Abstract
Objectives
l-isoleucine dioxygenase (IDO) specifically transforms l-isoleucine (Ile) to 4-hydroxyisoleucine (4-HIL), and 4-HIL is a promising drug for diabetes. To enhance the activity and catalytic efficiency of IDO, we used directed evolution and site-specific mutagenesis.
Results
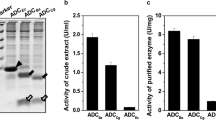
The IDO gene (ido) derived from Bacillus weihenstephanensis was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. Directed evolution using error prone (EP)-PCR and site-specific mutagenesis were conducted. Two improved mutants were obtained after one round of EP-PCR, with IdoN126H exhibiting a 2.8-fold increase in activity. Two improved mutants were obtained through site-specific mutagenesis, with IdoT130K showing a 170% increase in activity. Although the activity of the combined mutant IdoN126H/T130K (0.95 ± 0.08 U/mg) was slightly higher than that of the wild-type Ido, its catalytic efficiency was 2.4-fold and 3.0-fold higher than Ido with Ile and α-ketoglutaric acid as substrates. After biotransformation of Ile by E. coli BL21(DE3) expressing IdoN126H/T130K and Ido, 66.50 ± 0.99 mM and 26.09 ± 1.85 mM 4-HIL was synthesized, respectively, in 24 h.
Conclusion
IdoN126H/T130K had a higher enzyme activity and catalytic efficiency and can therefore be used as a more suitable candidate for 4-HIL production.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo JP, Reetz MT, Asenjo JA, Parra LP (2017) One-step combined focused epPCR and saturation mutagenesis for thermostability evolution of a new cold-active xylanase. Enzyme Microb Technol 100:60–70
Cadwell RC, Joyce GF (1994) Mutagenic PCR. PCR Methods Appl 3:136–140
Drummond DA, Iverson BL, Georgiou G, Arnold FH (2005) Why high-error-rate random mutagenesis libraries are enriched in functional and improved proteins. J Mol Biol 35:806–816
Fowden L, Pratt HM, Smith A (1973) 4-Hydroxyisoleucine from seed of Trigonella foenum-graecum. Phytochemistry 12:707–711
Hibi M, Kawashima T, Kodera T, Smirnov SV, Sokolov PM, Sugiyama M, Shimizu S, Yokozeki K, Ogawa J (2011) Characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis l-isoleucine dioxygenase for production of useful amino acids. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(19):6926–6930
Kivero AD, Novikova AE, Smirnov SV (2012) Modification of E. coli central metabolism to optimize the biotransformation of l-isoleucine into 4-hydroxyisoleucine by enzymatic hydroxylation. Appl Biochem Microbiol 48:639–644
Maurya CK, Singh R, Jaiswal N, Venkateswarlu K, Narender T, Tamrakar AK (2014) 4-Hydroxyisoleucine ameliorates fatty acid-induced insulin resistance and inflammatory response in skeletal muscle cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 39:551–560
Narender T, Puri A, Shweta Khaliq T, Saxena R, Bhatia G, Chandra R (2006) 4-Hydroxyisoleucine an unusual amino acid as antidyslipidemic and antihy-perglycemic agent. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:293–296
Neelakantan N, Narayanan M, de Souza RJ, van Dam RM (2014) Effect of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) intake on glycemia a meta-analysis of clinical trials. Nutr J 13:7
Ogawa J, Kodera T, Smirnov SV, Hibi M, Samsonova NN, Koyama R, Yamanaka H, Mano J, Kawashima T, Yokozeki K, Shimizu S (2011) A novel l-isoleucine metabolism in Bacillus thuringiensis generating (2S, 3R, 4S)-4-hydroxyisoleucine, a potential insulinotropic and anti-obesity amino acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:1929–1938
Sauvaire Y, Petit P, Broca C, Manteghetti M, Baissac Y, Fernandez-Alvarez J, Gross R, Roye M, Leconte A, Gomis R, Ribes G (1998) 4-Hydroxyisoleucine a novel amino acid potentiator of insulin secretion. Diabetes 47:206–210
Shi F, Li Y (2011) Synthesis of γ-aminobutyric acid by expressing Lactobacillus brevis-derived glutamate decarboxylase in the Corynebacterium glutamicum strain ATCC 13032. Biotechnol Lett 33:2469–2474
Shi F, Niu T, Fang H (2015) 4-Hydroxyisoleucine production of recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum ssp. lactofermentum under optimal corn steep liquor limitation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:3851–3863
Smirnov SV, Kodera T, Samsonova NN, Kotlyarova VA, Rushkevich NY, Kivero AD, Sokolov PM, Hibi M, Ogawa J, Shimizu S (2010) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli to produce (2S, 3R, 4S)-4-hydroxyisoleucine. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88:719–726
Zhang C, Ma J, Li Z, Liang Y, Xu Q, Xie X, Chen N (2018) A strategy for l-isoleucine dioxygenase screening and 4-hydroxyisoleucine production by resting cells. Bioengineered 9(1):72–79
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the “national first-class discipline program of Light Industry Technology and Engineering” (contract no. LITE2018-10) for financial support.
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1–Primers for amplifying the ido gene and the mutant ido genes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S., Shi, F. Directed evolution and site-specific mutagenesis of l-isoleucine dioxygenase derived from Bacillus weihenstephanensis. Biotechnol Lett 40, 1227–1235 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-018-2566-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-018-2566-8