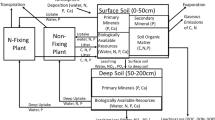
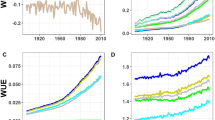
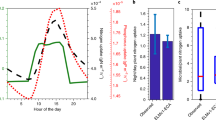
Abstract
Climate change has consequences for terrestrial functioning, but predictions of plant responses remain uncertain because of the gaps in the representation of nutrient cycles and C–N–P interactions in ecosystem models. Here, we review the processes that are included in ecosystem models, but focus on coupled C–N–P cycle models. We highlight important plant adjustments to climate change, elevated atmospheric CO2, and/or nutrient limitations that are currently not—or only partially—incorporated in ecosystem models by reviewing experimental studies and compiling data. Plant adjustments concern C:N:P stoichiometry, photosynthetic capacity, nutrient resorption rates, allocation patterns, symbiotic N2 fixation and root exudation (phosphatases, carboxylates) and the effect of root exudation on nutrient mobilization in the soil rhizosphere (P solubilization, biochemical mineralization of organic P and priming effect). We showed that several plant adjustments could be formulated and calibrated using existing experimental data in the literature. Finally, we proposed a roadmap for future research because improving ecosystem models necessitate specific data and collaborations between modelers and empiricists.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aber JD, Ollinger SV, Driscoll CT (1997) Modeling nitrogen saturation in forest ecosystems in response to land use and atmospheric deposition. Ecol Model 101:61–78
Abrahao A, Lambers H, Sawaya ACHF, Mazzafera P, Oliveira RS (2014) Convergence of a specialized root trait in plants from nutrient-impoverished soils: phosphorus-acquisition strategy in a nonmycorrhizal cactus. Oecologia 176:345–355
Achat DL, Bakker MR, Morel C (2009) Process-based assessment of phosphorus availability in a low phosphorus sorbing forest soil using isotopic dilution methods. Soil Sci Soc Am J 73:2131–2142
Achat DL, Bakker MR, Zeller B, Pellerin S, Bienaime S, Morel C (2010) Long term organic phosphorus mineralization in Spodosols under forests and its relation to carbon and nitrogen mineralization. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1479–1490
Achat DL, Augusto L, Bakker MR, Gallet-Budynek A, Morel C (2012) Microbial processes controlling P availability in forest Spodosols as affected by soil depth and soil properties. Soil Biol Biochem 44:39–48
Achat DL, Pousse N, Nicolas M, Brédoire F, Augusto L (2016) Soil properties controlling inorganic phosphorus availability: general results from a national forest network and a global compilation of the literature. Biogeochemistry 127:255–272
Ågren GI, Wetterstedt JÅ, Billberger MF (2012) Nutrient limitation on terrestrial plant growth–modeling the interaction between nitrogen and phosphorus. New Phytol 194:953–960
Ali MA, Louche J, Legname E, Duchemin M, Plassard C (2009) Pinus pinaster seedlings and their fungal symbionts show high plasticity in phosphorus acquisition in acidic soils. Tree Physiol 29:1587–1597
Allison SD, Martiny JBH (2008) Resistance, resilience, and redundancy in microbial communities. PNAS 105:11512–11519
Almeida JPF, Lüscher A, Frehner M, Oberson A, Nösberger J (1999) Partitioning of P and the activity of root acid phosphatase in white clover (Trifolium repens L.) are modified by increased atmospheric CO2 and P fertilization. Plant Soil 210:159–166
Annaheim KE, Doolette AL, Smernik RJ, Mayer J, Oberson A, Frossard E, Bünemann EK (2015) Long-term addition of organic fertilizers has little effect on soil organic phosphorus as characterized by 31P NMR spectroscopy and enzyme additions. Geoderma 257–258:67–77
Arain MA, Yuan F, Black TA (2006) Soil–plant nitrogen cycling modulated carbon exchanges in a western temperate conifer forest in Canada. Agric For Meteorol 140:171–192
Arróniz-Crespo M, Leake JR, Horton P, Phoenix GK (2008) Bryophyte physiological responses to, and recovery from, long-term nitrogen deposition and phosphorus fertilisation in acidic grassland. New Phytol 180:864–874
Asner GP, Knapp DE, Anderson CB, Martin RE, Vaughn N (2016) Large-scale climatic and geophysical controls on the leaf economics spectrum. PNAS 113:E4043–E4051
Augusto L, Delerue F, Gallet-Budynek A, Achat DL (2013) Global assessment of limitation to symbiotic nitrogen fixation by phosphorus availability in terrestrial ecosystems using a meta-analysis approach. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 27:804–815
Balemi T, Negisho K (2012) Management of soil phosphorus and plant adaptation mechanisms to phosphorus stress for sustainable crop production: a review. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 12:547–561
Barrow NJ (2008) The description of sorption curves. Eur J Soil Sci 59:900–910
Batterman SA, Wurzburger N, Hedin LO (2013) Nitrogen and phosphorus interact to control tropical symbiotic N2 fixation: a test in Inga punctata. J Ecol 101:1400–1408
Bloom AJ, Chapin FS, Mooney HA (1985) Resource limitation in plants—an economic analogy. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 16:363–392
Bown HE, Watt MS, Clinton PW, Mason EG, Richardson B (2007) Partititioning concurrent influences of nitrogen and phosphorus supply on photosynthetic model parameters of Pinus radiate. Tree Physiol 27:335–344
Bunemann EK (2008) Enzyme additions as a tool to assess the potential bioavailability of organically bound nutrients. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2116–2129
Bünemann EK (2015) Assessment of gross and net mineralization rates of soil organic phosphorus—a review. Soil Biol Biochem 89:82–98
Bünemann EK, Oberson A, Liebisch F, Keller F, Annaheim KE, Huguenin-Elie O, Frossard E (2012) Rapid microbial phosphorus immobilization dominates gross phosphorus fluxes in a grassland soil with low inorganic phosphorus availability. Soil Biol Biochem 51:84–95
Camenzind T, Hempel S, Homeier J, Horn S, Velescu A, Wilcke W, Rillig MC (2014) Nitrogen and phosphorus additions impact arbuscular mycorrhizal abundance and molecular diversity in a tropical montane forest. Glob Chang Biol 20:3646–3659
Cameron DR et al (2013) Environmental change impacts on the C- and N-cycle of European forests: a model comparison study. Biogeosciences 10:1751–1773
Canham CD, Berkowitz AR, Kelly VR, Lovett GM, Ollinger SV, Schnurr J (1996) Biomass allocation and multiple resource limitation in tree seedlings. Can J For Res 26:1521–1530
Carswell FE, Grace J, Lucas ME, Jarvis PG (2000) Interaction of nutrient limitation and elevated CO2 concentration on carbon assimilation of a tropical tree seedling (Cedrela odorata). Tree Physiol 20:977–986
Chadwick OA, Derry LA, Vitousek PM, Huebert BJ, Hedin LO (1999) Changing sources of nutrients during four million years of ecosystem development. Nature 397:491–497
Churkina G, Brovkin V, von Bloh W, Trusilova K, Jung M, Dentener F (2009) Synergy of rising nitrogen depositions and atmospheric CO2 on land carbon uptake moderately offsets global warming. Glob Biogeochem Cycle 23:GB4027
Condit R, Engelbrecht BMJ, Pino D, Perez R, Turner BL (2013) Species distributions in response to individual soil nutrients and seasonal drought across a community of tropical trees. PNAS 110:5064–5068
Cross AF, Schlesinger WH (1995) A literature review and evaluation of the Hedley fractionation: applications to the biogeochemical cycle of soil phosphorus in natural ecosystems. Geoderma 64:197–214
CSIRO, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (1997) Plant analysis: an interpretation manual. In: Reuter DJ, Robinson JB (ed), CSIRO Publishing, Collingwood
Cumming JR (1993) Growth and nutrition of nonmycorrhizal and mycorrhizal pitch pine (Pinus rigida) seedlings under phosphorus limitation. Tree Physiol 13:173–187
Davies JAC, Tipping E, Rowe EC, Boyle JF, Pannatier EG, Martinsen V (2016) Long-term P weathering and recent N deposition control contemporary plant-soil C, N and P. Glob Biogeochem Cycle. doi:10.1002/2015GB005167
De Kauwe MG et al (2014) Where does the carbon go? A model–data intercomparison of vegetation carbon allocation and turnover processes at two temperate forest free-air CO2 enrichment sites. New Phytol 203:883–899
Delgado D, Zúñiga-Feest A, Alvear M, Borie F (2013) The effect of phosphorus on cluster-root formation and functioning of Embothrium coccineum (R. et J. Forst.). Plant Soil 373:765–773
Devau N, Le Cadre E, Hinsinger P, Jaillard B, Gerard F (2009) Soil pH controls the environmental availability of phosphorus: experimental and mechanistic modelling approaches. Appl Geochem 24:2163–2174
Devau N, Hinsinger P, Le Cadre E, Gérard F (2011) Root-induced processes controlling phosphate availability in soils with contrasted P-fertilized treatments. Plant Soil 348:203–218
Drake JE et al (2011) Increases in the flux of carbon belowground stimulate nitrogen uptake and sustain the long-term enhancement of forest productivity under elevated CO2. Ecol Lett 14:349–357
Duputel M, Devau N, Brossard M, Jaillard B, Jones DL, Hinsinger P, Gérard F (2013) Citrate adsorption can decrease soluble phosphate concentration in soils: results of theoretical modeling. Appl Geochem 35:120–131
Egle K, Romer W, Keller H (2003) Exudation of low molecular weight organic acids by Lupinus albus L., Lupinus angustifolius L. and Lupinus luteus L. as affected by phosphorus supply. Agronomie 23:511–518
Ellsworth DS, Crous KY, Lambers H, Cooke J (2015) Phosphorus recycling in photorespiration maintains high photosynthetic capacity in woody species. Plant Cell Environ 38:1142–1156
Elser J, Bracken M, Cleland E, Gruner D, Harpole W, Hillebrand H, Ngai J, Seabloom E, Shurin J, Smith J (2007) Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 10:1135–1142
Esser G, Kattge J, Sakalli A (2011) Feedback of carbon and nitrogen cycles enhances carbon sequestration in the terrestrial biosphere. Glob Chang Biol 17:819–842
Evans JR (1989) Photosynthesis and nitrogen relationships in leaves of C3 plants. Oecologia 78:9–19
Farquhar GD, von Caemmerer S, Berry JA (1980) A biochemical model of photosynthetic CO2 assimilation in leaves of C3 species. Planta 149:78–90
Finzi AC, Cole JJ, Doney SC, Holland EA, Jackson RB (2011) Research frontiers in the analysis of coupled biogeochemical cycles. Front Ecol Environ 9:74–80
Finzi AC et al (2015) Rhizosphere processes are quantitatively important components of terrestrial carbon and nutrient cycles. Glob Chang Biol 21:2082–2094
Fontaine S, Henault C, Aamor A, Bdioui N, Bloor JMG, Maire V, Mary B, Revaillot S, Maron PA (2011) Fungi mediate long term sequestration of carbon and nitrogen in soil through their priming effect. Soil Biol Biochem 43:86–96
Fox TR, Comerford NB (1992) Rhizosphere phosphatase activity and phosphatase hyrolyzable organic phosphorus in two forested spodosols. Soil Biol Biochem 24:579–583
Fung IY, Doney SC, Lindsay K, John J (2005) Evolution of carbon sinks in a changing climate. PNAS 102:11201–11206
Galloway JN et al (2004) Nitrogen cycles: past, present, and future. Biogeochemistry 70:153–226
Garcia-Palacios P, Vandegehuchte ML, Shaw EA, Dam M, Post KH, Ramirez KS, Sylvain ZA, de Tomasel CM, Wall DH (2015) Are there links between responses of soil microbes and ecosystem functioning to elevated CO2, N deposition and warming? A global perspective. Glob Chang Biol 21:1590–1600
Gardner LB (1990) The role of rock weathering in the phosphorus budget of terrestrial watersheds. Biogeochemistry 11:97–110
Gaume A, Mächler F, De Leon C, Narro L, Frossard E (2001) Low-P tolerance by maize (Zea mays L.) genotypes: Significance of root growth, and organic acids and acid phosphatase root exudation. Plant Soil 228:253–264
Gerard F (2016) Clay minerals, iron/aluminum oxides, and their contribution to phosphate sorption in soils—a myth revisited. Geoderma 262:213–226
Gerber S, Hedin LO, Oppenheimer M, Pacala SW, Shevliakova E (2010) Nitrogen cycling and feedbacks in a global dynamic land model. Global Biogeochem Cycle 24:GB1001
Gerke J (2015) The acquisition of phosphate by higher plants: Effect of carboxylate release by the roots. A critical review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 178:351–364
Ghannoum O, Paul MJ, Ward JL, Beale MH, Corol DI, Conroy JP (2008) The sensitivity of photosynthesis to phosphorus deficiency differs between C3 and C4 tropical grasses. Funct Plant Biol 35:213–221
Gifford RM, Lutze JL, Barrett D (1996) Global atmospheric change effects on terrestrial carbon sequestration: Exploration with a global C- and N-cycle model (CQUESTN). Plant Soil 187:369–387
Gilhespy SL et al (2014) First 20 years of DNDC (denitrification decomposition): Model evolution. Ecol Model 292:51–62
Goll DS, Brovkin V, Parida BR, Reick CH, Kattge J, Reich PB, van Bodegom PM, Niinemets U (2012) Nutrient limitation reduces land carbon uptake in simulations with a model of combined carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycling. Biogeosciences 9:3547–3569
Grant RF (1991) A technique for estimating denitrification rates at different soil temperatures, water contents, and nitrate concentrations. Soil Sci 152:41–52
Grant RF, Nyborg M, Laidlaw J (1993a) Evolution of nitrous oxide from soil: 1. Model development. Soil Sci 156:259–265
Grant RF, Nyborg M, Laidlaw J (1993b) Evolution of nitrous oxide from soil: II. Experimental results and model testing. Soil Sci 156:266–277
Grant RF et al (1999) Diurnal and annual exchanges of mass and energy between an aspen-hazelnut forest and the atmosphere: Testing the mathematical model Ecosys with data from the BOREAS experiment. J Geophys Res 104:27699–27717
Grant RF et al (2001) Controls on carbon and energy exchange by a black spruce-moss ecosystem: testing the mathematical model Ecosys with data from the BOREAS experiment. Global Biogeochem Cycle 15:129–147
Gruber N, Galloway JN (2008) An earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 451:293–296
Güsewell S, Gessner MO (2009) N: P ratios influence litter decomposition and colonization by fungi and bacteria in microcosms. Funct Ecol 23:211–219
Han W, Tang L, Chen Y, Fang J (2013) Relationship between the relative limitation and resorption efficiency of nitrogen vs phosphorus in woody plants. PLoS ONE 8:e83366
Hanson PJ et al (2004) Oak forest carbon and water simulations: model intercomparisons and evaluations against independent data. Ecol Monogr 74:443–489
Harpole WS, Ngai JT, Cleland EE, Seabloom EW, Borer ET, Bracken MES, Elser JJ, Gruner DS, Hillebrand H, Shurin JB, Smith JE (2011) Nutrient co-limitation of primary producer communities. Ecol Lett 14:852–862
Hedin LO, Vitousek PM, Matson PA (2003) Nutrient losses over four million years of tropical forest development. Ecology 84:2231–2255
Heimann M, Reichstein M (2008) Terrestrial ecosystem carbon dynamics and climate feedbacks. Nature 451:289–292
Herridge DF, Peoples MB, Boddey RM (2008) Global inputs of biological nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems. Plant Soil 311:1–18
Heuck C, Weig A, Spohn M (2015) Soil microbial biomass C:N:P stoichiometry and microbial use of organic phosphorus. Soil Biol Biochem 85:119–129
Hinsinger P (2001) Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes: a review. Plant Soil 237:173–195
Houlton BZ, Wang YP, Vitousek PM, Field CB (2008) A unifying framework for dinitrogen fixation in the terrestrial biosphere. Nature 454:327–330
Hungate BA, Dukes JS, Shaw MR, Luo Y, Field CB (2003) Nitrogen and climate change. Science 302:1512–1513
Hunt ER Jr, Lavigne MB, Franklin SE (1999) Factors controlling the decline of net primary production with stand age for balsam fir in Newfoundland assessed using an ecosystem simulation model. Ecol Model 122:151–164
Iversen CM (2010) Digging deeper: fine-root responses to rising atmospheric CO2 concentration in forested ecosystems. New Phytol 186:346–357
Jansson PE, Karlberg L (2001) Coupled heat and mass transfer model for soil-plant-atmosphere systems. Royal Institute of Technology, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Stockholm. (ftp://www.lwr.kth.se/CoupModel/CoupModel.pdf), p 321
Jarosch KA, Doolette AL, Smernik RJ, Tamburini F, Frossard E, Bünemann EK (2015) Characterisation of soil organic phosphorus in NaOH-EDTA extracts: a comparison of 31P NMR spectroscopy and enzyme addition assays. Soil Biol Biochem 91:298–309
Jin J, Tang C, Salte P (2015) The impact of elevated carbon dioxide on the phosphorus nutrition of plants: a review. Ann Bot 116:987–999
Johnson D, Leake JR, Lee JA (1999) The effects of quantity and duration of simulated pollutant nitrogen deposition on root-surface phosphatase activities in calcareous and acid grasslands: a bioassay approach. New Phytol 141:433–442
Kamh M, Abdou M, Chude V, Wiesler F, Horst WJ (2002) Mobilization of phosphorus contributes to positive rotational effects of leguminous cover crops on maize grown on soils from northern Nigeria. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 165:566–572
Karam SL, Weisberg PJ, Scheller RM, Johnson DW, Miller WW (2013) Development and evaluation of a nutrient cycling extension for the LANDIS-II landscape simulation model. Ecol Model 250:45–57
Keller M, Oberson A, Annaheim KE, Tamburini F, Mäder P, Mayer J, Frossard E, Bünemann EK (2012) Phosphorus forms and enzymatic hydrolyzability of organic phosphorus in soils after 30 years of organic and conventional farming. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 175:385–393
Kimmins JP, Mailly D, Seely B (1999) Modelling forest ecosystem net primary production: the hybrid simulation approach used in FORECAST. Ecol Model 122:195–224
Kirschbaum MUF (1999) CenW, a forest growth model with linked carbon, energy, nutrient and water cycles. Ecol Model 118:17–59
Kirschbaum MUF, Paul KI (2002) Modelling carbon and nitrogen dynamics in forest soils with a modified version of the CENTURY model. Soil Biol Biochem 34:341–354
Kohler IH, MacDonald A, Schnyder H (2012) Nutrient supply enhanced the increase in intrinsic water use efficiency of a temperate semi natural grassland in the last century. Glob Chang Biol 18:3367–3376
Lambers H, Shane MW, Cramer MD, Pearse SJ, Veneklaas EJ (2006) Root structure and functioning for efficient acquisition of phosphorus: matching morphological and physiological traits. Ann Bot 98:693–713
Leff JW et al (2015) Consistent responses of soil microbial communities to elevated nutrient inputs in grasslands across the globe. PNAS 112:10967–10972
Lewis DR, McGechan MB (2002) A review of field scale phosphorus dynamics models. Biosyst Eng 82:359–380
Li C, Frolking S, Frolking TA (1992) A model of nitrous oxide evolution from soil driven by rainfall events: 1. Model structure and sensitivity. J Geophys Res 97:9759–9776
Li M, Osaki M, Rao IM, Tadano T (1997) Secretion of phytase from the roots of several plant species under phosphorus-deficient conditions. Plant Soil 195:161–169
Liebig J (1842) Animal chemistry, or organic chemistry in its application to physiology and pathology. Johnson Reprint Corporation, New York
Liu S, Munson R, Johnson DW, Gherini S, Summers K, Hudson R, Wilkinson K, Pitelka LF (1991) Application of a nutrient cycling model (NuCM) to northern mixed hardwood and southern coniferous forests. Tree Physiol 9:173–182
Liu Y, Mi G, Chen F, Zhang J, Zhang F (2004) Rhizosphere effect and root growth of two maize (Zea mays L.) genotypes with contrasting P efficiency at low P availability. Plant Sci 167:217–223
Loustau D, Brahim MB, Gaudillere JP, Dreyer E (1999) Photosynthetic responses to phosphorus nutrition in two-year-old maritime pine seedlings. Tree Physiol 19:707–715
Lü XT, Reed SC, Yu Q, Han XG (2016) Nutrient resorption helps drive intra-specific coupling of foliar nitrogen and phosphorus under nutrient-enriched conditions. Plant Soil 398:111–120
Luo Y et al (2004) Progressive nitrogen limitation of ecosystem responses to rising atmospheric carbon dioxide. Bioscience 54:731–739
Marklein AR, Houlton BZ (2012) Nitrogen inputs accelerate phosphorus cycling rates across a wide variety of terrestrial ecosystems. New Phytol 193:696–704
Marklein AR et al (2015) Mineralization ratios of nitrogen and phosphorus from decomposing litter in temperate versus tropical forests. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 25:335–346
Matear RJ, Wang YP, Lenton A (2010) Land and ocean nutrient and carbon cycle interactions. Curr Opin Environ Sustain 2:258–263
McGechan MB (2002) Sorption of phosphorus by soil, Part 2: measurement methods, results and model parameter values. Biosyst Eng 82:115–130
McGechan MB, Lewis DR (2002) Sorption of phosphorus by soil, Part 1: principles, equations and models. Biosyst Eng 82:1–24
McGill WB, Cole CV (1981) Comparative aspects of cycling of organic C, N, S and P through soil organic matter. Geoderma 26:267–286
McMurtrie RE, Dewar RC, Medlyn BE, Jeffreys MP (2000) Effects of elevated [CO2] on forest growth and carbon storage: a modelling analysis of the consequences of changes in litter quality/quantity and root exudation. Plant Soil 224:135–152
Medlyn BE, Duursma RA, Zeppel MJB (2011) Forest productivity under climate change: a checklist for evaluating model studies. Wiley Interdiscip Rev-Clim Chang 2:332–355
Menge DN, Lichstein JW, Ángeles-Pérez G (2014) Nitrogen fixation strategies can explain the latitudinal shift in nitrogen-fixing tree abundance. Ecology 95:2236–2245
Menge DN, Wolf AA, Funk JL (2015) Diversity of nitrogen fixation strategies in Mediterranean legumes. Nature Plants 1:1–5
Metherell AK, Harding LA, Cole CV, Parton WJ (1993) CENTURY soil organic matter model environment. Technical documentation. Agroecosystem Version 4.0. Great Plains System Research Unit. Technical Report No. 4. USDA-ARS, Fort Collins. https://www.nrel.colostate.edu/projects/century/
Meunier CL, Gundale MJ, Sanchez IS, Liess A (2016) Impact of nitrogen deposition on forest and lake food webs in nitrogen-limited environments. Glob Chang Biol 22:164–179
Meyerholt J, Zaehle S (2015) The role of stoichiometric flexibility in modelling forest ecosystem responses to nitrogen fertilization. New Phytol 208:1042–1055
Montzka SA, Dlugokencky EJ, Butler JH (2011) Non-CO2 greenhouse gases and climate change. Nature 476:43–50
Morel C, Ziadi N, Messiga A, Belanger G, Denoroy P, Jeangros B, Jouany C, Fardeau JC, Mollier A, Parent LE, Proix N, Rabeharisoa L, Sinaj S (2014) Modeling of phosphorus dynamics in contrasting agroecosystems using long-term field experiments. Can J Soil Sci 94:377–387
Negrin MA, Gonzalez-Carcedo S, Hernandez-Moreno JM (1995) P fractionation in sodium bicarbonate extracts of andic soils. Soil Biol Biochem 21:761–766
Newman EI (1995) Phosphorus inputs to terrestrial ecosystems. J Ecol 83:713–726
Noormets A, Epron D, Domec JC, McNulty SG, Fox T, Sun G, King JS (2015) Effects of forest management on productivity and carbon sequestration: a review and hypothesis. For Ecol Manage 355:124–140
Norby RJ et al (2016) Model-data synthesis for the next generation of forest free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) experiments. New Phytol 209:17–28
O’Hara GW (2001) Nutritional constraints on root nodule bacteria affecting symbiotic nitrogen fixation: a review. Aust J Exp Agr 41:417–433
Oburger E, Jones DL, Wenzel WW (2011) Phosphorus saturation and pH differentially regulate the efficiency of organic acid anion-mediated P solubilization mechanisms in soil. Plant Soil 341:363–382
Oehl F, Oberson A, Sinaj S, Frossard E (2001) Organic phosphorus mineralization studies using isotopic dilution techniques. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:780–787
Oehl F, Frossard E, Fliessbach A, Dubois D, Oberson A (2004) Basal organic phosphorus mineralization in soils under different farming systems. Soil Biol Biochem 36:667–675
Olander L, Vitousek P (2000) Regulation of soil phosphatase and chitinase activity by N and P availability. Biogeochemistry 49:175–191
Otani T, Ae N (1999) Extraction of organic phosphorus in Andosols by various methods. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 45:151–161
Pant HK, Warman PR (2000) Enzymatic hydrolysis of soil organic phosphorus by immobilized phosphatases. Biol Fertil Soils 30:306–311
Parton WJ, Schimel DJ, Cole CV, Ojima DS (1987) Analysis of factors controlling soil organic matter levels in great plains grasslands. Soil Sci Soc Am J 51:1173–1179
Parton WJ, Stewart JWB, Cole CV (1988) Dynamics of C, N, P and S in grassland soils: a model. Biogeochemistry 5:109–131
Parton WJ, Hartman M, Ojima D, Schimel D (1998) DAYCENT and its land surface submodel: description and testing. Glob Planet Chang 19:35–48
Parton WJ, Hanson PJ, Swanston C, Torn M, Trumbore SE, Riley W, Kelly R (2010) ForCent model development and testing using the enriched background isotope study experiment. J Geophys Res 115:G04001
Penuelas J et al (2013) Human-induced nitrogen–phosphorus imbalances alter natural and managed ecosystems across the globe. Nat Commun 4:2934
Persson J, Nasholm T (2002) Regulation of amino acid uptake in conifers by exogenous and endogenous nitrogen. Planta 215:639–644
Phillips RP, Bernhardt ES, Schlesinger WH (2009) Elevated CO2 increases root exudation from loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) seedlings as an N-mediated response. Tree Physiol 29:1513–1523
Phillips RP, Finzi AC, Bernhardt ES (2011) Enhanced root exudation induces microbial feedbacks to N cycling in a pine forest under long-term CO2 fumigation. Ecol Lett 14:187–194
Phoenix GK, Booth RE, Leake JR, Read DJ, Grime JP, Lee JA (2003) Simulated pollutant nitrogen deposition increases P demand and enhances root-surface phosphatase activities of three plant functional types in a calcareous grassland. New Phytol 161:279–289
Phuyal M, Artz RRE, Sheppard L, Leith ID, Johnson D (2008) Long-term nitrogen deposition increases phosphorus limitation of bryophytes in an ombrotrophic bog. Plant Ecol 196:111–121
Plassard C, Dell B (2010) Phosphorus nutrition of mycorrhizal trees. Tree Physiol 30:1129–1139
Playsted CWS, Johnston ME, Ramage CM, Edwards DG, Cawthray GR, Lambers H (2006) Functional significance of dauciform roots: exudation of carboxylates and acid phosphatase under phosphorus deficiency in Caustis blakei (Cyperaceae). New Phytol 170:491–500
Porté A, Loustau D (1998) Variability of the photosynthetic characteristics of mature needles within the crown of a 25-year-old Pinus pinaster. Tree Physiol 18:223–232
Qualls RG, Richardson CJ (2003) Factors controlling concentration, export, and decomposition of dissolved organic nutrients in the Everglades of Florida. Biogeochemistry 62:197–229
Rasse DP (2002) Nitrogen deposition and atmospheric CO2 interactions on fine root dynamics in temperate forests: a theoretical model analysis. Glob Chang Biol 8:486–503
Rastetter EB (2011) Modeling coupled biogeochemical cycles. Front Ecol Environ 9:68–73
Reddell P, Yun Y, Shipton WA (1997) Do Casuarina cunninghamiana seedlings dependent on symbiotic N2 fixation have higher phosphorus requirements than those supplied with adequate fertilizer nitrogen? Plant Soil 189:213–219
Reed SC, Cleveland CC, Townsend AR (2011) Functional ecology of free-living nitrogen fixation: A contemporary perspective. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 42:489–512
Reed SC, Yang X, Thornton PE (2015) Incorporating phosphorus cycling into global modeling efforts: a worthwhile, tractable endeavor. New Phytol 208:324–329
Reich PB, Oleksyn J, Wright IJ (2009) Leaf phosphorus influences the photosynthesis-nitrogen relation: a cross-biome analysis of 314 species. Oecologia 160:207–212
Rejmankova E, Snyder JM (2008) Emergent macrophytes in phosphorus limited marshes: do phosphorus usage strategies change after nutrient addition? Plant Soil 313:141–153
Requejo MI, Eichler-Lobermann B (2014) Organic and inorganic phosphorus forms in soil as affected by long-term application of organic amendments. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 100:245–255
Ribet J, Drevon JJ (1996) The phosphorus requirement of N2-fixing and urea-fed Acacia mangium. New Phytol 132:383–390
Robson AD, Ohara GW, Abbott LK (1981) Involvement of phosphorus in nitrogen-fixation by subterranean clover (Trifolium subterraneum L). Aust J Plant Physiol 8:427–436
Roelofs RFR, Rengel Z, Cawthray GR, Dixon KW, Lambers H (2001) Exudation of carboxylates in Australian Proteaceae: chemical composition. Plant Cell Environ 24:891–903
Rousk J, Brookes PC, Baath E (2011) Fungal and bacterial growth responses to N fertilization and pH in the150-year ‘Park Grass’ UK grassland experiment. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 76:89–99
Runing SW, Coulghan JC (1988) A general model of forest ecosystem processes for regional applications. I. Hydrologic balance, canopy gas exchange and primary production processes. Ecol Model 42:125–154
Sardans J et al (2016) Foliar and soil concentrations and stoichiometry of nitrogen and phosphorus across European Pinus sylvestris forests: relationships with climate, N deposition and tree growth. Funct Ecol. doi:10.1111/1365-2435.12541
Scheller RM, Mladenoff DJ (2004) A forest growth and biomass module for a landscape simulation model, LANDIS: design, validation, and application. Ecol Model 180:211–229
Schimel JP, Bennett J (2004) Nitrogen mineralization: challenges of a changing paradigm. Ecology 85:591–602
See CR, Yanai RD, Fisk MC, Vadeboncoeur MA, Quintero BA, Fahey TJ (2015) Soil nitrogen affects phosphorus recycling: foliar resorption and plant–soil feedbacks in a northern hardwood forest. Ecology 96:2488–2498
Seeling B, Jungk A (1996) Utilization of organic phosphorus in calcium chloride extracts of soil by barley plants and hydrolysis by acid and alkaline phosphatases. Plant Soil 178:179–184
Shahzad T, Chenu C, Genet P, Barot S, Perveen N, Mougin C, Fontaine S (2015) Contribution of exudates, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and litter depositions to the rhizosphere priming effect induced by grassland species. Soil Biol Biochem 80:146–155
Shane MW, de Vos M, de Roock S, Cawthray GR, Lambers H (2003) Effects of external phosphorus supply on internal phosphorus concentration and the initiation, growth and exudation of cluster roots in Hakea prostrata R. Br. Plant Soil 248:209–219
Shen J, Li H, Neumann G, Zhang F (2005) Nutrient uptake, cluster root formation and exudation of protons and citrate in Lupinus albus as affected by localized supply of phosphorus in a split-root system. Plant Sci 168:837–845
Smaill SJ, Clinton PW, Hock BK (2011) A nutrient balance model (NuBalM) to predict biomass and nitrogen pools in Pinus radiata forests. For Ecol Manag 262:270–277
Smith B, Warlind D, Arneth A, Hickler T, Leadley P, Siltberg J, Zaehle S (2014) Implications of incorporating N cycling and N limitations on primary production in an individual-based dynamic vegetation model. Biogeosciences 11:2027–2054
Sokolov AP et al (2008) Consequences of considering carbon–nitrogen interactions on the feedbacks between climate and the terrestrial carbon cycle. J Clim 21:3776–3796
Soussana JF, Tallec T (2010) Can we understand and predict the regulation of biological N2 fixation in grassland ecosystems? Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 88:197–213
Spohn M, Ermak A, Kuzyakov Y (2013) Microbial gross organic phosphorus mineralization can be stimulated by root exudates—A 33P isotopic dilution study. Soil Biol Biochem 65:254–263
Sulman BN, Phillips RP, Oishi AC, Shevliakova E, Pacala SW (2014) Microbe-driven turnover offsets mineral-mediated storage of soil carbon under elevated CO2. Nat Clim Chang 4:1099–1102
Tadano T, Sakai H (1991) Secretion of acid phosphatase by the roots of several crop species under phosphorus-deficient conditions. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 37:129–140
Tang JY, Riley WJ (2013) A total quasi-steady-state formulation of substrate uptake kinetics in complex networks and an example application to microbial litter decomposition. Biogeosciences 10:8329–8351
Tang JY, Riley WJ (2014) Weaker soil carbon-climate feedbacks resulting from microbial and abiotic interactions. Nat Clim Chang 5:56–60
Tang C, Han XZ, Qiao YF, Zheng SJ (2009) Phosphorus deficiency does not enhance proton release by roots of soybean [Glycine max (L.) Murr.]. Environ Exp Bot 67:228–234
Tang HL, Shen JB, Zhang FS, Rengel Z (2013) Interactive effects of phosphorus deficiency and exogenous auxin on root morphological and physiological traits in white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). Sci China Life Sci 56:313–323
Thomas RQ, Brookshire ENJ, Gerber S (2015) Nitrogen limitation on land: how can it occur in Earth system models? Glob Chang Biol 21:1777–1793
Thornton PE, Lamarque JF, Rosenbloom NA, Mahowald NM (2007) Influence of carbon-nitrogen cycle coupling on land model response to CO2 fertilization and climate variability. Global Biogeochem Cycle 21:GB4018
Thornton PE, Doney SC, Lindsay K, Moore JK, Mahowald N, Randerson JT, Fung I, Lamarque JF, Feddema JJ, Lee YH (2009) Carbon-nitrogen interactions regulate climate-carbon cycle feedbacks: results from an atmosphere-ocean general circulation model. Biogeosciences 6:2099–2120
Tipping E, Rowe E, Evans C, Mills R, Emmett B, Chaplow J, Hall J (2012) N14C: a plant–soil nitrogen and carbon cycling model to simulate terrestrial ecosystem responses to atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Ecol Model 247:11–26
Todd-Brown KEO, Hopkins FM, Kivlin SN, Talbot JM, Allison SD (2012) A framework for representing microbial decomposition in coupled climate models. Biogeochemistry 109:19–33
Townsend AR, Cleveland CC, Asner GP, Bustamante MMC (2007) Controls over foliar N:P ratios in tropical rain forests. Ecology 88:107–118
Townsend AR, Cleveland CC, Houlton BZ, Alden CB, White JWC (2011) Multi-element regulation of the tropical forest carbon cycle. Front Ecol Environ 9:9–17
Treseder K, Vitousek P (2001) Effects of soil nutrient availability on investment in acquisition of N and P in Hawaiian rain forests. Ecology 82:946–954
Treseder KK et al (2012) Integrating microbial ecology into ecosystem models: challenges and priorities. Biogeochemistry 109:7–18
Turner BL (2005) Storage-induced changes in phosphorus solubility of air-dried soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 69:630–633
Turner BL, McKelvie ID, Haygarth PM (2002) Characterisation of water-extractable soil organic phosphorus by phosphatase hydrolysis. Soil Biol Biochem 34:27–35
Ushio M, Fujiki Y, Hidaka A, Kitayama K (2015) Linkage of root physiology and morphology as an adaptation to soil phosphorus impoverishment in tropical montane forests. Funct Ecol 29:1235–1245
van Groenigen KJ, Six J, Hungate BA, de Graaff MA, van Breemen N, van Kessel C (2006) Element interactions limit soil carbon storage. PNAS 103:6571–6574
Vargas R, Carbone MS, Reichstein M, Baldocchi DD (2011) Frontiers and challenges in soil respiration research: from measurements to model-data integration. Biogeochemistry 102:1–13
Verburg PSJ, Johnson DW (2001) A spreadsheet-based biogeochemical model to simulate nutrient cycling processes in forest ecosystems. Ecol Model 141:185–200
Vergutz L et al (2012) Global resorption efficiencies and concentrations of carbon and nutrients in leaves of terrestrial plants. Ecol Monogr 82:205–220
Vitousek PM, Howarth RW (1991) Nitrogen limitation on land and in the sea: how can it occur? Biogeochemistry 13:87–115
Vitousek PM et al (2002) Towards an ecological understanding of biological nitrogen fixation. Biogeochemistry 57:1–45
Vitousek PM, Menge DN, Reed SC, Cleveland CC (2013) Biological nitrogen fixation: rates, patterns and ecological controls in terrestrial ecosystems. Philos Trans R Soc B 368:20130119
Walker TW, Syers JK (1976) The fate of phosphorus during pedogenesis. Geoderma 15:1–19
Walker AP et al (2014a) The relationship of leaf photosynthetic traits—Vcmax and Jmax—to leaf nitrogen, leaf phosphorus, and specific leaf area: a meta-analysis and modeling study. Ecol Evol 4:3218–3235
Walker AP et al (2014b) Comprehensive ecosystem model-data synthesis using multiple data sets at two temperate forest free-air CO2 enrichment experiments: model performance at ambient CO2 concentration. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 119(5):937–964
Wang YP, Houlton BZ, Field CB (2007) A model of biogeochemical cycles of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus including symbiotic nitrogen fixation and phosphatase production. Glob Biogeochem Cycle 21:GB1018
Wang YP, Law RM, Pak B (2010) A global model of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycles for the terrestrial biosphere. Biogeosciences 7:2261–2282
Wang F et al (2014) Multimodel simulations of forest harvesting effects on long-term productivity and CN cycling in aspen forests. Ecol Appl 24:1374–1389
Wassen MJ, de Boer HJ, Fleischer K, Rebel KT, Dekker SC (2013) Vegetation-mediated feedback in water, carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycles. Landsc Ecol 28:599–614
Wei L, Chen C, Xu Z (2010) Citric acid enhances the mobilization of organic phosphorus in subtropical and tropical forest soils. Biol Fertil Soils 46:765–769
Wieder WR, Cleveland CC, Smith WK, Todd-Brown K (2015) Future productivity and carbon storage limited by terrestrial nutrient availability. Nat Geosci 8:441–444
Wilson KB, Baldocchi DD, Hanson PJ (2000) Spatial and seasonal variability of photosynthetic parameters and their relationship to leaf nitrogen in a deciduous forest. Tree Physiol 20:565–578
Wyngaard N, Cabrera ML, Jarosch KA, Bünemann EK (2016) Phosphorus in the coarse soil fraction is related to soil organic phosphorus mineralization measured by isotopic dilution. Soil Biol Biochem 96:107–118
Xu-Ri, Prentice IC (2008) Terrestrial nitrogen cycle simulation with a dynamic global vegetation model. Glob Chang Biol 14:1745–1764
Yang X, Wittig V, Jain AK, Post W (2009) Integration of nitrogen cycle dynamics into the Integrated Science Assessment Model for the study of terrestrial ecosystem responses to global change. Glob Biogeochem Cycle 23:GB4029
Yang X, Post WM, Thornton PE, Jain A (2013) The distribution of soil phosphorus for global biogeochemical modeling. Biogeosciences 10:2525–2537
Yang X, Thornton PE, Ricciuto DM, Post WM (2014) The role of phosphorus dynamics in tropical forests—a modeling study using CLM-CNP. Biogeosciences 11:1667–1681
Zaehle S, Dalmonech D (2011) Carbon–nitrogen interactions on land at global scales: current understanding in modelling climate biosphere feedbacks. Curr Opin Environ Sustain 3:311–320
Zaehle S, Friend AD (2010) Carbon and nitrogen cycle dynamics in the O-CN land surface model: 1. Model description, site-scale evaluation, and sensitivity to parameter estimates. Global Biogeochem Cycle 24:GB1005
Zaehle S, Friedlingstein P, Friend AD (2010a) Terrestrial nitrogen feedbacks may accelerate future climate change. Geophys Res Lett 37:L01401
Zaehle S, Friend AD, Friedlingstein P, Dentener F, Peylin P, Schulz M (2010b) Carbon and nitrogen cycle dynamics in the O-CN land surface model: 2. Role of the nitrogen cycle in the historical terrestrial carbon balance. Global Biogeochem Cycle 24:GB1006
Zaehle S et al (2014) Evaluation of 11 terrestrial carbon–nitrogen cycle models against observations from two temperate Free-Air CO2 Enrichment studies. New Phytol 202:803–822
Zhang Q, Wang YP, Pitman AJ, Dai YJ (2011) Limitations of nitrogen and phosphorous on the terrestrial carbon uptake in the 20th century. Geophys Res Lett 38:L22701
Zhang Q, Pitman AJ, Wang YP, Dai YJ, Lawrence PJ (2013a) The impact of nitrogen and phosphorous limitation on the estimated terrestrial carbon balance and warming of land use change over the last 156 yr. Earth Syst Dyn 4:333–345
Zhang Y, Zhou Z, Yang Q (2013b) Nitrogen (N) deposition impacts seedling growth of Pinus massoniana via N:P ratio effects and the modulation of adaptive responses to low P (phosphorus). PLoS ONE 8:e79229
Zhang S, Jiang H, Zhao H, Korpelainen H, Li C (2014) Sexually different physiological responses of Populus cathayana to nitrogen and phosphorus deficiencies. Tree Physiol 34:343–354
Zhu Z, Arp PA, Meng F, Bourque CPA, Foster NW (2003) A forest nutrient cycling and biomass model (ForNBM) based on year-round, monthly weather conditions, part I: assumption, structure and processing. Ecol Model 169:347–360
Zhu Q, Riley WJ, Tang J, Koven CD (2016) Multiple soil nutrient competition between plants, microbes, and mineral surfaces: model development, parameterization, and example applications in several tropical forests. Biogeosciences 13:341–363
Zhu-Barker X, Cavazos AR, Ostrom NE, Horwath WR, Glass JB (2015) The importance of abiotic reactions for nitrous oxide production. Biogeochemistry 126:251–267
Zou X, Binkley D, Caldwell BA (1995) Effects of dinitrogen-fixing trees on phosphorus biogeochemical cycling in contrasting forests. Soil Sci Soc Am J 59:1452–1458
Acknowledgements
This review was made in the framework of the David Achat’s research project, and the EVAFORA and MACACC projects supported by the French agency for energy and environment (ADEME) and the French National Research Agency (ANR), respectively. We thank Bruno Ringeval, Delphine Picard, Simon Martel and Sébastien Lafont for useful discussions. Finally, we thank editors Stephen Porder and Sharon Billings and two anonymous reviewers for improving the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Stephen Porder.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Achat, D.L., Augusto, L., Gallet-Budynek, A. et al. Future challenges in coupled C–N–P cycle models for terrestrial ecosystems under global change: a review. Biogeochemistry 131, 173–202 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-016-0274-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-016-0274-9