Abstract
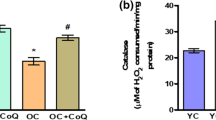
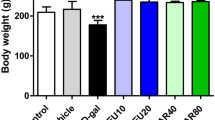
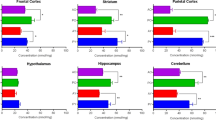
The present study has attempted to understand how oxidative stress contributes to the development of proinflammatory state in the brain during aging. Three groups of rats have been used in this study: young (4–6 months, Group I), aged (22–24 months, Group II) and aged with dietary antioxidant supplementation (Group III). The antioxidants were given daily from 18 months onwards in the form of a combination of N-acetyl cysteine (50 mg/100 g body weight), α-lipoic acid (3 mg/100 g body weight), and α-tocopherol (1.5 mg/100 g body weight) till the animals were used for the experiments between 22 and 24 months. Several measurements have been made to evaluate the ROS (reactive oxygen species) production rate, the levels of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α) and the activation status of NF-κβ (p65 subunit) in brain of the three groups of rats under the study. Our results reveal that brain aging is accompanied with a significant increase in NADPH oxidase activity and mitochondrial ROS production, a distinct elevation of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α levels along with increased nuclear translocation of NF-κβ (p65 subunit) and all these phenomena are partially but significantly prevented by the long-term dietary antioxidant treatment. The results imply that chronic dietary antioxidants by preventing oxidative stress and proinflammatory state may produce beneficial effects against multiple age-related deficits of the brain.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annunziato L, Pannaccione A, Cataldi M, Secondo A, Castaldo P, Di Renzo G, Taglialatela M (2002) Modulation of ion channels by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: a pathophysiological role in brain aging? Neurobiol Aging 23:819–834
Bagh MB, Maiti AK, Roy A, Chakrabarti S (2008) Dietary supplementation with N-acetylcysteine, α-tocopherol and α-lipoic acid prevents age related decline in Na+, K+ -ATPase activity and associated peroxidative damage in rat brain synaptosomes. Biogerontology 9:421–428
Bagh MB, Thakurta IG, Biswas M, Behera P, Chakrabarti S (2011) Age-related oxidative decline of mitochondrial functions in rat brain is prevented by long term oral antioxidant supplementation. Biogerontology 12:119–131
Behrens MM, Ali SS, Dugan LL (2008) Interleukin-6 mediates the increase in NADPH-oxidase in the ketamine model of schizophrenia. J Neurosci 28:13957–13966
Blandino P Jr, Barnum CJ, Deak T (2006) The involvement of norepinephrine and microglia in hypothalamic and splenic IL-1β responses to stress. J Neuroimmunol 173:87–95
Block ML, Zecca L, Jau-Shyong Hong J (2007) Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:57–69
Bruce-Keller AJ, White CL, Gupta S, Knight AG, Pistell PJ, Ingram DK, Morrison CD, Keller JN (2010) NOX activity in brain aging: exacerbation by high fat diet. Free Radic Biol Med 49:22–30
Bubici C, Papa S, Dean K, Franzoso G (2006) Mutual cross-talk between reactive oxygen species and nuclear factor-kappa B: molecular basis and biological significance. Oncogene 25:6731–6748
Burton MD, Sparkman NL, Johnson RW (2011) Inhibition of interleukin-6 trans-signaling in the brain facilitates recovery from lipopolysaccharide-induced sickness behavior. J Neuroinflamm 8:54
Calabrese V, Guagliano E, Sapienza M, Panebianco M, Calafato S, Puleo E, Pennisi G, Mancuso C, Butterfield DA, Stella AG (2007) Redox regulation of cellular stress response in aging and neurodegenerative disorders: role of vitagenes. Neurochem Res 32:757–773
Campuzano O, Castillo-Ruiz MM, Acarin L, Castellano B, Gonzalez B (2009) Increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines in the aged rat brain attenuate injury-induced cytokine response after excitotoxic damage. J Neurosci Res 87:2484–2497
Chakraborty H, Sen P, Sur A, Chatterjee U, Chakrabarti S (2003) Age-related oxidative inactivation of Na + , K + -ATPase in rat brain crude synaptosomes. Exp Gerontol 38:705–710
Chen Q, Vazquez EJ, Moghaddas S, Hoppel CL, Lesnefsky EJ (2003) Production of reactive oxygen species by mitochondria. central role of complex III. J Biol Chem 278:36027–36031
Cui X, Douglas JG (1997) Arachidonic acid activates c-jun N-terminal kinase through NADPH oxidase in rabbit proximal tubular epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 94:3771–3776
Driver AS, Kodavanti PR, Mundy WR (2002) Age-related changes in reactive oxygen species production in rat brain homogenates. Neurotoxicol Teratol 22:175–181
Dröge W, Schipper HM (2007) Oxidative stress and aberrant signaling in aging and cognitive decline. Aging Cell 6:361–370
Dugan LL, Ali SS, Shekhtman G, Roberts AJ, Lucero J, Quick KL, Behrens MM (2009) IL-6 mediated degeneration of forebrain GABAergic interneurons and cognitive impairment in aged mice through activation of neuronal NADPH oxidase. PLoS One 4(5):e5518
Gemma C, Mesches MH, Sepesi B, Choo K, Holmes DB, Bickford PC (2002) Diets enriched in foods with high antioxidant activity reverse age-induced decreases in cerebellar beta-adrenergic function and increases in proinflammatory cytokines. J Neurosci 22:6114–6120
Godbout JP, Johnson RW (2004) Interleukin-6 in the aging brain. J Neuroimmunol 147:141–144
Goyarzu P, Malin DH, Lau FC, Taglialatela G, Moon WD, Jennings R, Moy E, Moy D, Lippold S, Shukitt-Hale B, Joseph JA (2004) Blueberry supplemented diet: effects on object recognition memory and nuclear factor-kappa β levels in aged rats. Nutr Neurosci 7:75–83
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1999) Free radicals in biology and medicine, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Head E (2009) Oxidative damage and cognitive dysfunction: antioxidant treatments to promote healthy brain aging. Neurochem Res 34:670–678
Hulbert AJ (2005) On the importance of fatty acid composition for membranes in aging. J Theor Biol 234:277–288
Infanger DW, Sharma RV, Davisson RL (2006) NADPH oxidases of the brain: distribution, regulation, and function. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:1583–1596
Jana S, Sinha M, Chanda D, Roy T, Banerjee K, Munshi S, Patro BS, Chakrabarti S (2011) Mitochondrial dysfunction mediated by quinone oxidation products of dopamine: implications in dopamine cytotoxicity and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812:663–673
Jobin C, Sartor RB (2000) The IkB/NF-kB system: a key determinant of mucosal inflammation and protection. Am J Physio Cell Physiol 278:C451–C462
Kozlowski H, Janicka-Klos A, Brasun J, Elena Gaggelli E, Valensin D, Valensin G (2009) Copper, iron, and zinc ions homeostasis and their role in neurodegenerative disorders (metal uptake, transport, distribution and regulation). Coordin Chem Rev 253:2665–2685
Kregel KC, Zhang HJ (2007) An integrated view of oxidative stress in aging: basic mechanisms, functional effects, and pathological considerations. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 292:R18–R36
Lee HA, Hughes DA (2002) Alpha-lipoic acid modulates NF-kappaB activity in human monocytic cells by direct interaction with DNA. Exp Gerontol 37:401–410
Leutner S, Eckert A, Müller WE (2001) ROS generation, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities in the aging brain. J Neural Transm 108:955–967
Mattson MP, Cheng A (2006) Neurohormetic phytochemicals: low-dose toxins that induce adaptive neuronal stress responses. Trends Neurosci 29:632–639
Murphy MP (2009) How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species? Biochem J 417:1–13
Muthuswamy AD, Vedagiri K, Ganesan M, Chinnakannu P (2006) Oxidative stress-mediated macromolecular damage and dwindle in antioxidant status in aged rat brain regions: role of l-carnitine and dl-alpha-lipoic acid. Clin Chim Acta 368:84–92
Paradies G, Petrosillo G, Paradies V, Ruggiero FM (2011) Mitochondrial dysfunction in brain aging: role of oxidative stress and cardiolipin. Neurochem Int 58:447–457
Poon HF, Calabrese V, Scapagnini G, Butterfield DA (2004a) Free radicals: key to brain aging and heme oxygenase as a cellular response to oxidative stress. J Gerontol 59A:478–493
Poon HF, Calabrese V, Scapagnini G, Butterfield DA (2004b) Free radicals and brain aging. Clin Geriatr Med 20:329–359
Poynter ME, Daynes RA (1998) Peroxisome Proliferator-activated receptor α activation modulates cellular redox status, represses nuclear factor- κβ signaling, and reduces inflammatory cytokine production in aging. J Biol Chem 273:32833–32841
Prasad KN, Cole WC, Hovland AR, Prasad KC, Nahreini P, Kumar B, Edwards-Prasad J, Andreatta CP (1999) Multiple antioxidants in the prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative disease: analysis of biologic rationale. Curr Opin Neurol 12:761–770
Rattan SI (2008) Hormesis in aging. Ageing Res Rev 7:63–78
Salminen A, Huuskonen J, Ojala J, Kauppinen A, Kaarniranta K, Suuronen T (2008) Activation of innate immunity system during aging: NF-κβ signaling is the molecular culprit of inflamm-aging. Ageing Res Rev 7:83–105
Sandhu SK, Kaur G (2002) Alterations in oxidative stress scavenger system in aging rat brain and lymphocytes. Biogerontology 3:161–173
Sen T, Sen N, Jana S, Khan FH, Chatterjee U, Chakrabarti S (2007) Depolarization and cardiolipin depletion in aged rat brain mitochondria: relationship with oxidative stress and electron transport chain activity. Neurochem Int 50:719–725
Son TG, Zou Y, Jung KJ, Yu BP, Ishigami A, Maruyama N, Lee J (2006) SMP30 deficiency causes increased oxidative stress in brain. Mech Ageing Dev 127:451–457
Tha KK, Okuma Y, Miyazaki H, Murayama T, Ueharaa T, Hatakeyamaa R, Hayashib Y, Nomura Y (2000) Changes in expressions of proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 in the brain of senescence accelerated mouse (SAM) P8. Brain Res 885:25–31
Tong L, Toliver-Kinsky T, Edwards M, Rassin DK, Werrbach-Perez K, Perez-Polo JR (2002) Attenuated transcriptional responses to oxidative stress in the aged rat brain. J Neurosci Res 70:318–326
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci 76:4350–4354
Vallières L, Campbell IL, Gage FH, Sawchenko PE (2002) Reduced hippocampal neurogenesis in adult transgenic mice with chronic astrocytic production of interleukin-6. J Neurosci 22:486–492
Von Bernhardi R, Tichauer JE, Eugenin J (2010) Aging dependent changes in microglial cells and their relevance for neurodegenerative disorders. J Neurochem 112:1099–1114
Ye S, Johnson RW (2001) Regulation of interleukin-6 gene expression in brain of aged mice by nuclear factor κB. J Neuroimmunol 117:87–96
Yu BP, Chung HY (2006) Adaptive mechanisms to oxidative stress during aging. Mech Ageing Dev 127:436–443
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), Govt. of India (48/12/2006-TF/Aging brain/BMS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thakurta, I.G., Chattopadhyay, M., Ghosh, A. et al. Dietary supplementation with N-acetyl cysteine, α-tocopherol and α-lipoic acid reduces the extent of oxidative stress and proinflammatory state in aged rat brain. Biogerontology 13, 479–488 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-012-9392-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-012-9392-5