Abstract
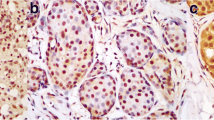
FABP7 is a member of the multi-gene fatty acid binding protein family. It is expressed in the mammary gland and has been shown to function as inhibitor of proliferation of breast tumour cells and to promote differentiation through the JAK/Stat pathway. Cytoplasmic FABP7 expression has been shown to be associated with a favourable prognosis of basal-like breast cancer. In other tissues, varying sub-cellular localization of FABP7 between the nucleus and cytoplasm has been observed. Tissue microarray preparations of well-characterized series of 1,249 unselected and 245 ER-negative invasive breast cancers with a long-term follow-up were investigated in this study to assess the biological and clinical significance of FABP7 sub-cellular localization using immunohistochemistry. Both nuclear and cytoplasmic FABP7 were observed. Nuclear FABP7 was associated with high histologic grade, mitotic frequency, pleomorphism and stage, in addition to basal phenotype (BP) and triple-negative (TN) phenotype. Nuclear FABP7 expression showed an association with expression of markers associated with proliferation and cell-cycle control including Ki67, p53 and p21; however, cytoplasmic FABP7 was associated only with Ki67 and P53 (P = 0.001, < 0.001 respectively). Interestingly, in multivariate analysis, nuclear FABP7 expression in BP was significantly associated with longer DFI (P = 0.025) independent of cytoplasmic expression. Tumours with only nuclear positive FABP7 expression had significantly better prognosis than those with only cytoplasmic expression. This is the first study elucidating the sub-cellular localization of FABP7 in a large series of breast cancer cases. Our observations demonstrate the considerable heterogeneity in expression patterns of FABP7 within breast cancer that relates to differences in biological behaviour especially in basal-like breast cancer. Further investigation of the biology of FABP7 in breast cancer is warranted.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BCSS:
-
Breast cancer specific survival
- BLBC:
-
Basal-like breast cancer
- BP:
-
Basal phenotype
- CaKi-2:
-
Human kidney clear cell carcinoma cell line
- CISH:
-
Chromogenic in situ hybridisation
- CK5:
-
Cytokeratin5
- CK14:
-
Cytokeratin14
- CK17:
-
Cytokeratin17
- DFI:
-
Disease-free interval
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor 1
- ER:
-
Estrogen
- FABP7:
-
Fatty acid binding protein 7
- FAS:
-
Fatty acid synthase
- HER2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- JAK/STAT:
-
Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription
- LBP:
-
Lipid-binding protein
- MIB1:
-
Mindbomb homolog 1
- NST:
-
No special type
- PPAR:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
- PgR:
-
Progesterone
- TMA:
-
Tissue micro array
- PIAS γ:
-
Protein inhibitor of activated STAT protein γ
References
Xu LZ, Sánchez R, Sali A, Heintz N (1996) Ligand specificity of brain lipid-binding protein. J Biol Chem 271(40):24711–24719
Wolfrum C, Borrmann CM, Borchers T, Spener F (2001) Fatty acids and hypolipidemic drugs regulate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha—and gamma-mediated gene expression via liver fatty acid binding protein: a signaling path to the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(5):2323–2328. doi:10.1073/pnas.051619898051619898
Huang H, Starodub O, McIntosh A, Kier AB, Schroeder F (2002) Liver fatty acid-binding protein targets fatty acids to the nucleus. J Biol Chem 277(32):29139
Feng L, Heintz N (1995) Differentiating neurons activate transcription of the brain lipid-binding protein gene in radial glia through a novel regulatory element. Development 121(6):1719–1730
Shimizu F, Watanabe TK, Shinomiya H, Nakamura Y, Fujiwara T (1997) Isolation and expression of a cDNA for human brain fatty acid-binding protein (B-FABP). Biochim Biophys Acta 1354(1):24–28. doi:S0167-4781(97)00115-2
Godbout R, Bisgrove DA, Shkolny D, Day RS 3rd (1998) Correlation of B-FABP and GFAP expression in malignant glioma. Oncogene 16(15):1955–1962. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201740
Kaloshi G, Mokhtari K, Carpentier C, Taillibert S, Lejeune J, Marie Y, Delattre JY, Godbout R, Sanson M (2007) FABP7 expression in glioblastomas: relation to prognosis, invasion and EGFR status. J Neurooncol 84(3):245–248
Mita R, Beaulieu MJ, Field C, Godbout R (2010) Brain fatty acid-binding protein and omega-3/omega-6 fatty acids: mechanistic insight into malignant glioma cell migration. J Biol Chem 285(47):37005–37015. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.170076
Haunerland NH, Spener F (2004) Fatty acid-binding proteins–insights from genetic manipulations. Prog Lipid Res 43(4):328–349. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2004.05.001S016378270400013X
Wang M, Liu YE, Ni J, Aygun B, Goldberg ID, Shi YE (2000) Induction of mammary differentiation by mammary-derived growth inhibitor-related gene that interacts with an omega-3 fatty acid on growth inhibition of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 60(22):6482–6487
Shi YE, Ni J, Xiao G, Liu YE, Fuchs A, Yu G, Su J, Cosgrove JM, Xing L, Zhang M (1997) Antitumor activity of the novel human breast cancer growth inhibitor, mammary-derived growth inhibitor-related gene, MRG. Cancer Res 57(15):3084
Tölle A, Krause H, Miller K, Jung K, Stephan C (2011) Importance of brain–type fatty acid binding protein for cell-biological processes in human renal carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep 25(5):1307–1312
Takaoka N, Takayama T, Teratani T, Sugiyama T, Mugiya S, Ozono S (2011) Analysis of the regulation of fatty acid binding protein 7 expression in human renal carcinoma cell lines. BMC Mol Biol 12:31. doi:10.1186/1471-2199-12-31
Glatz JFC, Luiken JJFP, van Bilsen M, van der Vusse GJ (2002) Cellular lipid binding proteins as facilitators and regulators of lipid metabolism. Mol Cell Biochem 239(1):3–7
Molyneux G, Geyer FC, Magnay FA, McCarthy A, Kendrick H, Natrajan R, Mackay A, Grigoriadis A, Tutt A, Ashworth A, Reis-Filho JS, Smalley MJ (2010) BRCA1 basal-like breast cancers originate from luminal epithelial progenitors and not from basal stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 7(3):403–417
Zhang H, Rakha EA, Ball GR, Spiteri I, Aleskandarany M, Paish EC, Powe DG, Macmillan RD, Caldas C, Ellis IO, Green AR (2010) The proteins FABP7 and OATP2 are associated with the basal phenotype and patient outcome in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 121(1):41–51. doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0450-x
Madjd Z, Pinder SE, Paish C, Ellis IO, Carmichael J, Durrant LG (2003) Loss of CD59 expression in breast tumours correlates with poor survival. J Pathol 200(5):633–639. doi:10.1002/path.1357
Rakha EA, Reis-Filho JS, Ellis IO (2008) Basal-like breast cancer: a critical review. J Clin Oncol 26(15):2568–2581
García-Caballero T, Grabau D, Green AR, Gregory J, Schad A, Kohlwes E, Ellis IO, Watts S, Mollerup J (2010) Determination of HER2 amplification in primary breast cancer using dual-colour chromogenic in situ hybridization is comparable to fluorescence in situ hybridization: a European multicentre study involving 168 specimens. Histopathology 56:472–480
Aleskandarany MA, Green AR, Benhasouna AA, Barros FF, Neal KR, Reis-Filho JS, Ellis IO, Rakha EA (2011) Prognostic value of proliferation assay in the luminal, HER2 positive and triple negative biological classes of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 14(1):R3
Rimm DL, Camp RL, Charette LA, Olsen DA, Provost E (2001) Amplification of tissue by construction of tissue microarrays. Exp Mol Pathol 70(3):255–264
Callagy G, Cattaneo E, Daigo Y, Happerfield L, Bobrow LG, Pharoah PDP, Caldas C (2003) Molecular classification of breast carcinomas using tissue microarrays. Diagn Mol Pathol 12(1):27
Ginestier C, Charafe-Jauffret E, Bertucci F, Eisinger F, Geneix J, Bechlian D, Conte N, Adélaïde J, Toiron Y, Nguyen C, Viens P, Mozziconacci MJ, Houlgatte R, Birnbaum D, Jacquemier J (2002) Distinct and complementary information provided by use of tissue and DNA microarrays in the study of breast tumor markers. Am J Pathol 161(4):1223–1233
Feng L, Hatten ME, Heintz N (1994) Brain lipid-binding protein (BLBP): a novel signaling system in the developing mammalian CNS. Neuron 12(4):895–908
Liang Y, Bollen AW, Aldape KD, Gupta N (2006) Nuclear FABP7 immunoreactivity is preferentially expressed in infiltrative glioma and is associated with poor prognosis in EGFR-overexpressing glioblastoma. BMC Cancer 6:97. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-6-97
Goto Y, Koyanagi K, Narita N, Kawakami Y, Takata M, Uchiyama A, Nguyen L, Nguyen T, Ye X, Morton DL (2009) Aberrant fatty acid-binding protein-7 gene expression in cutaneous malignant melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 130(1):221–229
Yang Y, Morin PJ, Han WF, Chen T, Bornman DM, Gabrielson EW, Pizer ES (2003) Regulation of fatty acid synthase expression in breast cancer by sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c. Exp Cell Res 282(2):132–137
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Thorsen T, Quist H, Matese JC, Brown PO, Botstein D, Eystein Lonning P, Borresen-Dale AL (2001) Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(19):10869–10874. doi:10.1073/pnas.19136709898/19/10869
Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, Dressler LG, Cowan D, Conway K, Karaca G, Troester MA, Tse CK, Edmiston S, Deming SL, Geradts J, Cheang MC, Nielsen TO, Moorman PG, Earp HS, Millikan RC (2006) Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. JAMA 295(21):2492–2502. doi:10.1001/jama.295.21.2492
Rakha EA, El-Rehim DA, Paish C, Green AR, Lee AH, Robertson JF, Blamey RW, Macmillan D, Ellis IO (2006) Basal phenotype identifies a poor prognostic subgroup of breast cancer of clinical importance. Eur J Cancer 42(18):3149–3156. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2006.08.015
Fulford LG, Reis-Filho JS, Ryder K, Jones C, Gillett CE, Hanby A, Easton D, Lakhani SR (2007) Basal-like grade III invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: patterns of metastasis and long-term survival. Breast Cancer Res 9(1):R4. doi:10.1186/bcr1636
Tang XY, Umemura S, Tsukamoto H, Kumaki N, Tokuda Y, Osamura RY (2010) Overexpression of fatty acid binding protein-7 correlates with basal-like subtype of breast cancer. Pathol Res Pract 206(2):98–101. doi:10.1016/j.prp.2009.06.010
Aksglaede L, Wikstrom AM, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Dunkel L, Skakkebaek NE, Juul A (2006) Natural history of seminiferous tubule degeneration in Klinefelter syndrome. Hum Reprod Update 12(1):39–48. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmi039
Ray PS, Wang J, Qu Y, Sim MS, Shamonki J, Bagaria SP, Ye X, Liu B, Elashoff D, Hoon DS, Walter MA, Martens JW, Richardson AL, Giuliano AE, Cui X (2010) FOXC1 is a potential prognostic biomarker with functional significance in basal-like breast cancer. Cancer Res 70(10):3870–3876. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4120
Liang Y, Bollen AW, Nicholas MK, Gupta N (2005) Id4 and FABP7 are preferentially expressed in cells with astrocytic features in oligodendrogliomas and oligoastrocytomas. BMC Clin Pathol 5:6. doi:10.1186/1472-6890-5-6
Solomayer EF, Diel I, Meyberg G, Gollan C, Bastert G (2000) Metastatic breast cancer: clinical course, prognosis and therapy related to the first site of metastasis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 59(3):271–278
Weigelt B, Peterse JL, van’t Veer LJ (2005) Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer 5(8):591–602
Niwińska A, Murawska M, Pogoda K (2010) Breast cancer brain metastases: differences in survival depending on biological subtype, RPA RTOG prognostic class and systemic treatment after whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT). Ann Oncol 21(5):942–948
Hicks DG, Short SM, Prescott NL, Tarr SM, Coleman KA, Yoder BJ, Crowe JP, Choueiri TK, Dawson AE, Budd GT (2006) Breast cancers with brain metastases are more likely to be estrogen receptor negative, express the basal cytokeratin CK5/6, and overexpress HER2 or EGFR. The American journal of surgical pathology 30(9):1097
Klein A, Olendrowitz C, Schmutzler R, Hampl J, Schlag PM, Maass N, Arnold N, Wessel R, Ramser J, Meindl A (2009) Identification of brain- and bone-specific breast cancer metastasis genes. Cancer Lett 276(2):212–220
Goto Y, Matsuzaki Y, Kurihara S, Shimizu A, Okada T, Yamamoto K, Murata H, Takata M, Aburatani H, Hoon DSB (2006) A new melanoma antigen fatty acid-binding protein 7, involved in proliferation and invasion, is a potential target for immunotherapy and molecular target therapy. Cancer Res 66(8):4443
Michalik L, Desvergne B, Wahli W (2004) Peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptors and cancers: complex stories. Nat Rev Cancer 4(1):61–70. doi:10.1038/nrc1254nrc1254
Liu B, Liao J, Rao X, Kushner SA, Chung CD, Chang DD, Shuai K (1998) Inhibition of Stat1-mediated gene activation by PIAS1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(18):10626–10631
Slipicevic A, Jørgensen K, Skrede M, Rosnes AK, Trøen G, Davidson B, Flørenes VA (2008) The fatty acid binding protein 7 (FABP7) is involved in proliferation and invasion of melanoma cells. BMC Cancer 8(1):276
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alshareeda, A.T., Rakha, E.A., Nolan, C.C. et al. Fatty acid binding protein 7 expression and its sub-cellular localization in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 134, 519–529 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2083-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2083-8