Abstract
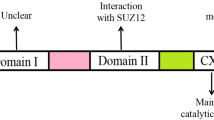
Apoptosis-antagonizing transcription factor (AATF) is involved in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle control, DNA damage responses and in the execution of cell death programs. It also interacts directly with nuclear hormone receptors to enhance their transactivation. This study highlights the RNomics of AATF gene in the pathogenesis of breast cancer: RNA interference gave 64 % reduction in AATF mRNA and 47 % decline in AATF protein expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cell proliferation decreased by 41 % after transfection and was accompanied by apoptosis induction in 30 % MCF-7 cells. Pro-apoptotic genes (Bax, Bag4, Fas, Faslg, Fadd, Casp5, Casp6, Abl 1, Apaf1, Bcl2l 11, Card4, -6, -8, Bnip2 and Bnip3l) were up-regulated and anti-apoptotic genes (Bcl2, Mcl1dc, TNF, Pycard, Tradd, Bcl2A1 and Birc1) were down-regulated as were estrogen receptor mRNA (42 %) and protein expression (30 %). In normal non-malignant mammary epithelial cells (MCF-10A) apoptosis induction was only 18 % with a 9 % fall in ER protein expression. Thus, AATF-silencing can be used to induce apoptosis and regulate ER expression in breast cancer cells for therapeutic interventions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruno T, De Angelis R, De Nicola F, Barbato C, Di Padova M, Corbi N, Libri V, Benassi B, Mattei E, Chersi A, Soddu S, Floridi A, Passananti C, Fanciulli M (2002) Che-1 affects cell growth by interfering with the recruitment of HDAC1 by Rb. Cancer Cell 2:387–399
Bruno T, De Nicola F, Iezzi S, Lecis D, D’Angelo C, Di Padova M, Corbi N, Dimiziani L, Zannini L, Jekimovs C, Scarsella M, Porrello A, Chersi A, Crescenzi M, Leonetti C, Khanna KK, Soddu S, Floridi A, Passananti C, Delia D, Fanciulli M (2006) Che-1 phosphorylation by ATM/ATR and Chk2 kinases activates p53 transcription and the G2/M checkpoint. Cancer Cell 10:479–486
Burgdorf S, Leister P, Scheidtmann KH (2004) TSG101 interacts with AATF and enhances AR-mediated transcription by promoting its mono-ubiquitination. J Biol Chem 279:17524–17534
De Nicola F, Bruno T, Iezzi S, Di Padova M, Floridi F, Passananti C, Del Sal G, Fanciulli M (2007) The prolyl isomerase Pin1 affects Che-1 stability in response to apoptotic DNA damage. J Biol Chem 282:19685–19691
Di Certo MG, Corbi N, Bruno T, Iezzi S, De Nicola F, Desantis A, Ciotti MT, Mattei E, Floridi A, Fanciulli M, Passananti C (2007) NRAGE associates with the anti-apoptotic factor Che-1 and regulates its degradation to induce cell death. J Cell Sci 120:1852–1858
Di Padova M, Bruno T, De Nicola F, Iezzi S, D’Angelo C, Gallo R, Nicosia D, Corbi N, Biroccio A, Floridi A, Passananti C, Fanciulli M (2003) Che-1 arrests human colon carcinoma cell proliferation by displacing HDAC1 from the p21WAF1/CIP1 promoter. J Biol Chem 278:36496–36504
Fanciulli M, Bruno T, Di Padova M, De Angelis R, Iezzi S, Iacobini C, Floridi A, Passananti C (2000) Identification of a novel partner of RNA polymerase II subunit 11, Che-1, which interacts with and affects the growth suppression function of Rb. FASEB J 14:904–912
Guo Q, Xie J (2004) AATF inhibits aberrant production of amyloid b peptide 1–42 by interacting directly with Par-4. J Biol Chem 279:4596–4603
Heery DM, Kalkhoven E, Hoare S, Parker MG (1997) A signature motif in transcriptional co-activators mediates binding to nuclear receptors. Nature 387:733–736
Kaul D, Mehrotra A (2007) Functional characterization of AATF transcriptome in human leukemic cells. Mol Cell Biochem 297:215–220
Leister P, Burgdorf S, Scheidtmann KH (2003) Apoptosis antagonizing transcription factor AATF is a novel coactivator of hormone receptors. Signal Transd 1–2:17–25
Leister P, Felten A, Chasan AI, Scheidtmann KH (2008) ZIP kinase plays a crucial role in androgen receptor-mediated transcription. Oncogene 27:3292–3300
McKenna NJ, O’Malley BW (2002) Combinatorial control of gene expression by nuclear receptors and coregulators. Cell 108:465–474
Page G, Lodige I, Kogel D, Scheidtman KH (1999) AATF, a novel transcription factor that interacts with Dlk/ZIP kinase and interferes with apoptosis. FEBS Lett 462:187–191
Robyr D, Wolffe AP, Wahli W (2000) Nuclear hormone receptor coregulators in action: diversity for shared tasks. Mol Endocrinol 14:329–347
Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK (2001) Coregulator codes of transcriptional regulation by nuclear receptors. J Biol Chem 276:36865–36868
Shanle EK, Xu W (2010) Selectively targeting estrogen receptors for cancer treatment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62:1265–1276
Xie J, Guo Q (2006) Apoptosis antagonizing transcription factor protects renal tubule cells against oxidative damage and apoptosis induced by ischemia-reperfusion. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:3336–3346
Acknowledgments
The author is highly grateful to the Chairperson, Department of Biotechnology, Panjab University, Chandigarh, India, for providing the facilities to conduct the research work. The financial assistance for carrying out the research was provided by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Ministry of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, under the Fast Track Young Scientist Scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, M. Apoptosis-antagonizing transcription factor (AATF) gene silencing: role in induction of apoptosis and down-regulation of estrogen receptor in breast cancer cells. Biotechnol Lett 35, 1561–1570 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1257-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1257-8