Abstract
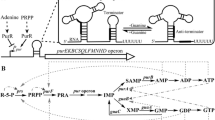
Wild-type B. subtilis strain W168 was de novo engineered for inosine biosynthesis. Inactivation of deoD and purA led to 0.15 ± 0.04 and 6.44 ± 0.39 g inosine/l yields, respectively. The deoD purA double mutant accumulated 7.6 ± 0.34 g inosine/l, with a 4.7% (w/w) conversion ratio from glucose to inosine. Comparative metabolic flux analysis revealed that the fluxes from inosine to hypoxanthine and from inosine monophosphate to adenosine monophosphate in the double mutant decreased to 14.0 and 0.61% of those in the wild-type strain. The major role of purA was demonstrated when inactivation of deoD and purA were found to contribute additively to inosine accumulation. This work is expected to contribute to the improvement of the fermentative production of purine nucleosides in the microbial industry.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anagnostopoulos C, Spizizen J (1961) Requirements for transformation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 81:741–746
Chen N, Huang J, Feng Z, Yu L, Xu Q, Wen T (2009) Optimization of fermentation conditions for the biosynthesis of l-threonine by Escherichia coli. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 158:595–604
Duan Y, Chen T, Chen X, Zhao X (2010) Overexpression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enhances riboflavin production in Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1907–1914
Kunst F, Ogasawara N, Moszer I, Albertini A, Alloni G, Azevedo V, Bertero M, Bessieres P, Bolotin A, Borchert S (1997) The complete genome sequence of the gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Nature 390:237–238
Sauer U, Cameron D, Bailey J (1998) Metabolic capacity of Bacillus subtilis for the production of purine nucleosides, riboflavin, and folic acid. Biotechnol Bioeng 59:227–238
Schuch R, Garibian A, Saxild H, Piggot P, Nygaard P (1999) Nucleosides as a carbon source in Bacillus subtilis: characterization of the drm-pupG operon. Microbiology 145:2957
Shimaoka M, Kawasaki H, Takenaka Y, Kurahashi O, Matsui H (2005) Effects of edd and pgi disruptions on inosine accumulation in Escherichia coli. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 69:1248–1255
Shimaoka M, Takenaka Y, Mihara Y, Kurahashi O, Kawasaki H, Matsui H (2006) Effects of xapA and guaA disruption on inosine accumulation in Escherichia coli. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:3069–3072
Shimaoka M, Takenaka Y, Kurahashi O, Kawasaki H, Matsui H (2007) Effect of amplification of desensitized purF and prs on inosine accumulation in Escherichia coli. J Biosci Bioeng 103:255–261
Srivatsan A, Han Y, Peng J, Tehranchi A, Gibbs R, Wang J, Chen R (2008) High-precision, whole-genome sequencing of laboratory strains facilitates genetic studies. PLoS Genet 4:e1000139
Torii T, Izawa K, Jang D, Cho D (2010) Inosine derivatives and production methods therefor. United States Patent 7816513
Wang H, Isaacs F, Carr P, Sun Z, Xu G, Forest C, Church G (2009) Programming cells by multiplex genome engineering and accelerated evolution. Nature 460:894–898
Wu L, Li Z, Ye Q (2009) Enhanced d-ribose biosynthesis in batch culture of a transketolase-deficient Bacillus subtilis strain by citrate. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:1289–1296
Zakataeva NP, Gronskiy SV, Sheremet AS, Kutukova EA, Novikova AE, Livshits VA (2007) A new function for the Bacillus PbuE purine base efflux pump: efflux of purine nucleosides. Res Microbiol 158:659–665
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Bacillus Genetic Stock Center (BGSC) and Prof. Ciarán Condon for providing the plasmids and strains used in this study. This research was funded by the National Drug Discovery Program of China (2008ZX09401-05), and Key Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (KSCX2-EW-J-6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Haojian Li, Guoqiang Zhang: Co-first authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Zhang, G., Deng, A. et al. De novo engineering and metabolic flux analysis of inosine biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis . Biotechnol Lett 33, 1575–1580 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0597-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0597-5