Summary
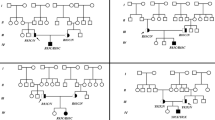
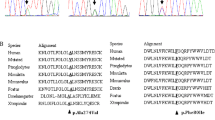
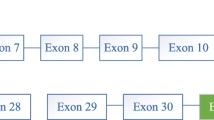
In patients with late-onset glycogen storage disease type II, one mutation, c.−32−13T>G, in the α-glucosidase (GAA) gene is identified frequently in European populations from different regions along with many rarer mutations. We have performed molecular genetic investigations in 18 German index patients with late-onset disease. The c.−32−13T>G, c.525delT (p.Glu176fsX45), and c.2481+102_2646+31del mutations were detected by PCR/restriction enzyme digest. Other mutations were detected by sequencing. All patients were compound heterozygous and 17 patients harboured the c.−32−13T>G mutation. Seven other previously described mutations (including the c.−32−13T>G) were identified, of which the p.C103G (c.307T>G) and the c.2481+102_2646+31del mutations were present each in three unrelated patients. Sequencing revealed five novel mutations. Conclusions: Genetic testing was able to identify the genetic defects in all patients and screening of the c.−32−13T>G mutation identified 94% of the cases. This is important for quick and reliable diagnosis, especially in view of enzyme replacement. Among the rarer mutations, c.2481+102_2646+31del and p.C103G are rather frequent in Germany.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GAA:
-
α-glucosidase
- GSD II:
-
glycogen storage disease type II
- PAS:
-
periodic acid–Schiff
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- RFLP:
-
restriction fragment length polymorphism
References
Bodamer OA, Haas D, Hermans MM, Reuser AJ, Hoffmann GF (2002) l-Alanine supplementation in late infantile glycogen storage disease type II. Pediatr Neurol 27: 145–146.
Boerkoel CF, Exelbert R, Nicastri C, et al (1995) Leaky splicing mutation in the acid maltase gene is associated with delayed onset of glycogenosis type II. Am J Hum Genet 56: 887–897.
Hermans MM, Kroos MA, de Graaff E, Oostra BA, Reuser AJ (1993) Two mutations affecting the transport and maturation of lysosomal alpha-glucosidase in an adult case of glycogen storage disease type II. Hum Mutat 12: 268–273.
Hermans MM, De Graaff E, Kroos MA, et al (1994) The effect of a single base pair deletion (T525) and a C1634T missense mutation (pro545leu) on the expression of lysosomal alpha-glucosidase in patients with glycogen storage disease type II. Hum Mol Genet 3: 2213–2218.
Hermans MPP, van Leenen D, Kroos MA, et al (2004) Twenty-two novel mutations in the lysosomal α-glucosidase gene (GAA) underscore the genotype-phenotype correlation in glycogen storage disease type II. Hum Mutat 23: 47–56.
Huie ML, Chen AS, Brooks SS, Grix A, Hirschhorn R (1994a) A de novo 13 nt deletion, a newly identified C647W missense mutation and a deletion of exon 18 in infantile onset glycogen storage disease type II (GSD II). Hum Mol Genet 3: 1081–1087.
Huie ML, Chen AS, Tsujino S, et al (1994b) Aberrant splicing in adult onset glycogen storage disease type II (GSD II): molecular identification of an IVS1 (−13T>G) mutation in a majority of patients and a novel IVS10 (+1GT>CT) mutation. Hum Mol Genet 3: 2231–2236.
Ko TM, Hwu WL, Lin YW, et al (1999) Molecular genetic study of Pompe disease in Chinese patients in Taiwan. Hum Mutat 13: 380–384.
Kroos MA, van der Kraan M, van Diggelen OP, et al (1995) Glycogen storage disease type II: frequency of three common mutant alleles and their associated clinical phenotypes studied in 121 patients. J Med Genet 32: 836–840.
Kroos MA, Pomponio RJ, Hagemans ML, et al (2007) Broad spectrum of Pompe disease in patients with the same c.−32−13T>G haplotype. Neurology 68: 110–115.
Laforêt P, Nicolino M, Eymard PB, et al (2000) Juvenile and adult-onset acid maltase deficiency in France: genotype–phenotype correlation. Neurology 55: 1122–1128.
McCready ME, Carson NL, Chakraborty P, et al (2007) Development of a clinical assay for detection of GAA mutations and characterization of the GAA mutation spectrum in a Canadian cohort of individuals with glycogen storage disease, type II. Mol Genet Metab 92: 325–335.
Montalvo AL, Bembi B, Donnarumma M, et al (2006) Mutation profile of the GAA gene in 40 Italian patients with late onset glycogen storage disease type II. Hum Mutat 27: 999–1006.
Müller-Felber W, Horvath R, Gempel K, et al (2007) Late onset Pompe disease: clinical and neurophysiological spectrum of 38 patients including long-term follow-up in 18 patients. Neuromuscul Disord 17: 698–706.
Palmer RE, Amartino HM, Niizawa G, Blanco M, Pomponio RJ, Chamoles NA (2007) Pompe disease (glycogen storage disease type II) in Argentineans: Clinical manifestations and identification of 9 novel mutations. Neuromuscul Disord 17: 16–22.
Sharma MC, Schultze C, von Moers A, et al (2005) Delayed or late-onset type II glycogenosis with globular inclusions. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 110: 151–157.
Van den Hout JMP, Kamphoven JHJ, Winkel LPF, et al (2004) Long-term intravenous treatment of Pompe disease with recombinant human alpha-glucosidase from milk. Pediatrics 113: 448–457.
van der Kraan M, Kroos MA, Joosse M, et al (1994) Deletion of exon 18 is a frequent mutation in glycogen storage disease type II. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 203: 1535–1541.
Vorgerd M, Burwinkel B, Reichmann H, Malin J-P, Kilimann MW (1998) Adult-onset glycogen storage disease type II: phenotypic and allelic heterogeneity in German patients. Neurogenetics 1: 205–211.
Winchester B, Bali D, Bodamer AO, et al (2008) Methods for a prompt and reliable laboratory diagnosis of Pompe disease: report from an international consensus meeting. Mol Genet Metab 93(3): 275–281. Epub 19 Dec. 2007
Wokke JHJ, Ausems GEM, van den Boogaard MJH, et al (1995) Genotype–phenotype correlation in adult-onset acid maltase deficiency. Ann Neurol 38: 450–454.
Acknowledgement
We thank Silke Heinz for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicating editor: Alberto Burlina
JIMD Short Report #113 (2008) Online
Competing interests: None declared
References to electronic databases: Glycogen storage disease II: OMIM 232300. Alpha-glucosidase: OMIM 606800; EC 3.2.1.20/3. GAA: GenBank Y00839.1 (cDNA); NM_000152.2 (mRNA), X55079-X55097 (gDNA); RefSeq and version, NT_024871.11; GI: 37544588.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, P.R., Gläser, D., Schmidt, S. et al. Molecular diagnosis of German patients with late-onset glycogen storage disease type II. J Inherit Metab Dis 31 (Suppl 2), 261–265 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-008-0820-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-008-0820-2