Moreno MJ, Onichtchenko A, Abulrob A, Ball M, Ekiel I, Pietrzynski G, Stanimirovic D, Alakhov V (2005) Metastasis-associated protein S100A4 induces angiogenesis through interaction with annexin II and accelerated plasmin formation. J Biol Chem 280:20833–20841
Okada H, Danoff TM, Kalluri R, Neilson EG (1997) Early role of Fsp1 in epithelial–mesenchymal transformation. Am J Physiol 273:F563–574
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R, Thompson EW (2006) The epithelial–mesenchymal transition: new insights in signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol 172:973–981
Thiery JP, Sleeman JP (2006) Complex networks orchestrate epithelial–mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:131–142
Strutz F, Okada H, Lo CW, Danoff T, Carone RL, Tomaszewski JE, Neilson EG (1995) Identification and characterization of a fibroblast marker: FSP1. J Cell Biol 130:393–405
Garrett SC, Varney KM, Weber DJ, Bresnick AR (2006) S100A4, a mediator of metastasis. J Biol Chem 281:677–680
Mazzucchelli L (2002) Protein S100A4: too long overlooked by pathologists? m J Pathol 160:7–13
Agerbaek M, Alsner J, Marcussen N, Lundbeck F, Von der Maase H (2006) Focal S100A4 protein expression is an independent predictor of development of metastatic disease in cystectomized bladder cancer patients. Eur Urol 50:777–785
Cho YG, Nam SW, Kim TY, Kim YS, Kim CJ, Park JY, Lee JH, Kim HS, Lee JW, Park CH, Song YH, Lee SH, Yoo NJ, Lee JY, Park WS (2003) Overexpression of S100A4 is closely related to the aggressiveness of gastric cancer. Apmis 111:539–545
Davies BR, O’ Donnell M, Durkan GC, Rudland PS, Barraclough R, Neal DE, Mellon JK (2002) Expression of S100A4 protein is associated with metastasis and reduced survival in human bladder cancer. J Pathol 196:292–299
de Silva Rudland S, Martin L, Roshanlall C, Winstanley J, Leinster S, Platt-Higgins A, Carroll J, West C, Barraclough R, Rudland P (2006) Association of S100A4 and osteopontin with specific prognostic factors and survival of patients with minimally invasive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12:1192–1200
Flatmark K, Pedersen KB, Nesland JM, Rasmussen H, Aamodt G, Mikalsen SO, Bjornland K, Fodstad O, Maelandsmo GM (2003) Nuclear localization of the metastasis-related protein S100A4 correlates with tumour stage in colorectal cancer. J Pathol 200:589–595
Gongoll S, Peters G, Mengel M, Piso P, Klempnauer J, Kreipe H, von Wasielewski R (2002) Prognostic significance of calcium-binding protein S100A4 in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 123:1478–1484
Gupta S, Hussain T, MacLennan GT, Fu P, Patel J, Mukhtar H (2003) Differential expression of S100A2 and S100A4 during progression of human prostate adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol 21:106–112
Hemandas AK, Salto-Tellez M, Maricar SH, Leong AF, Leow CK (2006) Metastasis-associated protein S100A4—a potential prognostic marker for colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol 93:498–503
Kimura K, Endo Y, Yonemura Y, Heizmann CW, Schafer BW, Watanabe Y, Sasaki T (2000) Clinical significance of S100A4 and E-cadherin-related adhesion molecules in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol 16:1125–1131
Lee WY, Su WC, Lin PW, Guo HR, Chang TW, Chen HH (2004) Expression of S100A4 and Met: potential predictors for metastasis and survival in early-stage breast cancer. Oncology 66:429–438
Matsubara D, Niki T, Ishikawa S, Goto A, Ohara E, Yokomizo T, Heizmann CW, Aburatani H, Moriyama S, Moriyama H, Nishimura Y, Funata N, Fukayama M (2005) Differential expression of S100A2 and S100A4 in lung adenocarcinomas: clinicopathological significance, relationship to p53 and identification of their target genes. Cancer Sci 96:844–857
Miyazaki N, Abe Y, Oida Y, Suemizu H, Nishi M, Yamazaki H, Iwasaki M, Inoue H, Ueyama Y, Nakamura M (2006) Poor outcome of patients with pulmonary adenocarcinoma showing decreased E-cadherin combined with increased S100A4 expression. Int J Oncol 28:1369–1374
Moriyama-Kita M, Endo Y, Yonemura Y, Heizmann CW, Schafer BW, Sasaki T, Yamamoto E (2004) Correlation of S100A4 expression with invasion and metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 40:496–500
Nakamura T, Ajiki T, Murao S, Kamigaki T, Maeda S, Ku Y, Kuroda Y (2002) Prognostic significance of S100A4 expression in gallbladder cancer. Int J Oncol 20:937–941
Ninomiya I, Ohta T, Fushida S, Endo Y, Hashimoto T, Yagi M, Fujimura T, Nishimura G, Tani T, Shimizu K, Yonemura Y, Heizmann CW, Schafer BW, Sasaki T, Miwa K (2001) Increased expression of S100A4 and its prognostic significance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol 18:715–720
Oida Y, Yamazaki H, Tobita K, Mukai M, Ohtani Y, Miyazaki N, Abe Y, Imaizumi T, Makuuchi H, Ueyama Y, Nakamura M (2006) Increased S100A4 expression combined with decreased E-cadherin expression predicts a poor outcome of patients with pancreatic cancer. Oncol Rep 16:457–463
Platt-Higgins AM, Renshaw CA, West CR, Winstanley JH, De Silva Rudland S, Barraclough R, Rudland PS (2000) Comparison of the metastasis-inducing protein S100A4 (p9ka) with other prognostic markers in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer 89:198–208
Rudland PS, Platt-Higgins A, Renshaw C, West CR, Winstanley JH, Robertson L, Barraclough R (2000) Prognostic significance of the metastasis-inducing protein S100A4 (p9Ka) in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 60:1595–1603
Yonemura Y, Endou Y, Kimura K, Fushida S, Bandou E, Taniguchi K, Kinoshita K, Ninomiya I, Sugiyama K, Heizmann CW, Schafer BW, Sasaki T (2000) Inverse expression of S100A4 and E-cadherin is associated with metastatic potential in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 6:4234–4242
Strutz F, Zeisberg M, Ziyadeh FN, Yang CQ, Kalluri R, Muller GA, Neilson EG (2002) Role of basic fibroblast growth factor-2 in epithelial-mesenchymal transformation. Kidney Int 61:1714–1728
Zeisberg EM, Potenta S, Xie L, Zeisberg M, Kalluri R (2007) Discovery of endothelial to mesenchymal transition as a source for carcinoma-associated fibroblasts. Cancer Res 67:10123–10128
Barraclough R (1998) Calcium-binding protein S100A4 in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1448:190–199
Stein U, Arlt F, Walther W, Smith J, Waldman T, Harris ED, Mertins SD, Heizmann CW, Allard D, Birchmeier W, Schlag PM, Shoemaker RH (2006) The metastasis-associated gene S100A4 is a novel target of beta-catenin/T-cell factor signaling in colon cancer. Gastroenterology 131:1486–1500
Fodde R, Brabletz T (2007) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cancer stemness and malignant behavior. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19:150–158
Venkov CD, Link AJ, Jennings JL, Plieth D, Inoue T, Nagai K, Xu C, Dimitrova YN, Rauscher FJ, Neilson EG (2007) A proximal activator of transcription in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest 117:482–491
Watanabe Y, Usuda N, Tsugane S, Kobayashi R, Hidaka H (1992) Calvasculin, an encoded protein from mRNA termed pEL-98, 18A2, 42A, or p9Ka, is secreted by smooth muscle cells in culture and exhibits Ca(2+)-dependent binding to 36-kDa microfibril-associated glycoprotein. J Biol Chem 267:17136–17140
Duarte WR, Iimura T, Takenaga K, Ohya K, Ishikawa I, Kasugai S (1999) Extracellular role of S100A4 calcium-binding protein in the periodontal ligament. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 255:416–420
Flatmark K, Maelandsmo GM, Mikalsen SO, Nustad K, Varaas T, Rasmussen H, Meling GI, Fodstad O, Paus E (2004) Immunofluorometric assay for the metastasis-related protein S100A4: release of S100A4 from normal blood cells prohibits the use of S100A4 as a tumor marker in plasma and serum. Tumour Biol 25:31–40
Cabezon T, Celis JE, Skibshoj I, Klingelhofer J, Grigorian M, Gromov P, Rank F, Myklebust JH, Maelandsmo GM, Lukanidin E, Ambartsumian N (2007) Expression of S100A4 by a variety of cell types present in the tumor microenvironment of human breast cancer. Int J Cancer 121:1433–1444
Pedersen KB, Andersen K, Fodstad O, Maelandsmo GM (2004) Sensitization of interferon-gamma induced apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells by extracellular S100A4. BMC Cancer 4:52
Huang CM, Ananthaswamy HN, Barnes S, Ma Y, Kawai M, Elmets CA (2006) Mass spectrometric proteomics profiles of in vivo tumor secretomes: capillary ultrafiltration sampling of regressive tumor masses. Proteomics 6:6107–6116
Liotta LA, Kohn EC (2001) The microenvironment of the tumour-host interface. Nature 411:375–379
Mueller MM, Fusenig NE (2004) Friends or foes—bipolar effects of the tumour stroma in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 4:839–849
Ryan DG, Taliana L, Sun L, Wei ZG, Masur SK, Lavker RM (2003) Involvement of S100A4 in stromal fibroblasts of the regenerating cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:4255–4262
Okada H, Inoue T, Kanno Y, Kobayashi T, Watanabe Y, Ban S, Neilson EG, Suzuki H (2003) Selective depletion of fibroblasts preserves morphology and the functional integrity of peritoneum in transgenic mice with peritoneal fibrosing syndrome. Kidney Int 64:1722–1732
Inoue T, Plieth D, Venkov CD, Xu C, Neilson EG (2005) Antibodies against macrophages that overlap in specificity with fibroblasts. Kidney Int 67:2488–2493
Le Hir M, Hegyi I, Cueni-Loffing D, Loffing J, Kaissling B (2005) Characterization of renal interstitial fibroblast-specific protein 1/S100A4-positive cells in healthy and inflamed rodent kidneys. Histochem Cell Biol 123:335–346
Gibbs FE, Barraclough R, Platt-Higgins A, Rudland PS, Wilkinson MC, Parry EW (1995) Immunocytochemical distribution of the calcium-binding protein p9Ka in normal rat tissues: variation in the cellular location in different tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 43:169–180
Grigorian M, Tulchinsky E, Burrone O, Tarabykina S, Georgiev G, Lukanidin E (1994) Modulation of mts1 expression in mouse and human normal and tumor cells. Electrophoresis 15:463–468
Klingelhofer J, Ambartsumian NS, Lukanidin EM (1997) Expression of the metastasis-associated mts1 gene during mouse development. Dev Dyn 210:87–95
Tomida Y, Terasawa M, Kobayashi R, Hidaka H (1992) Calcyclin and calvasculin exist in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 189:1310–1316
Brisset AC, Hao H, Camenzind E, Bacchetta M, Geinoz A, Sanchez JC, Chaponnier C, Gabbiani G, Bochaton-Piallat ML (2007) Intimal smooth muscle cells of porcine and human coronary artery express S100A4, a marker of the rhomboid phenotype in vitro. Circ Res 100:1055–1062
Ambartsumian N, Klingelhofer J, Grigorian M, Karlstrom O, Sidenius N, Georgiev G, Lukanidin E (1998) Tissue-specific posttranscriptional downregulation of expression of the S100A4(mts1) gene in transgenic animals. Invasion Metastasis 18:96–104
Davies M, Harris S, Rudland P, Barraclough R (1995) Expression of the rat, S-100-related, calcium-binding protein gene, p9Ka, in transgenic mice demonstrates different patterns of expression between these two species. DNA Cell Biol 14:825–832
Diaz R, Kim JW, Hui JJ, Li Z, Swain GP, Fong KS, Csiszar K, Russo PA, Rand EB, Furth EE, Wells RG (2008) Evidence for the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in biliary atresia fibrosis. Hum Pathol 39:102–115
Ward C, Forrest IA, Murphy DM, Johnson GE, Robertson H, Cawston TE, Fisher AJ, Dark JH, Lordan JL, Kirby JA, Corris PA (2005) Phenotype of airway epithelial cells suggests epithelial to mesenchymal cell transition in clinically stable lung transplant recipients. Thorax 60:865–871
Merklinger SL, Wagner RA, Spiekerkoetter E, Hinek A, Knutsen RH, Kabir MG, Desai K, Hacker S, Wang L, Cann GM, Ambartsumian NS, Lukanidin E, Bernstein D, Husain M, Mecham RP, Starcher B, Yanagisawa H, Rabinovitch M (2005) Increased fibulin-5 and elastin in S100A4/Mts1 mice with pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res 97:596–604
Spiekerkoetter E, Lawrie A, Merklinger S, Ambartsumian N, Lukanidin E, Schmidt AM, Rabinovitch M (2005) Mts1/S100A4 stimulates human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell migration through multiple signaling pathways. Chest 128:577S
Azhar M, Schultz Jel J, Grupp I, Dorn GW 2nd, Meneton P, Molin DG, Gittenberger-de Groot AC, Doetschman T (2003) Transforming growth factor beta in cardiovascular development and function. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 14:391–407
Strøm CC, Kruhøffer M, Knudsen S, Stensgaard-Hansen F, Jonassen TEN, Ørntoft TF, Haunsø S, Sheikh SP (2004) Identification of a core set of genes that signifies pathways underlying cardiac hypertrophy. Comp Funct Genomics 5:459–470
Stary M, Pasteiner W, Summer A, Hrdina A, Eger A, Weitzer G (2005) Parietal endoderm secreted SPARC promotes early cardiomyogenesis in vitro. Exp Cell Res 310:331–343
Lepilina A, Coon AN, Kikuchi K, Holdway JE, Roberts RW, Burns CG, Poss KD (2006) A dynamic epicardial injury response supports progenitor cell activity during zebrafish heart regeneration. Cell 127:607–619
Smart N, Risebro CA, Melville AA, Moses K, Schwartz RJ, Chien KR, Riley PR (2006) Thymosin beta4 induces adult epicardial progenitor mobilization and neovascularization. Nature 445:177–182
Zvaifler NJ (2006) Relevance of the stroma and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) for the rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther 8:210
Fang Z, Duthoit N, Wicher G, Kallskog O, Ambartsumian N, Lukanidin E, Takenaga K, Kozlova EN (2006) Intracellular calcium-binding protein S100A4 influences injury-induced migration of white matter astrocytes. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 111:213–219
Takenaga K, Nygren J, Zelenina M, Ohira M, Iuchi T, Lukanidin E, Sjoquist M, Kozlova EN (2007) Modified expression of Mts1/S100A4 protein in C6 glioma cells or surrounding astrocytes affects migration of tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Neurobiol Dis 25:455–463
Samolov B, Steen B, Seregard S, van der Ploeg I, Montan P, Kvanta A (2005) Delayed inflammation-associated corneal neovascularization in MMP-2-deficient mice. Exp Eye Res 80:159–166
Nielsen K, Vorum H, Fagerholm P, Birkenkamp-Demtroder K, Honore B, Ehlers N, Orntoft TF (2006) Proteome profiling of corneal epithelium and identification of marker proteins for keratoconus, a pilot study. Exp Eye Res 82:201–209
Serra-Pages C, Medley QG, Tang M, Hart A, Streuli M (1998) Liprins, a family of LAR transmembrane protein-tyrosine phosphatase-interacting proteins. J Biol Chem 273:15611–15620
Mandinova A, Atar D, Schafer BW, Spiess M, Aebi U, Heizmann CW (1998) Distinct subcellular localization of calcium binding S100 proteins in human smooth muscle cells and their relocation in response to rises in intracellular calcium. J Cell Sci 111(Pt 14):2043–2054
Most P, Boerries M, Eicher C, Schweda C, Ehlermann P, Pleger ST, Loeffler E, Koch WJ, Katus HA, Schoenenberger CA, Remppis A (2003) Extracellular S100A1 protein inhibits apoptosis in ventricular cardiomyocytes via activation of the extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2). J Biol Chem 278:48404–48412
Bruneval P, Rossert J, Bariety J (2005) Renewal of FSP1: a marker of fibrogenesis on human renal biopsies. Kidney Int 68:1366–1367
Cheng S, Pollock AS, Mahimkar R, Olson JL, Lovett DH (2006) Matrix metalloproteinase 2 and basement membrane integrity: a unifying mechanism for progressive renal injury. FASEB J 20:1898–1900
Okada H, Ban S, Nagao S, Takahashi H, Suzuki H, Neilson EG (2000) Progressive renal fibrosis in murine polycystic kidney disease: an immunohistochemical observation. Kidney Int 58:587–597
Rossini M, Cheunsuchon B, Donnert E, Ma LJ, Thomas JW, Neilson EG, Fogo AB (2005) Immunolocalization of fibroblast growth factor-1 (FGF-1), its receptor (FGFR-1), and fibroblast-specific protein-1 (FSP-1) in inflammatory renal disease. Kidney Int 68:2621–2628
Vongwiwatana A, Tasanarong A, Rayner DC, Melk A, Halloran PF (2005) Epithelial to mesenchymal transition during late deterioration of human kidney transplants: the role of tubular cells in fibrogenesis. Am J Transplant 5:1367–1374
Kozlova EN (2003) Differentiation and migration of astrocytes in the spinal cord following dorsal root injury in the adult rat. Eur J Neurosci 17:782–790
Acknowledgements
We thank Mark Aplin for critical reading of the manuscript. Mikael Schneider and Søren P Sheikh are supported by grants from The John and Birthe Meyer Foundation and the Danish Heart Foundation. Jakob L Hansen is supported by grants from The Danish Medical Research Council and The Danish National Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schneider, M., Hansen, J.L. & Sheikh, S.P. S100A4: a common mediator of epithelial–mesenchymal transition, fibrosis and regeneration in diseases?. J Mol Med 86, 507–522 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-007-0301-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-007-0301-3