Abstract
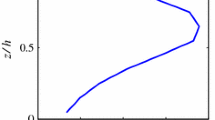
The statistics of turbulent flow across a forest edge have been examined using large-eddy simulation, and results compared with field and wind-tunnel observations. The moorland-to-forest transition is characterized by flow deceleration in the streamwise direction, upward distortion of the mean flow, formation of a high pressure zone immediately in front of the edge, suppression of the standard deviations and covariance of velocity components, and enhancement of velocity skewnesses. For the selected forest density, it is observed that the maximum distortion angle is about 8 degrees from the horizontal. Instead of approaching a downwind equilibrium state in a monotonic manner, turbulence (standard deviations and covariances of velocity components) and mean streamwise velocity undershoot in the transition zone behind the edge. Evolution of flow statistics clearly reveals the growth of an internal boundary layer, and the establishment of an equilibrium layer downwind of the edge. It is evident that lower-order moments generally adjust more quickly over the new rough surface than do higher-order moments. We also show that the streamwise velocity standard deviation at canopy height starts its recovery over the rough surface sooner than does the vertical velocity standard deviation, but completes full adjustment later than the latter. Despite the limited domain size upstream of the edge, large-eddy simulation has successfully reproduced turbulent statistics in good agreement with field and wind-tunnel measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonia R.A., Luxton R.E. (1971), ‘The Response of a Turbulent Boundary Layer to a Step Change in Surface Roughness, Part 1. Smooth to Rough’. J. Fluid Mech. 48, 721–761
Antonia R.A., Luxton R.E. (1972), ‘The Response of a Turbulent Boundary Layer to a Step Change in Surface Roughness, Part 2. Rough to Smooth’. J. Fluid Mech. 53, 737–757
Baldocchi D.D., Meyers T.P. (1988), ‘Turbulence Structure in a Deciduous Forest’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 43, 345–364
Belcher S.E., Xu D.P., Hunt J.C.R. (1990), ‘The Response of a Turbulent Boundary Layer to Arbitrarily Distributed Two-Dimensional Roughness Changes’. Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 116, 611–635
Bradley E.F. (1968), ‘A Micrometeorological Study of Velocity Profiles and Surface Drag in the Region Modified by a Change in Surface Roughness’. Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 94, 361–379
Breugel P.B., van Klaassen W., Moors E.J. (1999), ‘Fetch Requirements near a Forest Edge’. Phys. Chem. Earth(B) 24(1–2): 125–131
Brunet Y., Finnigan J.J., Raupach M.R. (1994), ‘A Wind Tunnel Study of Air Flow in Waving Wheat: Single-Point Velocity Statistics’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 70, 95–132
Chen, J. M., Black, T. A., Novak, M. D., and Adams, R. S. 1995, ‘ A Wind Tunnel Study of Turbulent Airflow in Forest Clearcuts’, in M. P. Coutts, and J. Grace (eds.), Wind and Trees, Cambridge University Press, pp. 71–87.
Cheng H., Castro I.P. (2002), ‘Near-Wall Flow Development after a Step Change in Surface Roughness’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 105, 411–432
Claussen M. (1987), ‘The Flow in a Turbulent Boundary Layer Upstream of a Change in Surface Roughness’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 40, 31–86
Deardorff J.W. (1980), ‘Stratocumulus-Capped Mixed Layers Derived from a Three-Dimensional Model’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 18, 495–527
Flesch T.K., Wilson J.D. (1999a), ‘Wind and Remnant Tree Sway in Forest Cutblocks, I. Measured Winds in Experimental Cutblocks’. Agric. For. Meteorol. 93, 229–242
Flesch T.K., Wilson J.D. (1999b), ‘Wind and Remnant Tree Sway in Forest Cutblocks, II. Relating Measured Tree Sway to Wind Statistics’. Agric. For. Meteorol. 93, 243–258
Gao W., Shaw R.H., Paw U.K.T. (1989), ‘Observation of Organized Structure in Turbulent Flow within and above a Forest Canopy’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 47, 349–377
Gardiner B.A. (1995), ‘ The Interactions of Wind and Tree Movement in Forest Canopies’, in M. P. Coutts, and J. Grace (eds.), Wind and Trees, Cambridge University Press, pp. 41–59.
Garratt J.R. (1990), ‘The Internal Boundary Layer – A Review’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 50, 171–203
Gash J.H.C. (1986), ‘Observations of Turbulence Downwind of a Forest-Heath Interface’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 36, 227–237
Germano M., Piomelli U., Moin P., Cabot W.H. (1991), ‘A Dynamic Subgrid-Scale Eddy Viscosity Model’. Phys. Fluids A 3, 1760–1765
Irvine M.R., Gardiner B.A., Hill M.K. (1997), ‘The Evolution of Turbulence across a Forest Edge’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 84, 467–496
Jackson P.S., Hunt J.C.R. (1975), ‘Turbulent Wind Flow over a Low Hill’. Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 101, 929–955
Klaassen W. (1992), ‘Average Fluxes from Heterogeneous Vegetated Regions’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 58, 329–354
Kruijt, B., Klaassen, W., and Hutjes, R. W. A. 1995, ‘Edge Effects on Diffusivity in the Roughness Layer over a Forest’, in M. P. Coutts and J. Grace (eds.), Wind and Trees, Cambridge University Press, pp. 60–70.
Lee X. (2000), ‘Air Motion within and above Forest Vegetation in Non-Ideal Conditions’. For. Ecol. Manage. 135, 3–18
Legg B.J., Coppin P.A., Raupach M.R. (1984), ‘A Three-Hot-Wire Anemometer for Measuring Two Velocity Components in High-Intensity Turbulent Boundary Layers’. J. Phys. E 17, 970–976
Li Z., Lin J.D., Miller D.R. (1990), ‘Air Flow over and through a Forest Edge: A Steady-State Numerical Simulation’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 51, 179–197
Liu J., Chen J.M., Black T.A., Novak M.D. (1996), ‘Modelling of Turbulent Air Flow Downwind of a Model Forest Edge’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 77, 21–44
Mason P.J. (1988), ‘The Formation of Areally-Averaged Roughness Lengths’. Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 114, 399–420
Mason P.J., Thomson D.J. (1992), ‘Stochastic Backscatter in Large-Eddy Simulations of Boundary Layers’. J. Fluid Mech. 242, 51–78
Miller D.R., Lin J.D., Lu Z.N. (1991), ‘Air Flow across an Alpine Forest Clearing: A Model and Field Measurements’. Agric. For. Meteorol. 56, 209–225
Miller D.R., Stoughton T.E. (2000), ‘Response of Spray Drift from Aerial Applications at a Forest Edge to Atmospheric Stability’. Agric. For. Meteorol. 100, 49–58
Mitchell S.J., Hailemariam T., Kulis Y. (2001), ‘Empirical Modeling of Cutblock Edge Windthrow Risk on Vancouver Island, Canada, Using Stand Level Information’. For. Ecol. Manage. 154, 117–130
Moeng C.-H. (1984), ‘A Large-Eddy-Simulation Model for the Study of Planetary Boundary-Layer Turbulence’. J. Atmos. Sci. 41, 2052–2062
Morse A.P., Gardiner B.A., Marshall B.J. (2002), ‘Mechanisms Controlling Turbulence Development across a Forest Edge’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 103, 227–251
Mulhearn P.J. (1978), ‘A Wind-Tunnel Boundary-Layer Study of the Effects of a Surface Roughness Change: Rough to Smooth’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 15, 3–30
Nieveen J.P., El-Kilani R.M.M., Jacobs A.F.G. (2001), ‘Behaviour of the Static Pressure around a Tussock Grassland-Forest Interface’. Agric. For. Meteorol. 106, 253–259
Panofsky H.A., Townsend A.A. (1964), ‘Change of Terrain Roughness and the Wind Profiles’. Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 90, 147–155
Patton E.G., Shaw R.H., Judd M.J., Raupach M.R. (1998), ‘Large-Eddy Simulation of Windbreak Flow’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 87, 275–306
Paw U.K.T., Baldocchi D.D., Meyers T.P., Wilson K.B. (2000), ‘Correction of Eddy-Covariance Measurements Incorporating Both Advective Effects and Density Fluxes’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 97, 487–511
Rao K.S., Wyngaard J.C., Cote O.R. (1974), ‘The Structure of the Two-Dimensional Internal Boundary Layer over a Sudden Change of Surface Roughness’. J. Atmos. Sci. 31, 738–746
Raupach M.R., Coppin P.A., Legg B.J. (1986), ‘Experiments on Scalar Dispersion within a Model Plant Canopy, Part I: The Turbulence Structure’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 35, 21–52
Raupach M.R., Finnigan J.J. (1995), ‘Scale Issues in Boundary-Layer Meteorology: Surface Energy Balances in Heterogeneous Terrain’. Hydrol. Processes 9, 589–612
Raupach M.R., Finnigan J.J., Brunet Y. (1996), ‘Coherent Eddies and Turbulence in Vegetation Canopies: The Mixing-Layer Analogy’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 78, 351–382
Sadeh W.Z. (1975). ‘Simulation of Flow above Forest Canopies’. In: DeVies D.A., Afgan N.H. (eds). Heat and Mass Transfer in the Biosphere, Part I. J. Wiley & Sons, N.Y., pp. 251–263
Shaw R.H., Den Hartog G., Neumann H.H. (1988), ‘Influence of Foliar Density and Thermal Stability on Profiles of Reynolds Stress and Turbulence Intensity in a Deciduous Forest’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 45, 391–409
Shaw R.H., Schumann U. (1992), ‘Large-Eddy Simulation of Turbulent Flow above and within a Forest’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 61, 47–64
Shir C.C. (1972), ‘A Numerical Computation of Air Flow over a Sudden Change in Surface Roughness’. J. Atmos. Sci. 29, 304–310
Stacey G.R., Belcher R.E., Wood C.J., Gardiner B.A. (1994), ‘Wind Flows and Forces in a Model Spruce Forest’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 69, 311–334
Su H.-B., Shaw R.H., Paw U.K.T. (2000), ‘Two-Point Correlation Analysis of Neutrally Stratified Flow with and above a Forest from Large-Eddy Simulation’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 94, 423–460
Su H.-B., Shaw R.H., Paw U.K.T., Moeng C.-H., Sullivan P.P. (1998), ‘Turbulent Statistics of Neutrally Stratified Flow within and above a Sparse Forest from Large-Eddy Simulation and Field Observations’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 88, 363–397
Sullivan P.P., McWilliams J.C., Moeng C.-H. (1994), ‘A Subgrid-Scale Model for Large-Eddy Simulation of Planetary Boundary-Layer Flows’. Boundary-layer Meteorol. 71, 247–276
Taylor P.A. (1969), ‘The Planetary Boundary Layer above a Change in Surface Roughness’. J. Atmos. Sci. 26, 432–440
Wilson J.D., Flesch T.K. (1999), ‘Wind and Remnant Tree Sway in Forest Cutblocks, III. A Windflow Model to Diagnose Spatial Variation’. Agric. For. Meteorol. 93, 259–282
Wright S.D., Elliott L., Ingham D.B., Hewson M.J.C. (1998), ‘The Adaptation of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer to a Change in Surface Roughness’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 89, 175–195
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, B., Raupach, M.R., Shaw, R.H. et al. Large-eddy Simulation of Turbulent Flow Across a Forest Edge. Part I: Flow Statistics. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 120, 377–412 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-006-9057-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-006-9057-5