Abstract
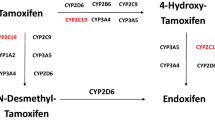
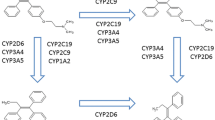
Tamoxifen is a widely utilized adjuvant anti-estrogen agent for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, known to undergo CYP2D6-mediated bioactivation to endoxifen. However, little is known regarding additional genetic and non-genetic determinants of optimal endoxifen plasma concentration. Therefore, 196 breast cancer patients on tamoxifen were enrolled in this prospective study over a 24-month period. Blood samples were collected for pharmacogenetic and drug-level analysis of tamoxifen and metabolites. Regression analysis indicated that besides CYP2D6, the recently described CYP3A4*22 genotype, seasonal variation, and concomitant use of CYP2D6-inhibiting antidepressants were significant predictors of endoxifen concentration. Of note, genetic variation explained 33 % of the variability while non-genetic variables accounted for 13 %. Given the proposed notion of a sub-therapeutic endoxifen concentration for predicting breast cancer recurrence, we set the therapeutic threshold at 18 nM, the 20th percentile for endoxifen level among enrolled patients in this cohort. Nearly 70 % of CYP2D6 poor metabolizers as well as extensive metabolizers on potent CYP2D6-inhibiting antidepressants exhibited endoxifen levels below 18 nM, while carriers of CYP3A4*22 were twofold less likely to be in sub-therapeutic range. Unexpectedly, endoxifen levels were 20 % lower during winter months than mean levels across seasons, which was also associated with lower vitamin D levels. CYP3A4*22 genotype along with sunshine exposure and vitamin D status may be unappreciated contributors of tamoxifen efficacy. The identified covariates along with demographic variables were integrated to create an endoxifen concentration prediction algorithm to pre-emptively evaluate the likelihood of individual patients falling below the optimal endoxifen concentration.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Higgins MJ, Stearns V (2011) Pharmacogenetics of endocrine therapy for breast cancer. Annu Rev Med 62:281–293
Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Lancet 351: 1451–1467 (1998)
Hoskins JM, Carey LA, McLeod HL (2009) CYP2D6 and tamoxifen: DNA matters in breast cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 9:576–586
Lim YC, Desta Z, Flockhart DA, Skaar TC (2005) Endoxifen (4-hydroxy-N-desmethyl-tamoxifen) has anti-estrogenic effects in breast cancer cells with potency similar to 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 55:471–478
Jin Y, Desta Z, Stearns V, Ward B, Ho H, Lee KH, Skaar T, Storniolo AM, Li L, Araba A, Blanchard R, Nguyen A, Ullmer L, Hayden J, Lemler S, Weinshilboum RM, Rae JM, Hayes DF, Flockhart DA (2005) CYP2D6 genotype, antidepressant use, and tamoxifen metabolism during adjuvant breast cancer treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:30–39
Borges S, Desta Z, Li L, Skaar TC, Ward BA, Nguyen A, Jin Y, Storniolo AM, Nikoloff DM, Wu L, Hillman G, Hayes DF, Stearns V, Flockhart DA (2006) Quantitative effect of CYP2D6 genotype and inhibitors on tamoxifen metabolism: implication for optimization of breast cancer treatment. Clin Pharmacol Ther 80:61–74
Murdter TE, Schroth W, Bacchus-Gerybadze L, Winter S, Heinkele G, Simon W, Fasching PA, Fehm T, Eichelbaum M, Schwab M, Brauch H (2011) Activity levels of tamoxifen metabolites at the estrogen receptor and the impact of genetic polymorphisms of phase I and II enzymes on their concentration levels in plasma. Clin Pharmacol Ther 89:708–717
Henry NL, Stearns V, Flockhart DA, Hayes DF, Riba M (2008) Drug interactions and pharmacogenomics in the treatment of breast cancer and depression. Am J Psychiatry 165:1251–1255
Goetz MP, Knox SK, Suman VJ, Rae JM, Safgren SL, Ames MM, Visscher DW, Reynolds C, Couch FJ, Lingle WL, Weinshilboum RM, Fritcher EG, Nibbe AM, Desta Z, Nguyen A, Flockhart DA, Perez EA, Ingle JN (2007) The impact of cytochrome P450 2D6 metabolism in women receiving adjuvant tamoxifen. Breast Cancer Res Treat 101:113–121
Regan MM, Leyland-Jones B, Bouzyk M, Pagani O, Tang W, Kammler R, Dell’orto P, Biasi MO, Thurlimann B, Lyng MB, Ditzel HJ, Neven P, Debled M, Maibach R, Price KN, Gelber RD, Coates AS, Goldhirsch A, Rae JM, Viale G (2012) CYP2D6 genotype and tamoxifen response in postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive breast cancer: the breast international group 1–98 trial. J Natl Cancer Inst 104:441–451
Schroth W, Goetz MP, Hamann U, Fasching PA, Schmidt M, Winter S, Fritz P, Simon W, Suman VJ, Ames MM, Safgren SL, Kuffel MJ, Ulmer HU, Bolander J, Strick R, Beckmann MW, Koelbl H, Weinshilboum RM, Ingle JN, Eichelbaum M, Schwab M, Brauch H (2009) Association between CYP2D6 polymorphisms and outcomes among women with early stage breast cancer treated with tamoxifen. JAMA 302:1429–1436
Wegman P, Elingarami S, Carstensen J, Stal O, Nordenskjold B, Wingren S (2007) Genetic variants of CYP3A5, CYP2D6, SULT1A1, UGT2B15 and tamoxifen response in postmenopausal patients with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 9:R7
Hertz DL, McLeod HL, Irvin WJ Jr (2012) Tamoxifen and CYP2D6: a contradiction of data. Oncologist 17:620–630
Irvin WJ Jr, Walko CM, Weck KE, Ibrahim JG, Chiu WK, Dees EC, Moore SG, Olajide OA, Graham ML, Canale ST, Raab RE, Corso SW, Peppercorn JM, Anderson SM, Friedman KJ, Ogburn ET, Desta Z, Flockhart DA, McLeod HL, Evans JP, Carey LA (2011) Genotype-guided tamoxifen dosing increases active metabolite exposure in women with reduced CYP2D6 metabolism: a multicenter study. J Clin Oncol 29:3232–3239
Teft WA, Mansell SE, Kim RB (2011) Endoxifen, the active metabolite of tamoxifen, is a substrate of the efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (multidrug resistance 1). Drug Metab Dispos 39:558–562
Madlensky L, Natarajan L, Tchu S, Pu M, Mortimer J, Flatt SW, Nikoloff DM, Hillman G, Fontecha MR, Lawrence HJ, Parker BA, Wu AH, Pierce JP (2011) Tamoxifen metabolite concentrations, CYP2D6 genotype, and breast cancer outcomes. Clin Pharmacol Ther 89:718–725
Gong IY, Teft WA, Ly J, Chen Y-H, Alicke B, Kim RB, Choo EF (2013) Determination of clinically therapeutic endoxifen concentrations based on efficacy from human MCF7 breast cancer xenografts. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-013-2530-1
Desta Z, Ward BA, Soukhova NV, Flockhart DA (2004) Comprehensive evaluation of tamoxifen sequential biotransformation by the human cytochrome P450 system in vitro: prominent roles for CYP3A and CYP2D6. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310:1062–1075
Oneda B, Crettol S, Jaquenoud Sirot E, Bochud M, Ansermot N, Eap CB (2009) The P450 oxidoreductase genotype is associated with CYP3A activity in vivo as measured by the midazolam phenotyping test. Pharmacogenet Genomics 19:877–883
Wang D, Guo Y, Wrighton SA, Cooke GE, Sadee W (2011) Intronic polymorphism in CYP3A4 affects hepatic expression and response to statin drugs. Pharmacogenomics J 11:274–286
Diczfalusy U, Nylen H, Elander P, Bertilsson L (2011) 4Beta-hydroxycholesterol, an endogenous marker of CYP3A4/5 activity in humans. Br J Clin Pharmacol 71:183–189
Schmiedlin-Ren P, Thummel KE, Fisher JM, Paine MF, Lown KS, Watkins PB (1997) Expression of enzymatically active CYP3A4 by Caco-2 cells grown on extracellular matrix-coated permeable supports in the presence of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Mol Pharmacol 51:741–754
Thummel KE, Brimer C, Yasuda K, Thottassery J, Senn T, Lin Y, Ishizuka H, Kharasch E, Schuetz J, Schuetz E (2001) Transcriptional control of intestinal cytochrome P-4503A by 1alpha,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3. Mol Pharmacol 60:1399–1406
Thirumaran RK, Lamba JK, Kim RB, Urquhart BL, Gregor JC, Chande N, Fan Y, Qi A, Cheng C, Thummel KE, Hall SD, Schuetz EG (2012) Intestinal CYP3A4 and midazolam disposition in vivo associate with VDR polymorphisms and show seasonal variation. Biochem Pharmacol 84:104–112
Goetz MP, Suman VJ, Hoskin TL, Gnant M, Filipits M, Safgren SL, Kuffel M, Jakesz R, Rudas M, Greil R, Dietze O, Lang A, Offner F, Reynolds CA, Weinshilboum RM, Ames MM, Ingle JN (2013) CYP2D6 metabolism and patient outcome in the Austrian Breast and Colorectal Cancer Study Group trial (ABCSG) 8. Clin Cancer Res 19:500–507
Rae JM, Drury S, Hayes DF, Stearns V, Thibert JN, Haynes BP, Salter J, Sestak I, Cuzick J, Dowsett M (2012) CYP2D6 and UGT2B7 genotype and risk of recurrence in tamoxifen-treated breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst 104:452–460
Wu X, Hawse JR, Subramaniam M, Goetz MP, Ingle JN, Spelsberg TC (2009) The tamoxifen metabolite, endoxifen, is a potent antiestrogen that targets estrogen receptor alpha for degradation in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 69:1722–1727
Wilkinson GR (2005) Drug metabolism and variability among patients in drug response. N Engl J Med 352:2211–2221
Lamba JK, Lin YS, Schuetz EG, Thummel KE (2002) Genetic contribution to variable human CYP3A-mediated metabolism. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 54:1271–1294
Binkhorst L, van Gelder T, Loos WJ, de Jongh FE, Hamberg P, Moghaddam-Helmantel IM, de Jonge E, Jager A, Seynaeve C, van Schaik RH, Verweij J, Mathijssen RH (2012) Effects of CYP Induction by rifampicin on tamoxifen exposure. Clin Pharmacol Ther 92:62–67
Cho YA, Lee W, Choi JS (2012) Effects of curcumin on the pharmacokinetics of tamoxifen and its active metabolite, 4-hydroxytamoxifen, in rats: possible role of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein inhibition by curcumin. Pharmazie 67:124–130
Kiyotani K, Mushiroda T, Imamura CK, Hosono N, Tsunoda T, Kubo M, Tanigawara Y, Flockhart DA, Desta Z, Skaar TC, Aki F, Hirata K, Takatsuka Y, Okazaki M, Ohsumi S, Yamakawa T, Sasa M, Nakamura Y, Zembutsu H (2010) Significant effect of polymorphisms in CYP2D6 and ABCC2 on clinical outcomes of adjuvant tamoxifen therapy for breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 28:1287–1293
Anderson LN, Cotterchio M, Kirsh VA, Knight JA (2011) Ultraviolet sunlight exposure during adolescence and adulthood and breast cancer risk: a population-based case-control study among Ontario women. Am J Epidemiol 174:293–304
Vrieling A, Hein R, Abbas S, Schneeweiss A, Flesch-Janys D, Chang-Claude J (2011) Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and postmenopausal breast cancer survival: a prospective patient cohort study. Breast Cancer Res 13:R74
Fan J, Liu S, Du Y, Morrison J, Shipman R, Pang KS (2009) Up-regulation of transporters and enzymes by the vitamin D receptor ligands, 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and vitamin D analogs, in the Caco-2 cell monolayer. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 330:389–402
Virtanen JK, Nurmi T, Voutilainen S, Mursu J, Tuomainen TP (2011) Association of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D with the risk of death in a general older population in Finland. Eur J Nutr 50:305–312
Moan J, Porojnicu AC, Dahlback A, Setlow RB (2008) Addressing the health benefits and risks, involving vitamin D or skin cancer, of increased sun exposure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:668–673
de Graan AJ, Teunissen SF, de Vos FY, Loos WJ, van Schaik RH, de Jongh FE, de Vos AI, van Alphen RJ, van der Holt B, Verweij J, Seynaeve C, Beijnen JH, Mathijssen RH (2011) Dextromethorphan as a phenotyping test to predict endoxifen exposure in patients on tamoxifen treatment. J Clin Oncol 29:3240–3246
Acknowledgments
Dr. Richard B. Kim holds the Wolfe Medical Research Chair in Pharmacogenomics at Western. We would like to thank Matilde Leon-Ponte, Cameron Ross, and Sara Mansell for their technical assistance and Julie Mayo for her administrative support. We would also like to thank the Breast Disease Site Team at the London Regional Cancer Program (LRCP). This study was funded by the Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Research Chair Award (Tier-1) in Experimental Therapeutics (Richard B Kim) and the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research (OICR) Translational Research Team grant.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teft, W.A., Gong, I.Y., Dingle, B. et al. CYP3A4 and seasonal variation in vitamin D status in addition to CYP2D6 contribute to therapeutic endoxifen level during tamoxifen therapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 139, 95–105 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2511-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2511-4