Abstract
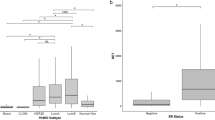
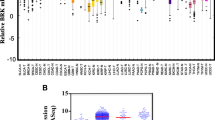
Interactions between kinases and the estrogen receptor α (ERα) are thought to be a critical signaling pathway in the majority of human breast cancers. We have recently identified a previously uncharacterized molecule, lemur tyrosine kinase-3 (LMTK3) as a prognostic and predictive oncogenic ERα regulator with a central role in endocrine resistance. Unusually this protein has undergone Darwinian positive selection between Chimpanzees and humans suggesting it may contribute to human susceptibility to ERα-positive tumors. Using over 600 European primary breast cancer cases, we wished to establish tumor characteristics associated with both cytoplasmic and nuclear LMTK3 expression, and then externally validate our observed European clinical outcomes with samples from Asian individuals receiving chemotherapy. Both nuclear and cytoplasmic expression correlated with tumor grade (P < 0.001) and in the Asian cohort, independent blinded analyses demonstrated that high basal LMTK3 expression was associated with advanced stage of primary breast cancers as well as decreased overall (P = 0.03) and disease-free survival (P = 0.006). In summary, higher LMTK3 expression is associated with more aggressive cancers. These data support our previous findings and suggest LMTK3 expression may be a reliable new biomarker in breast cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stebbing J, Crane J, Gaya A (2006) Breast cancer (metastatic). Clin Evid 15:2331–2359
Stebbing J, Delaney G, Thompson A (2007) Breast cancer (non-metastatic). Clin Evid (Online) 6718–6753
Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M et al (2010) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:2784–2795
Kato S, Endoh H, Masuhiro Y et al (1995) Activation of the estrogen receptor through phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science 270:1491–1494
Ali S, Coombes RC (2002) Endocrine-responsive breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nat Rev Cancer 2:101–112
Amanchy R, Kalume DE, Iwahori A, Zhong J, Pandey A (2005) Phosphoproteome analysis of HeLa cells using stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture (SILAC). J Proteome Res 4:1661–1671
Atsriku C, Britton DJ, Held JM et al (2009) Systematic mapping of posttranslational modifications in human estrogen receptor-alpha with emphasis on novel phosphorylation sites. Mol Cell Proteomics 8:467–480
Campbell RA, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Patel NM, Constantinidou D, Ali S, Nakshatri H (2001) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor alpha: a new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J Biol Chem 276:9817–9824
Britton DJ, Scott GK, Schilling B et al (2008) A novel serine phosphorylation site detected in the N-terminal domain of estrogen receptor isolated from human breast cancer cells. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 19:729–740
Wu RC, Qin J, Yi P et al (2004) Selective phosphorylations of the SRC-3/AIB1 coactivator integrate genomic responses to multiple cellular signaling pathways. Mol Cell 15:937–949
Jiang J, Sarwar N, Peston D et al (2007) Phosphorylation of estrogen receptor-alpha at Ser167 is indicative of longer disease-free and overall survival in breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 13:5769–5776
Giamas G, Castellano L, Feng Q et al (2009) CK1delta modulates the transcriptional activity of ERalpha via AIB1 in an estrogen-dependent manner and regulates ERalpha-AIB1 interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 37:3110–3123
Chen D, Washbrook E, Sarwar N et al (2002) Phosphorylation of human estrogen receptor alpha at serine 118 by two distinct signal transduction pathways revealed by phosphorylation-specific antisera. Oncogene 21:4921–4931
Giamas G, Filipovic A, Jacob J et al (2011) Kinome screening for regulators of the estrogen receptor identifies LMTK3 as a new therapeutic target in breast cancer. Nat Med (Advanced online publication) 17(6):715–719
Bowen RL, Stebbing J, Jones LJ (2006) A review of the ethnic differences in breast cancer. Pharmacogenomics 7:935–942
Dunn BK, Agurs-Collins T, Browne D, Lubet R, Johnson KA (2010) Health disparities in breast cancer: biology meets socioeconomic status. Breast Cancer Res Treat 121:281–292
Chuah BY, Putti T, Salto-Tellez M et al (2011) Serial changes in the expression of breast cancer-related proteins in response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Oncol. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq755
Walker RA, Bartlett JM, Dowsett M et al (2008) HER2 testing in the UK: further update to recommendations. J Clin Pathol 61:818–824
Bartlett JM, Ellis IO, Dowsett M et al (2007) Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 status correlates with lymph node involvement in patients with estrogen receptor (ER) negative, but with grade in those with ER-positive early-stage breast cancer suitable for cytotoxic chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 25:4423–4430
Elston CW, Ellis IO (1991) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 19:403–410
Ellis IO, Galea M, Broughton N, Locker A, Blamey RW, Elston CW (1992) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. II. Histological type. Relationship with survival in a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 20:479–489
Parker C, Rampaul RS, Pinder SE et al (2001) E-cadherin as a prognostic indicator in primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer 85:1958–1963
Madjd Z, Parsons T, Watson NF, Spendlove I, Ellis I, Durrant LG (2005) High expression of Lewis y/b antigens is associated with decreased survival in lymph node negative breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res 7:R780–R787
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM (2006) REporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Breast Cancer Res Treat 100:229–235
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM (2006) Reporting recommendations for tumor marker prognostic studies (remark). Exp Oncol 28:99–105
Giamas G, Stebbing J, Vorgias CE, Knippschild U (2007) Protein kinases as targets for cancer treatment. Pharmacogenomics 8:1005–1016
Giamas G, Man YL, Hirner H et al (2010) Kinases as targets in the treatment of solid tumors. Cell Signal 22:984–1002
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stebbing, J., Filipovic, A., Ellis, I.O. et al. LMTK3 expression in breast cancer: association with tumor phenotype and clinical outcome. Breast Cancer Res Treat 132, 537–544 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1622-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1622-z