Abstract
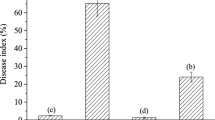
The antifungal properties and mechanism of three types of chitosan against the rice sheath blight pathogen, Rhizoctonia solani, were evaluated. Each chitosan had strong antifungal activity against R. solani and protected rice seedlings from sheath blight, in particular, two types of acid-soluble chitosan caused a 60–91 % inhibition in mycelial growth, 31–84 % inhibition of disease incidence, and 66–91 % inhibition in lesion length. The mechanism of chitosan in protection of rice from R. solani pathogen was attributed to direct destruction of the mycelium, evidenced by scanning and transmission electron microscopic observations and pathogenicity testing; indirect induced resistance was evidenced by the changes in the activities of the defense-related phenylalanine ammonia lyase, peroxidase and polyphenol oxidase in rice seedling. To our knowledge, this is the first report on the antifungal activity of chitosan against rice R. solani.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-El-Kareem F, El-Mougy NS, El-Gamal NG, Fotouh YO (2006) Use of chitin and chitosan against tomato root rot disease under greenhouse conditions. Res J Agric Biol Sci 2:147–152
Algam SAE, Xie GL, Li B, Yu SH, Su T, Larsen J (2010) Effects of Paenibacillus strains and chitosan on plant growth promotion and control of Ralstonia wilt in tomato. J Plant Pathol 92:593–600
Almeida FBR, Cerqueira FM, Silva RN, Ulhoa CJ, Lima AL (2007) Mycoparasitism studies of Trichoderma harzianum strains against Rhizoctonia solani: evaluation of coiling and hydrolytic enzyme production. Biotechnol Lett 29:1189–1193
Badawy MEI (2007) Effect of depolymerization degree of the natural biopolymer chitosan on some plant pathogenic bacteria and fungi. J Pest Cont Environ Sci 15:69–85
Badawy MEI (2010) Structure and antimicrobial activity relationship of quaternary N-alkyl chitosan derivatives against some plant pathogens. J Appl Polym Sci 117:960–969
Bautista-Baños S, Hernández-Lauzardo AN, Velázquez-Del Valle MG, Hernández-López M, Ait Barka E, Bosquez-Molina E, Wilson CL (2006) Chitosan as a potential natural compound to control pre and post harvest diseases of horticultural commodities. Crop Prot 25:108–118
Benhamou N (1996) Elicitor-induced plant defence pathways. Trends Plant Sci 1:233–240
Ben-Shalom N, Ardi R, Pinto R, Aki C, Fallik E (2003) Controlling gray mould caused by Botrytis cinerea in cucumber plants by means of chitosan. Crop Prot 22:285–290
El Hadrami A, Adam LR, El Hadrami I, Daayf F (2010) Chitosan in plant protection. Mar Drugs 8:968–987
El-Ghaouth JA, Grenier J, Benhamou N, Asselin A, Belanger R (1994) Effect of chitosan on cucumber plants: suppression of Pythium aphanidermatum and induction of defense reactions. Phytopathology 84:313–320
Falcón-Rodríguez AB, Costales-Menéndez D, Ortega-Delgado E, León-Díaz O, Cabrera-Pino JC (2007) Evaluation of chitosan as an inhibitor of soil-borne pathogens and as an elicitor of defence markers and resistance in tobacco plants. Span J Agric Res 5:533–541
Gil G, del Mónaco S, Cerrutti P, Galvagno M (2004) Selective antimicrobial activity of chitosan on beer spoilage bacteria and brewing yeasts. Biotechnol Lett 26:569–574
Hammerschimidt R, Nuckles E, Kuc J (1982) Association of enhanced peroxidase activity with induced systemic resistance of cucumber to Colletotrichum lagenarium. Physiol Plant Pathol 20:73–82
Li L, Steffens JC (2002) Overexpression of polyphenol oxidase in transgenic tomato plants results in enhanced bacterial disease resistance. Planta 215:239–247
Li B, Wang X, Chen R, Huangfu WG, Xie GL (2008) Antibacterial activity of chitosan solution against Xanthomonas pathogenic bacteria isolated from Euphorbia pulcherrima. Carbohydr Polym 72:287–292
Li B, Liu BP, Su T, Wang F, Tang QM, Fang Y, Xie GL, Sun GC (2010) Effect of chitosan solution on the inhibition of Pseudomonas fluorescens causing bacterial head rot of broccoli. J Plant Pathol 26:189–193
Li B, Liu BP, Yu RR, Lou MM, Wang YL, Xie GL, Li HY, Sun GC (2011) Phenotypic and molecular characterization of rhizobacterium Burkholderia sp. strain R456 antagonistic to Rhizoctonia solani, sheath blight of rice. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:2305–2313
Lisker N, Coren L, Chalutz E, Fucus Y (1983) Fungal infections suppress ethylene induced phenylalanine ammonia lyase activity in grape fruits. Physiol Plant Pathol 22:331–338
Lou MM, Zhu B, Ibrahim M, Li B, Xie GL, Wang YL, Li HY, Sun GC (2011) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of chitosan solution against apricot fruit rot pathogen Burkholderia seminalis. Carbohydr Res 346:1294–1301
Manjunatha G, Roopa KS, Prashanth GN, Shetty HS (2008) Chitosan enhances disease resistance in pearl millet against downy mildew caused by Sclerospora graminicola and defence-related enzyme activation. Pest Manag Sci 64:1250–1257
Manjunatha G, Niranjan-Raj S, Prashanth GN, Deepak S, Amruthesh KN, Shetty HS (2009) Nitric oxide is involved in chitosan-induced systemic resistance in pearl millet against downy mildew disease. Pest Manag Sci 65:737–743
Muñoz Z, Moret A (2010) Sensitivity of Botrytis cinerea to chitosan and acibenzolar-S-methyl. Pest Manag Sci 66:974–979
Nandeeshkumar P, Sudisha J, Ramachandra KK, Prakash HS, Niranjana SR, Shekar SH (2008) Chitosan induced resistance to downy mildew in sunflower caused by Plasmopara halstedii. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 72:188–194
Rabea EI, Badawy MET, Stevens CV, Smagghe G, Steurbaut W (2003) Chitosan as antimicrobial agent: applications and mode of action. Biomacromolecules 4:1457–1465
Rabea EI, Badawy MEI, Steurbaut W, Stevens CV (2009) In vitro assessment of N-(benzyl)chitosan derivatives against some plant pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Eur Polym J 45:237–245
Romanazzi G, Mlikota Gabler F, Margosan D, Mackey BE, Smilanick JL (2009) Effect of chitosan dissolved in different acids on its ability to control postharvest gray mold of table grape. Phytopathol 99:1028–1036
Trotel-Aziz P, Couderchet M, Vernet G, Aziz A (2006) Chitosan stimulates defense reactions in grapevine leaves and inhibits development of Botrytis cinerea. Eur J Plant Pathol 114:405–413
Trung TS, Ng CH, Stevens WF (2003) Characterization of decrystallized chitosan and its application in biosorption of textile dyes. Biotechnol Lett 25:1185–1190
Zhang M, Tan TW, Yuan HZ, Rui CH (2003) Insecticidal and fungicidal activities of chitosan and oligo-chitosan. J Bioact Compat Pol 18:391–400
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Y3090150), Zhejiang Provincial Project (2010R10091), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, the Agricultural Ministry of China (nyhyzx 201003029; 201003066; 201303015), State Education Ministry and Key Subject Construction Program of Zhejiang for Modern Agricultural Biotechnology and Crop Disease Control (2010DS700124-KF1101; 2010DS700124- KF1203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Tian, W., Li, B. et al. Antifungal effect and mechanism of chitosan against the rice sheath blight pathogen, Rhizoctonia solani . Biotechnol Lett 34, 2291–2298 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1035-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1035-z