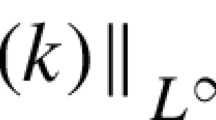Abstract
A meandering plume model that explicitly incorporates the effects of small-scale structure in the instantaneous plume has been formulated. The model requires the specification of two physically based input parameters; namely, the meander ratio,M, which is dependent on the ratio of the meandering plume dispersion to the instantaneous relative plume dispersion and, a relative in-plume fluctuation measure,k, that is related inversely to the fluctuation intensity in relative coordinates. Simple analytical expressions for crosswind profiles of the higher moments (including the important shape parameters such as fluctuation intensity, skewness, and kurtosis) and for the concentration pdf have been derived from the model. The model has been tested against some field data sets, indicating that it can reproduce many key aspects of the observed behavior of concentration fluctuations, particularly with respect to modeling the change in shape of the concentration pdf in the crosswind direction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C :
-
Mean concentration in absolute coordinates
- C r :
-
Mean concentration in relative coordinates
- C0 :
-
Centerline mean concentration in absolute coordinates
- C r,0 :
-
Centerline mean concentration in relative coordinates
- f :
-
Probability density function of concentration in absolute coordinates
- f c :
-
Probability density function of plume centroid position
- f r :
-
Probability density function of concentration in relative coordinates
- i :
-
Absolute concentration fluctuation intensity (standard deviation to mean ratio)
- i r :
-
Relative concentration fluctuation intensity (standard deviation to mean ratio)
- k :
-
Relative in-plume fluctuation measure:k=1/i 2r
- K :
-
Concentration fluctuation kurtosis
- M :
-
Meander ratio of meandering plume variance to relative plume variance
- S :
-
Concentration fluctuation skewness
- x :
-
Downwind distance from source
- y :
-
Crosswind distance from mean-plume centerline
- z :
-
Vertical distance above ground
- Θ:
-
Instantaneous (random) concentration
- Θ:
-
Crosswind dispersion ofnth concentration moment about zero
- σ ny :
-
Mean-plume crosswind (absolute) dispersion
- σ y :
-
Plume centroid (meandering) dispersion in crosswind direction
- σ y,c :
-
Instantaneous plume crosswind (relative) dispersion
- ϕ:
-
Normalized mean concentration in absolute coordinates:C/C 0
- χ:
-
Particular value taken on by instantaneous concentration, Θ
References
Bara, B. M., Wilson, D. J., and Zelt, B. W.: 1992, ‘Concentration Fluctuation Profiles from a Water Channel Simulation of a Ground-Level Release’,Atmos. Environ. 26A, 1053–1062.
Biltoft, C. A.: 1991, ‘Concentration Fluctuation Modeling of Chemical Hazards (Field Test)’, U.S. Army Dugway Proving Ground, Dugway, Utah, 96 pp.
Chandler, G. M.: 1991, ‘Development of Fast-Response Tracer Gas Sensors for Use in Full-Scale Atmospheric Dispersion Field Trials. Part 1: Hardware Component. Part II: Field Testing Component’, Technical Report for Defence Research Establishment Suffield (DRES-CR-04-92), S & J Engineering, Inc., Scarborough, Ontario, 82 pp.
Csanady, G. T.: 1973,Turbulent Diffusion in the Environment, D. Reidel, Dordrecht, Holland.
Deardorff, J. W. and Willis, G. E.: 1988, ‘Concentration Fluctuations Within a Laboratory Convectively Mixed Layer’, in A. Venkatram and J. C. Wyngaard (eds.),Lectures on Air Pollution Modeling, Amer. Meteorol. Soc., Boston, MA, pp. 357–384.
Dinar, N., Kaplan, H., and Kleiman, M.: 1988, ‘Characterization of Concentration Fluctuations of a Surface Plume in a Neutral Boundary Layer’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 45, 157–175.
Fackrell, J. E. and Robins, A. G.: 1982, ‘The Effect of Source Size on Concentration Fluctuations in Plumes’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 22, 335–350.
Gifford, F. A.: 1959, ‘Statistical Properties of a Fluctuating Plume Dispersion Model’,Adv. Geophys. 6, 117–137.
Gifford, F. A.: 1960, ‘Peak to Average Concentration Ratios According to a Fluctuating Plume Dispersion Model’,Int. J. Air Pollut. 3, 253–260.
Gifford, F. A.: 1982, ‘Horizontal Diffusion in the Atmosphere: A Lagrangian-Dynamical Theory’,Atmos. Environ. 16, 505–512.
Hanna, S. R.: 1984, ‘The Exponential Probability Density Function and Concentration Fluctuations in Smoke Plumes’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 29, 361–375.
Hanna, S. R.: 1986, ‘Spectra of Concentration Fluctuations: The Two Time Scales of a Meandering Plume’,Atmos. Environ. 20, 1131–1137.
Irwin, J. S.: 1983, ‘Estimating Plume Dispersion — A Comparison of Several Sigma Schemes’,J. Climate Appl. Meteorol. 22, 92–114.
Kendall, M. G. and Stuart, A.: 1977,The Advanced Theory of Statistics, Volume 1, Distribution Theory, Charles Griffin, London, England.
Kimura, F., Yoshikawa, T., and Sato, J.: 1981, ‘Frequency Distributions of the Concentration on the Center of Mean Plume Axis in the Surface Layer’,Papers in Meteorol. and Geophys. 32, 149–154.
Lee, J. T., Stone, G. L., Lawson, R. E., Jr., and Shipman, M.: 1986, ‘Monte Carlo Simulation of Two-Particle Relative Diffusion Using Eulerian Statistics’,Atmos. Environ. 20, 2185–2197.
Mylne, K. R. and Mason, P. J.: 1991, ‘Concentration Fluctuation Measurements in a Dispersing Plume at a Range of up to 1000 m’,Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 117, 177–206.
Pasquill, F. and Smith, F. B.: 1983,Atmospheric Diffusion, Ellis Horwood, Chichester.
Sawford, B. L.: 1982, ‘Comparison of Some Different Approximations in the Statistical Theory of Relative Dispersion’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 108, 191–206.
Sawford, B. L. and Stapountzis, H.: 1986, ‘Concentration Fluctuations According to Fluctuating Plume Models in One and Two Dimensions’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 37, 89–105.
Smith, F. B. and Hay, J. S.: 1961, ‘The Expansion of Clusters of Particles in the Atmosphere’,Quart. J. Roy. Meterol. Soc. 87, 89–91.
Yee, E., Kosteniuk, P. R., Chandler, G. M., Biltoft, C. A., and Bowers, J. F.: 1993a, ‘Statistical Characteristics of Concentration Fluctuations in Dispersing Plumes in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 65, 69–109.
Yee, E., Wilson, D. J., and Zelt, B. W.: 1993b, ‘Probability Distributions of Concentration Fluctuations of a Weakly Diffusive Passive Plume in a Turbulent Boundary Layer’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 64, 321–354.
Yee, E., Kosteniuk, P. R., Chandler, G. M., Biltoft, C. A., and Bowers, J. F.: 1993c, ‘Recurrence Statistics of Concentration Fluctuations in Plumes Within a Near-Neutral Atmospheric Surface Layer’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 66, 127–153.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yee, E., Chan, R., Kosteniuk, P.R. et al. Incorporation of internal fluctuations in a meandering plume model of concentration fluctuations. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 67, 11–39 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00705506
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00705506