Abstract
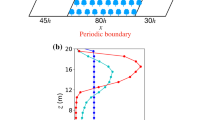
Topography influences many aspects of forest-atmosphere carbon exchange; yet only a small number of studies have considered the role of topography on the structure of turbulence within and above vegetation and its effect on canopy photosynthesis and the measurement of net ecosystem exchange of CO2 (Nee) using flux towers. Here, we focus on the interplay between radiative transfer, flow dynamics for neutral stratification, and ecophysiological controls on CO2 sources and sinks within a canopy on a gentle cosine hill. We examine how topography alters the forest-atmosphere CO2 exchange rate when compared to uniform flat terrain using a newly developed first-order closure model that explicitly accounts for the flow dynamics, radiative transfer, and nonlinear eco physiological processes within a plant canopy. We show that variation in radiation and airflow due to topography causes only a minor departure in horizontally averaged and vertically integrated photosynthesis from their flat terrain values. However, topography perturbs the airflow and concentration fields in and above plant canopies, leading to significant horizontal and vertical advection of CO2. Advection terms in the conservation equation may be neglected in flow over homogeneous, flat terrain, and then Nee = Fc, the vertical turbulent flux of CO2. Model results suggest that vertical and horizontal advection terms are generally of opposite sign and of the same order as the biological sources and sinks. We show that, close to the hilltop, Fc departs by a factor of three compared to its flat terrain counterpart and that the horizontally averaged Fc-at canopy top differs by more than 20% compared to the flat-terrain case.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. D. Albertson G. G. Katul P. Wiberg (2001) ArticleTitle‘Relative Importance of Local and Regional Controls on Coupled Water, Carbon, and Energy Fluxes’ Adv. Water Res. 24 IssueID9–10 1103–1118
D. Baldocchi E. Falge L. H. Gu R. Olson D. Hollinger S. Running P. Anthoni C. Berhofer K. Davis R. Evens J. Fuentes A. Goldstein G. Katul B. Law X. H. Lee Y. Malhi T. Meyers W. Munger W. Oechel K. T. Paw U. K. Polegaard H. P. Schmid R. Valentini S. Verma T. Vesala K. Wilson S. Wofsy (2001) ArticleTitle‘FLUXNET: A New Tool to Study the Temporal and Spatial Variability of Ecosystem – Scale Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor, and Energy Flux Densities’ Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 82 2415–2434
S. E. Belcher C. R. Hunt (1998) ArticleTitle‘Turbulent Flow over Hills and Waves’ Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30 507–538 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.fluid.30.1.507
S. E. Belcher N. Jerram J. C. R. Hunt (2003) ArticleTitle‘Adjustment of a Turbulent Boundary Layer to a Canopy of Roughness Elements’ J. Fluid Mech. 488 369–398 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0022112003005019
Y. Brunet J. J. Finnigan M. R. Raupach (1994) ArticleTitle‘A Wind-Tunnel Study of Air-flow in Waving Wheat–Single-Point Velocity Statistics’ Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 70 95–132 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00712525
G. S. Campbell J. M. Norman (1998) An Introduction to Environmental Biophysics Springer New York 286
G. J. Collatz J. T. Ball C. Grivet J. A. Berry (1991) ArticleTitle‘Physiological and Environmental Regulation of Stomatal Conductance, Photosynthesis and Transpiration: A Model that Includes a Laminar Boundary Layer’ Agric. For. Meteorl. 54 107–136
Carruthers, D. J. and Hunt, J. C. R.: 1990, ‘Fluid Mechanics of Airflow over Hills: Turbulence, Fluxes, and Waves in the Boundary Layer’, in Atmospheric Processes over Complex Terrain, Meteorolpgical Monographs, Vol. 23, American Meteorological Society, Boston; MA, pp. 83–103.
O. T. Denmead E. F. Bradley (1985) ‘F1ux Gradient Relationships in a Forest Canopy’ B. A. Hutchison B. B. Hicks (Eds) The Forest-Atmosphere Interaction D. Reidel Publishing Norwell, Mass. 421–422
G. D. Farquhar S. Caemmerer ParticleVon J. A. Berry (1980) ArticleTitle‘A Biochemical Model of Photosynthetic CO2 Assimilation in Leaves of C3 Species Planta 149 78–90 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00386231
Feigenwinter, C., Bernhofer, C., and Vogt, R.(2004). ‘The Influence of Advection on the Short Term CO2 Budget in and Above a Forest Canopy’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol., in press
J. J. Finnigan (1985) ‘Turbulent Transport in Plant Canopies’ B. A. Hutchinson B. B. Hicks (Eds) The Forest-Atmosphere Interactions, D Reidel Publishing Norwell, Mass. 443–480
J. J. Finnigan (1998) ‘Air Flow over Complex Terrain’ W. L. Steffen O. T. Denmead (Eds) Flow and Transport in the Natural Environment, Advances and Applications Springer Berlin 183–229
J. J. Finnigan (2000) ArticleTitle‘Turbulence Inside Plant Canopies’ Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 32 519–571 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.fluid.32.1.519
J. J. Finnigan (2004) ‘Advection and Modeling’ X. Lee W. J. (Eds) Handbook of Micrometeorology: A Guide for Surface Flux Measurements Kluwer Academic Publishers Dordrecht 209–244
J. J. Finnigan M. R. Raupach (1987) ‘Transfer Process Within Plant Canopies in Relation to Stomatal Characteristics’ E. M. Zeiger G. D. Farquhar I. R. Cowan (Eds) Stomatal Function Stanford University Press Stanford, CA 385
J.J. Finnigan S.E. Belcher (2004) ArticleTitle‘Flow over Hill Covered with a Plant Canopy’ Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 130 IssueID596 1–29 Occurrence Handle10.1256/qj.02.177
J. C. R. Hunt S. Leibovich K. J. Richards (1998) ArticleTitle‘Turbulent Shear Flows over Low Hills’ Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 114 1435–1470
P. S. Jackson J. C. R. Hunt (1975) ArticleTitle‘Turbulent Wind Flow over a Low Hill’ Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 101 929–955 Occurrence Handle10.1256/smsqj.43014
J. C. Kaimal J. J. Finnigan (1994) Atmospheric Boundary Layer Flows: Their Structure and Measurement Oxford University Press New York 289
G. G Katul L. Mahrt D. Poggi C. Sanz (2004) ArticleTitle‘One and Two Equation Models for Canopy Turbulence’ Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 113 81–109 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:BOUN.0000037333.48760.e5
G. G. Katul D. Ellsworth C. T. Lai (2000) ArticleTitle‘Modeling Assimilation and Intercellular CO2 from Measured Conductance: A Synthesis of Approaches’ Plant, Cell Environ 23 1313–1328 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-3040.2000.00641.x
G. G. Katul W. H. Chang (1999) ArticleTitle‘Principal Length Scales in Second-order Closure Models for Canopy Turbulence’ J. Appl. Meteorol. 38 1631–1643 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0450(1999)038<1631:PLSISO>2.0.CO;2
G. G. Katul C. D. Geron C. I. Hsieh B. Vidakovic A. B. Guenther (1998) ArticleTitle‘Active Turbulence and Scalar Transport Near the Land-Atmosphere Interface’ J. Appl. Meterol. 37 1533–1546
C. T. Lai G. G. Katul J. Butnor D. Ellsworth R. Oren (2002) ArticleTitleModelling Night-time Ecosystem Respiration by a Constrained Source Optimization Method Global Change Biol. 8 124–141 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1354-1013.2001.00447.x
C. T. Lai G. G. Katul R. Oren D. Ellsworth K. Scháfer (2000) ArticleTitle‘Modeling CO2 and Water Vapor Turbulent Flux Distributions Within a Forest Canopy’ J. Geophys. Res. 105 26333–26351 Occurrence Handle10.1029/2000JD900468
X. Lee (1998) ArticleTitle‘On Micrometeorological Observations of Surface-air Exchanges over Tall Vegetation’ Agric. Forest Meteorol. 91 39–49 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-1923(98)00071-9
R. Leuning (1995) ArticleTitle‘A Critical Appraisal of a Combined Stomatal-Photosynthesis Model for C3Plants’ Plant, Cell Environ. 18 339–355
W. J. Massman J. C. Weil (1999) ArticleTitle‘An Analytical One-dimensional Second Order Closure Model of Turbulence Statistics and the Lagrangian Time Scale Within and Above Plant Canopies of Arbitrary Structure’ Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 91 81–107 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1001810204560
W. L. Physick J. R. Garratt (1995) ArticleTitle‘Incorporation of a High Roughness Lower Boundary Into a Mesoscale Model for Studies of Dry Deposition over Complex Terrain’ Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 74 IssueID1–2 55–71
J. P. Pinard J. D. Wilson (2001) ArticleTitle‘First- and Second Order Closure Models for Wind in a Plant Canopy’ J. Appl. Meteorol. 40 1762–1768 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0450(2001)040<1762:FASOCM>2.0.CO;2
D. Poggi A. Porporato L. Ridolfi J. D. Albertson G. G. Katul (2004a) ArticleTitle‘The Effect of Vegetation Density on Canopy Sub-Layer Turbulence’ Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 111 565–587
D. Poggi G. G. Katul J. D. Albertson (2004b) ArticleTitle‘A Note on the Contribution of Dispersive Fluxes to Momentum Transfer within Canopies’ Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 111 615–621
W. H. Press S. A. Teukolsky W. Vetterling B. P. Flannery (1992) Numerical Recipes in Fortran: The Art of Scientific Computing EditionNumber2 Cambridge University Press New York 963
M. R. Raupach J. J. Finnigan (1997) ArticleTitle‘The Influence of Topography on Meteorological Variables and Surface-Atmosphere Interactions J. Hydrol. 190 182–213 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-1694(96)03127-7
M. R. Raupach J. J. Finnigan Y. Brunet (1996) ArticleTitle‘Coherent Eddies and Turbulence in Vegetation Canopies: The Mixing Layer Analogy’ Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 78 351–382 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00120941
M. R. Raupach W. S. Weng D. J. Carruthers J. C. R. Hunt (1992) ArticleTitle‘Temperature and Humidity Fields and Fluxes over Low Hills’ Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 118 191–225 Occurrence Handle10.1256/smsqj.50402
P. A. Taylor P. J. Mason E. F. Bradley (1987) ArticleTitle‘Boundary Layer Flow over Low Hills’ Boundary-Layer Meterol. 39 15–39
J. D. Wilson J. J. Finnigan M. R. Raupach (1998) ArticleTitle‘A First Order Closure for Disturbed Plant-canopy Flows and Its Application to Winds in a Canopy on a Ridge’ Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 124 705–732 Occurrence Handle10.1256/smsqj.54703
N. R. Wilson R. H. Shaw (1977) ArticleTitle‘A Higher Order Closure Model for Canopy Flow’ J. Appl. Meteorol. 16 1198–1205 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0450(1977)016<1197:AHOCMF>2.0.CO;2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katul, G.G., Finnigan, J.J., Poggi, D. et al. The Influence of Hilly Terrain on Canopy-Atmosphere Carbon Dioxide Exchange. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 118, 189–216 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-005-6436-2
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-005-6436-2