Abstract
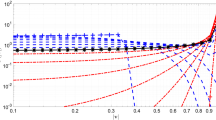
Fluctuating plume models provide a useful conceptual paradigm in the understanding of plume dispersion in a turbulent flow. In particular, these models have enabled analytical predictions of higher-order concentration moments, and the form of the one-point concentration probability density function (PDF). In this paper, we extend the traditional formalism of these models, grounded in the theory of homogeneous and isotropic turbulent flow, to two cases: namely, a simple sheared boundary layer and a large array of regular obstacles. Some very high-resolution measurements of plume dispersion in a water channel, obtained using laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) line-scan techniques are utilised. These data enable us to extract time series of plume centroid position (plume meander) and dispersion in the relative frame of reference in unprecedented detail. Consequently, experimentally extracted PDFs are able to be directly compared with various theoretical forms proposed in the literature. This includes the PDF of plume centroid motion, the PDF of concentration in the relative frame, and a variety of concentration moments in the absolute and relative frames of reference. The analysis confirms the accuracy of some previously proposed functional forms of model components used in fluctuating plume models, as well as suggesting some new forms necessary to deal with the complex boundary conditions in the spatial domain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bara BM, Wilson DJ, Zelt BW (1992) Concentration fluctuation profiles from a water channel simulation of a ground-level release. Atmos Environ 26A:1053–1062
Csanady GT (1973) Turbulent diffusion in the environment D. Reidel Publishing Company, Boston MA, 248 pp
Fackrell JE, Robins AG (1982) The effects of source size on concentration fluctuations in plumes. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 22:335–350
Franzese P (2003) Lagrangian stochastic modelling of a fluctuating plume in the convective boundary layer. Atmos Environ 37:1691–1701
Gailis RM, Hill A (2006) A wind tunnel simulation of plume dispersion within a large array of obstacles. Boundary-Layer Meterol 119:289–338
Gifford F (1959) Statistical properties of a fluctuating plume dispersion model. Adv Geophys 6:117–137
Gifford F (1960) Peak to average concentration ratios according to a fluctuating plume dispersion model. Int J Air Poll 3:253–260
Hanna SR (1986). Spectra of concentration fluctuations: the two scales of a meandering plume. Atmos Environ 20:1131–1137
Jaynes ET (2003) Probability theory: the logic of science. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge UK, 727 pp
Kimura F, Yoshikawa T, Sato J (1981) Frequency distribution of the concentration on the centre of mean plume axis in the surface layer. Papers Meteorol Geophys 32:149–154
Luhar AK, Hibberd MF, plume and Borgas MS (2000) A skewed meandering plume model for concentration statistics in the convective boundary layer. Atmos Environ 106:411–436
Munro RJ, Chatwin PC, Mole N (2003a) A concentration PDF for the relative dispersion of a contaminant plume in the atmosphere. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 22:411-436
Munro RJ, Chatwin PC, Mole N (2003b) Some simple statistical models for relative and absolute dispersion. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 22:253–271
Mylne KR, Mason PJ (1991) Concentration fluctuation measurements in a dispersing plume at a range of up to 1000 m. Quart J. Roy Meteorol Soc 117:177–206
Sawford BL, Stapountzis H (1986) Concentration fluctuations according to fluctuating plume models in one and two dimensions. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 37:89–105
Yee E, Biltoft CA (2004) Concentration fluctuation measurements in a plume dispersing through a regular array of obstacles. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 111:363–415
Yee E, Chan R (1997) A simple model for the probability density function of concentration fluctuations in atmospheric plumes. Atmos Environ 31:991–1002
Yee E, Chan R, Kosteniuk PR, Chandler GM, Biltoft CA, Bowers JF (1994a) Experimental measurements of concentration fluctuations and scales in a dispersing plume in the atmospheric surface layer obtained using a very fast response concentration detector. J Appl Meteorol 33:996–1016
Yee E, Chan R, Kosteniuk PR, Chandler GM, Biltoft CA, Bowers JF (1994b) Incorporation of internal fluctuations in a meandering plume model of concentration fluctuations. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 67:11–39
Yee E, Chan R, Kosteniuk PR, Chandler GM, Biltoft CA, Bowers JF (1995) The vertical structure of concentration fluctuation statistics in plumes dispersing in the atmospheric surface layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 76:41–67
Yee E, Gailis RM, Wilson DJ (2003) The interference of higher-order statistics of the concentration field produced by two point sources according to a generalized fluctuating plume model. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 116:297–348
Yee E, Gailis RM, Hill A, Hilderman T, Kiel D (2006) Comparison of wind tunnel and water channel simulations of plume dispersion through a large array of obstacles with a scaled field experiment. Boundary-Layer Meteorol in press
Yee E, Wilson DJ (2000) A comparison of the detailed structure in dispersing tracer plumes measured in grid-generated turbulence with a meandering plume model incorporating internal fluctuations. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 94:253–296
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gailis, R.M., Hill, A., Yee, E. et al. Extension of a fluctuating plume model of tracer dispersion to a sheared boundary layer and to a large array of obstacles. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 122, 577–607 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-006-9118-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-006-9118-9