Abstract
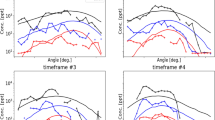
The effects of source size on plume behaviour have been examined in a 1.2 m wind tunnel boundary layer for isokinetic sources with diameters from 3 to 35 mm at source heights of 230 mm and at ground level. Experimental measurements of mean concentration and the variance, intermittency and probability density functions of the concentration fluctuations were obtained. In addition, a fluctuating Gaussian plume model is presented which reproduces many of the observed features of the elevated emission. The mean plume width becomes independent of source size much more rapidly than the instantaneous plume width. Since it is the meandering of the instantaneous plume which generates most of the concentration fluctuations near the source, these are also dependent on source size. The flux of variance in the plume reaches a maximum, whose value is greatest for the smallest source size, close to the source and thereafter is monotonically decreasing. The intermittency factor reaches a minimum, whose value is lowest for the smallest source, and increases back towards one. Concentration fluctuations for the ground-level source are much less dependent on source size due to the effects of the surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chatwin, P. C. and Sullivan, P. J.: 1979, ‘The Relative Diffusion of a Cloud of Passive Contaminant in Incompressible Turbulent Flow’, J. Fl. Mech. 91, 337–355.
Counihan, J.: 1969, ‘An Improved Method of Simulating an Atmospheric Boundary Layer in a Wind Tunnel’, Atmos. Env. 3, 197–214.
Durbin, P. A.: 1980, ‘A Stochastic Model of Two Particle Dispersion and Concentration Fluctuations in Homogeneous Turbulence’, J. Fl. Mech. 100, 279–302.
Fackrell, J. E.: 1980, ‘A Flame Ionisation Detector for Measuring Fluctuating Concentration’, J. Phys. E. Instrum. 13, 888–893.
Fackrell, J. E. and Robins, A. G.: 1982, ‘Concentration Fluctuations and Fluxes in Plumes from Point Sources in a Turbulent Boundary Layer’, (to be published in J. Fl. Mech).
Fackrell, J. E. and Robins, A. G.: 1980b, ‘Concentration Fields Associated with Emission from Point Sources in Turbulent Boundary Layers — Part III. Concentration Fluctuations and Fluxes’, CEGB Memo MM/MECH/TF 260.
Gifford, F. A.: 1959, ‘Statistical Properties of a Fluctuating Plume Dispersion Model’, Adv. Geophys. 6, 117–137.
Hay, J. S. and Pasquill, F.: 1959, ‘Diffusion from a Continuous Source in Relation to the Spectrum and Scale of Turbulence’, Adv. Geophys. 6, 345–365.
Hinze, J. O.: 1959, Turbulence, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Jones, C. D.: 1979, Mathematical Modelling of Turbulent Diffusion in the Environment, Academic Press, London, pp. 277–298.
Nakayama, A. and Bradshaw, P.: 1979, ‘Final Report on CEGB Contract “Turbulent Plume Dispersion”’, Dept. of Aeronautics, Imperial College, London.
Robins, A. G. and Fackrell, J. E.: 1979, Mathematical Modelling of Turbulent Diffusion in the Environment, Academic Press, London, pp. 55–114.
Smith, F. B. and Hay, J. S.: 1961, ‘The Expansion of Clusters of Particles in the Atmosphere’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 87, 89–91.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fackrell, J.E., Robins, A.G. The effects of source size on concentration fluctuations in plumes. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 22, 335–350 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120014
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120014